J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 Apr;72(4):300-303. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.4.300.
Glue Embolization of the Giant Aneurysm by Reducing Thrombosis-Induced Volume Expansion Effect
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dcsuh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1941763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.4.300
Abstract
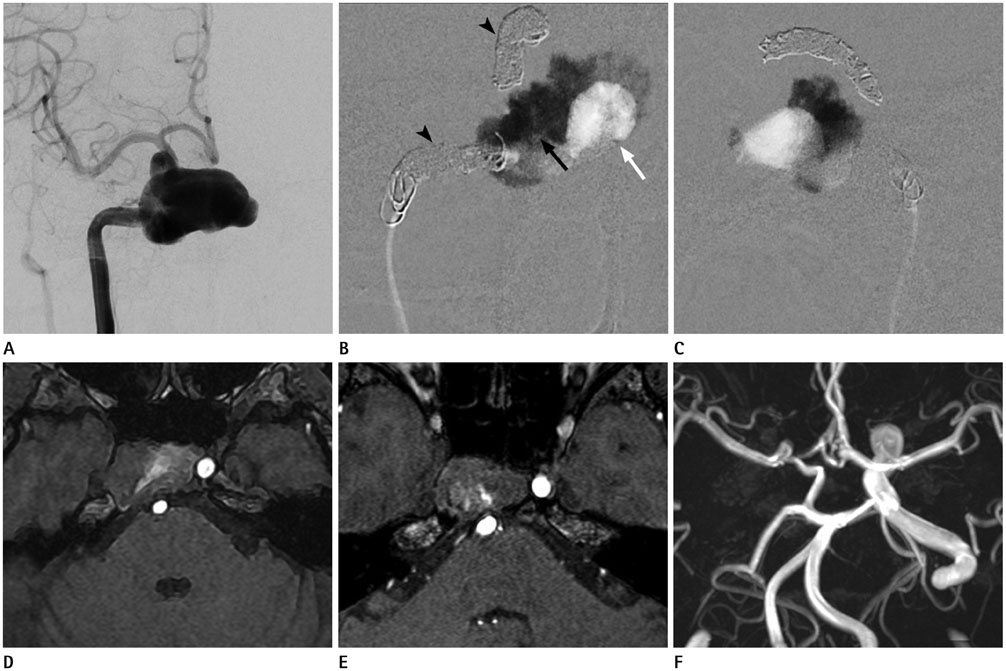
- A giant aneurysm due to a large intra-aneurysmal volume can be complicated by a delayed massive volume expansion caused by thrombus formation. To prevent such a severe mass effect, we obliterated the aneurysmal lumen by gluing and prevented further development of thrombosis. A 52-year-old female with a giant aneurysm at the cavernous segment of the internal carotid artery presented with tinnitus and intermittent diplopia. After confirming with a negative occlusion test, the right internal carotid artery was trapped by coiling and with further obliteration of the aneurysmal lumen by gluing. She developed a mild diplopia after the procedure and recovered without any deficit. The magnetic resonance angiography showed a stable occlusion of the aneurysm and good collateral filling of the cerebral vessel 15 months later.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Niiro M, Shimozuru T, Nakamura K, Kadota K, Kuratsu J. Long-term follow-up study of patients with cavernous sinus aneurysm treated by proximal occlusion. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2000; 40:88–96. discussion 96-97.2. Sluzewski M, Menovsky T, van Rooij WJ, Wijnalda D. Coiling of very large or giant cerebral aneurysms: long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:257–262.3. Choi IS, David C. Giant intracranial aneurysms: development, clinical presentation and treatment. Eur J Radiol. 2003; 46:178–194.4. Højer-Pedersen E, Haase J. Giant anterior communicating artery aneurysm with bitemporal hemianopsia: case report. Neurosurgery. 1981; 8:703–706.5. Hauck EF, Welch BG, White JA, Replogle RE, Purdy PD, Pride LG, et al. Stent/coil treatment of very large and giant unruptured ophthalmic and cavernous aneurysms. Surg Neurol. 2009; 71:19–24. discussion 24.6. Carneiro A, Rane N, Kuker W, Cellerini M, Corkill R, Byrne JV. Volume changes of extremely large and giant intracranial aneurysms after treatment with flow diverter stents. Neuroradiology. 2014; 56:51–58.7. Nelson PK, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Wetzel SG, Wanke I, Fiorella D. The pipeline embolization device for the intracranial treatment of aneurysms trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:34–40.8. Suh DC, Kim KS, Lim SM, Shi HB, Choi CG, Lee HK, et al. Technical feasibility of embolizing aneurysms with glue (N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate): experimental study in rabbits. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1532–1539.9. Suh DC, Shi HB, Park SS, Lee MS, Choi HY. Change of spontaneous reaction of glue and lipiodol mixture during embolization after the addition of tungsten powder: in vitro study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:1277–1279.10. de Gast AN, Sprengers ME, van Rooij WJ, Lavini C, Sluzewski M, Majoie CB. Midterm clinical and magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of large and giant carotid artery aneurysms after therapeutic carotid artery occlusion. Neurosurgery. 2007; 60:1029–1031.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Giant Vertebrobasilar Junction Aneurysm Treated with Proximal Occlusion of Parent Artery Followed by Coil Embolization of Partially Thrombosed Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Spontaneous Regression of an Unruptured and Non-Giant Intracranial Aneurysm
- Three-Dimensional Fusion Angiography of a Giant Basilar Aneurysm for Coil Embolization
- Unusual Clinical Course of Giant Vertebral Artery Aneurysm after Proximal Artery Embolization: Case Report
- Recanalization of Totally Thrombosed Giant Aneurysm: Case Report