J Korean Med Assoc.
2003 Oct;46(10):927-936. 10.5124/jkma.2003.46.10.927.
Recent Advancement in Renal Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery (Transplantation), Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Hospital, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1957987
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2003.46.10.927
Abstract
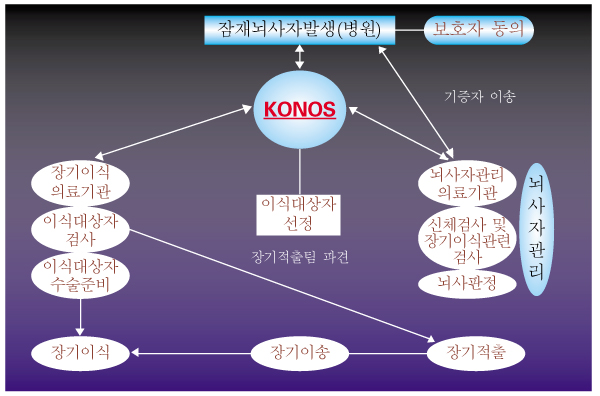
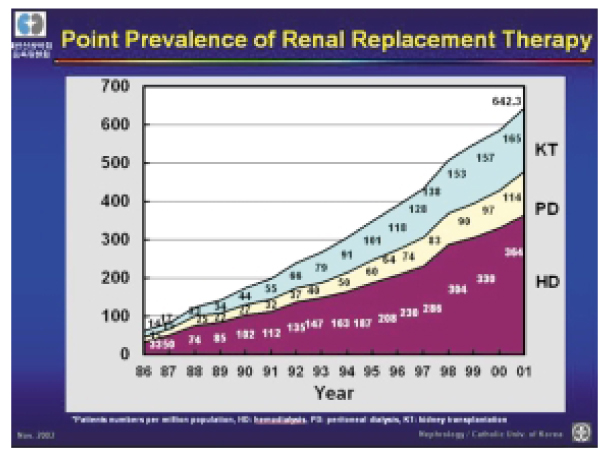
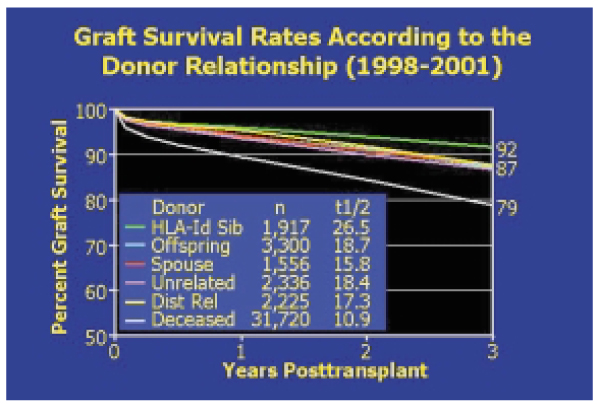
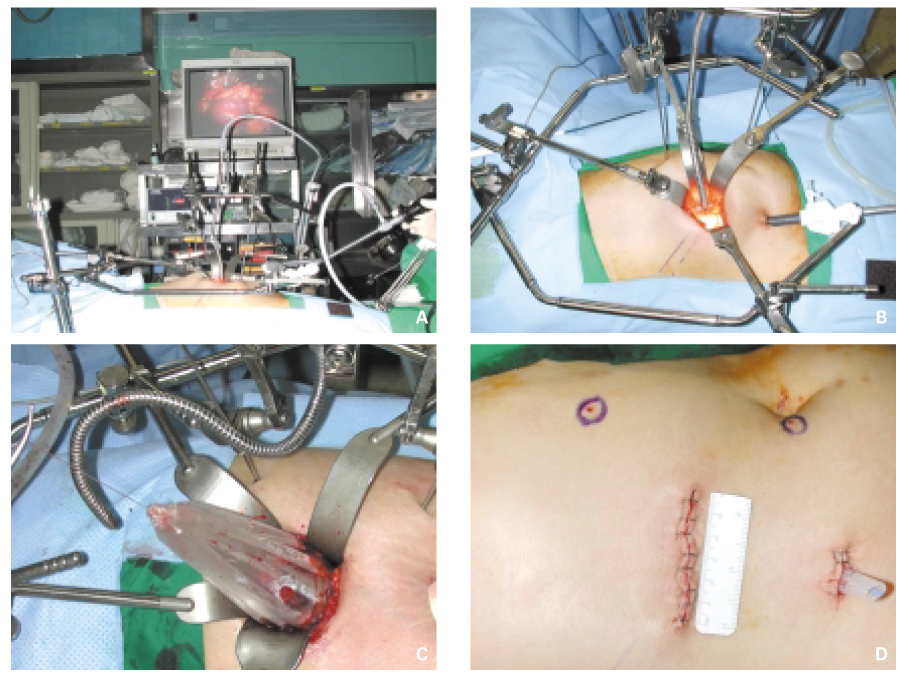
- This review will focus on the current issues in the government-driven regulation of transplantation practice in Korea, Korean renal transplant statistics, unrelated renal transplantation, renal transplantation in cross-match positive patients, preemptive renal transplantation, non-invasive renal imaging, novel minimally-invasive living donor nephrectomy, and tailored immunosuppression.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
6. Cecka JM. Cecka JM, Terasaki PI, editors. The UNOS renal transplant registry. Clinical Transplants 2002. 2003. Los Angeles, California: UCLA Tissue Typing Laboratory;1–20. 367–377.8. Kim SI, Kwon KH, Kim BS, Kim YS, Hong SJ, Yang SC, et al. Kidney transplantation in patients with crossmatch positive live donor : use of plasmapheresis and ATG. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:suppl 5. 175.9. Yang SC, Ko WJ, Byun YJ, Rha KH. Retroperitoneoscopy-assisted live donor nephrectomy : The Yonsei experience. J Urol. 2001. 165:1099–1102.
Article11. Joosten SA, Van Kooten C, Paul LC. Pathogenesis of chronic allograft rejection. Transplant Int. 2003. 16:137–145.
Article12. Kim YS, Kim MS, Han DS, Kim DK, Myoung SM, Kim SI, et al. Evidence that the ratio of donor kidney weight to recipient body weight, donor age, and episodes of acute rejection correlate independently with live donor graft function. Transplantation. 2002. 74:280–283.
Article13. Nam JH, Mun JI, Kim SI, Kang SW, Choi KH, Huh KB, et al. Beta-Cell dysfunction rather than insulin resistance is the main contributing factor for the development of post-renal transplantation diabetes mellitus. Transplantation. 2001. 71:1417–1423.
Article14. Cho YM, Park KS, Jung HS, Jeon HJ, Ahn C, Lee HK, et al. High incidence of tacrolimus-associated post-transplantation diabetes in the Korean renal allograft recipients according to American Diabetes Association criteria. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:1123–1128.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Advancement of Living Donor Renal Transplantation
- Recent Advancement in Heart and Lung Transplantation
- What's New in Transplantation Surgery and Medicine
- The Korean Journal of Transplantation’s quantum leap toward becoming an international journal for the advancement of Asian transplantation
- A Case of Femoral Neuropathy after Renal Transplantation