J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2007 Sep;14(3):164-170. 10.4184/jkss.2007.14.3.164.
The Changes in the Dimensions of Neural Foramen After Anterior Interbody Fusion in the Spondylolisthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ajou University Medical center, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallymm University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. gogjus@hanamail.net
- KMID: 1941648
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2007.14.3.164
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A prospective radiological assessment was performed using computerized tomography measurements.
OBJECTIVES
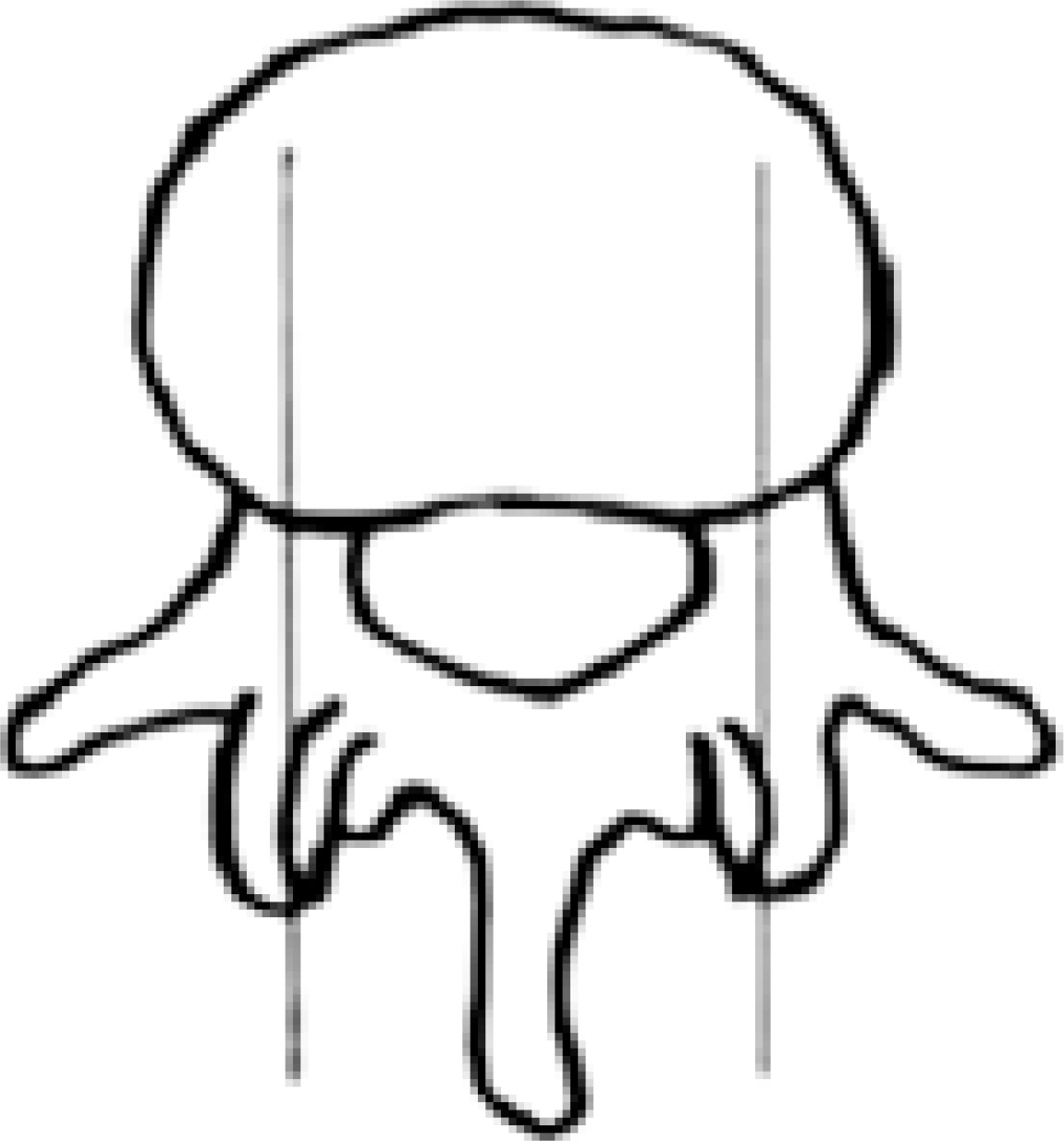
The aim of this study was to assess the changes in the dimensions of the neural foramen after anterior interbody fusion with posterior fixation in spondylolisthesis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Anterior lumbar interbody fusion distracts the height and width of the neural foramen.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
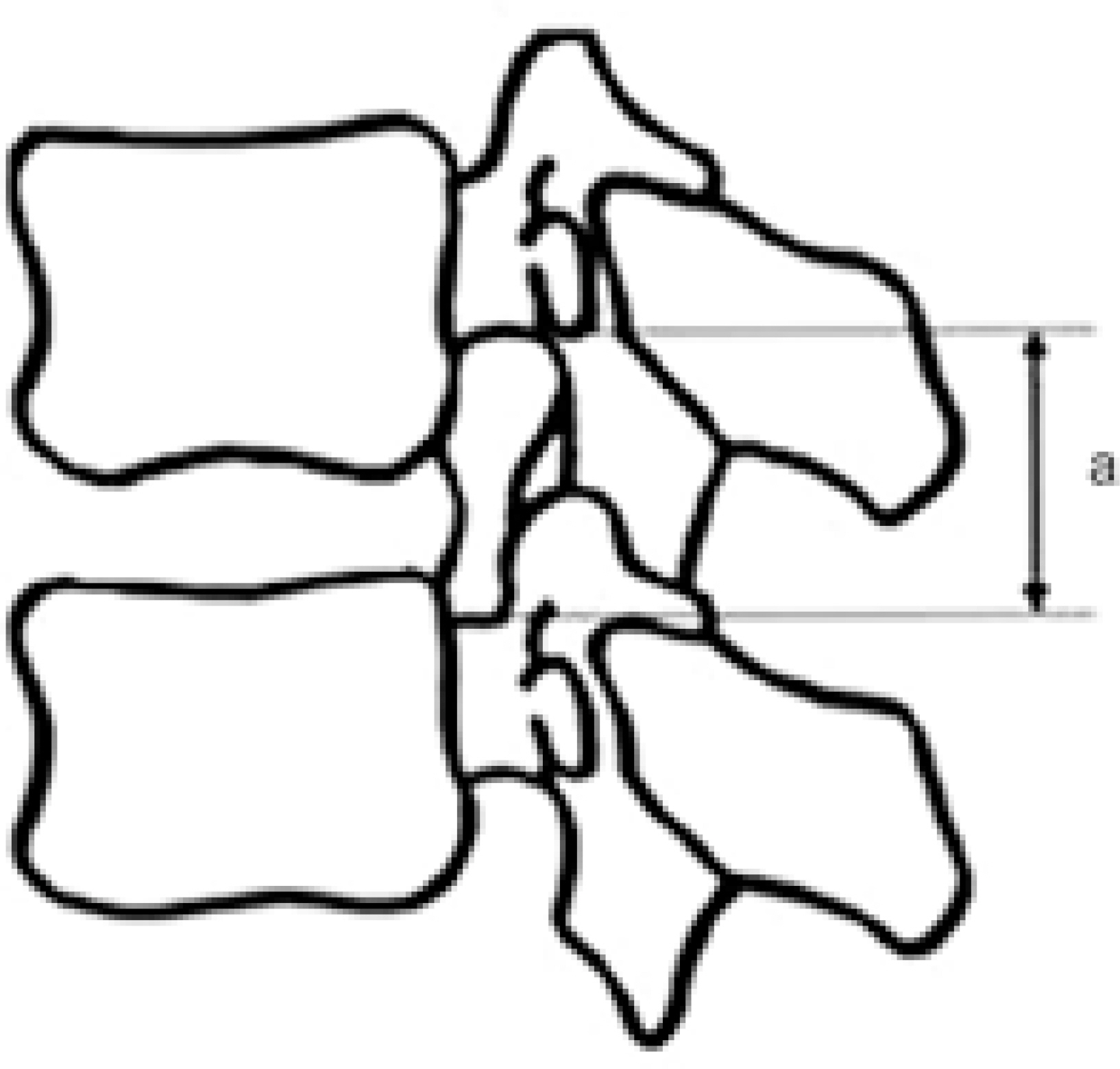
Anterior interboody fusion with posterior fixation was performed in twenty-five patients. The sagittal parameters were the height and area of the neural foramen. The fused lumbar segments was imaged in the direct sagittal projections in a CT (SOMATOM Senstaion; SIMENS, Germany) and 1-mm slice thickness before surgery and after solid fusion. Computer digitation was used for the measurements independently by three different observers. Statistical analysis was performed using a Wilcoxon signed test and a paired T-test to determine the correlation between the measurements, and Pearson correlation to determine the level of interobserver and intraobserver agreement.
RESULTS
After anterior interbody fusion and posterior fixation, the height and the area of the neural foramen had increased significantly by 15.5+/-14.0%(p.0.001) and 23.2+/-17.7%(p.0.001). There was a significant confidence in interobserver (0.9466~0.9996) and intraobserver(0.8896~0.9991) agreement.
CONCLUSIONS
Anterior interbody fusion significantly increased the changes in the dimensions of the neural foramen. Anterior distraction and decompression with anterior interbody fusion increased the area of the neural foramen This study shows that anterior interbody fusion can be used to decompress the neural foramen in the spondylolisthesis.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Wiltse LL, Winter RB. Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65:768–772.
Article2). Vamvanij V, Ferrara LA, Hai Y, Zhao J, Kolata R, Yuan HA. Quantitative changes in spinal canal dimensions using interbody distraction for spondylolilisthesis. Spine. 2001; 26:E13–E18.3). Herkowitz HN. Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1995; 20:1084–1090.4). Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Cho KJ, Kim HG. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolitic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997; 22:210–219.5). Freeman BJ, Licina P, Mehdian SH. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion combined with instrumented posterolateral fusion: 5-year results in 60 patients. Eur Spine J. 2000; 9:42–46.
Article6). Panjabi M, Takata K, Goel V. Kinematics of lumbar intervertebral foramen. Spine. 1983; 8:348–357.
Article7). Jeon CH, Kim YC, Jung NS. Height changes of intervertebral disc and neural foramen after anterior lumbar interbody fusion in the lumbar spine. J Kor Spine Surg. 2003; 10(3):226–232.
Article8). Jeon CH, Kim YC, Jung NS, Song KH. The changes of the dimension of intervertebral disc, neural foramen and spinal canal after lumbar interbidy fusion in the lumbar spine. J Kor Spine Surg. 2004; 11:40–47.9). Jeon CH. Anterior interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. J Kor Spine Surg. 2001; 8:350–355.10). Ciric I, Michael MA, Tarkington JA, Vick NA. The lateral recess syndrome. J Neurosurg. 1980; 53:433–439.
Article11). Hasegawa T, An HS, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH. Lumbar foraminal stenosis: Critical heights of the intervertebral discs and foramina: A cryomicrotome study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg. 1995; 77:32–38.12). Carragee EJ. Single-level posterolateral arthrodesis, with or without posterior decompression, for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1175–1180.
Article13). Epstein BS, Epstein JA, Laving IS. .:. The effect of anatomic variation in the lumbar vertebrae and spinal canal on cauda equina and nerve root syndromes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1964; 42:91–99.14). Inufusa A. The Ideal Amount of Lumbar Foraminal Distraction for pedicle Screw Instrumentation. Spine. 1996; 21:2218–2223.
Article15). Chen D, Fay LA, Lok J, Yuan P, Edwards WT, Yuan HA. Increasing neuroforaminal volume by anterior interbody distraction in degenerative lumbar spine. Spine. 1995; 20:74–79.
Article16). Suk KS, Jeon CH, LEE HM, Kim NH, Kim HC. Comparison between posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation and anterior interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine, J Kor Spine Surg. 1999; 6:397–406.17). Madan SS, Boeree NR. Comparison of instrumented anterior interbody fusion with instrumented circumferen-tial lumbar fusion. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12:567–575.
Article18). Inoue S, Watanabe T, Goto S, Takahashi K, Takata K, Sho E. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: pathophysiology and results of anterior interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1988; 227:90–98.
Article19). Satomi K, Hirabayashi K, Toyama Y, Fujimura Y. A clinical study of degenerativespondylolisthesis: Radiographic analysis and choice of treatment. Spine. 1992; 17:1329–1336.20). Kim NH, Kim HK, Suh JS. .:. A computed tomographic analysis of changes in the spinal c canal after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1993; 286:180–191.21). Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, Aebi M. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation: A 4-6 year followup study. Spine. 1993; 18:1655.22). Bradford DS, Boachie-Adjei O. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by anterior a and posterior reduction and stabilization: A longterm followup study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72:1060.23). Bayley JC, Yoo JU, Kruger DM, Schlegel J. The role of distraction in improving the space available for the cord in cervical spondylosis. Spine. 1995; 20:771–775.24). Schlegel JD, Champine J, Taylor MS, et al. The role of distraction in improving the space available in the lumbar stenotic canal and foramen. Spine. 1994; 19:2041–2047.
Article25). Shiradol O, Zdeblick TA, McAfee PC, Warden AK. Biomechanical evaluation of methods of posterior stabilization of the spine and posterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis for lumbosacral isthmic spondylolisthesis: A calf-spine model, J Bone Joint Surg. 1991; 73:518–526.26). Mayoux-Benhoumou MA, Revel M, Aaron C, et al. A morphologic study of lumbar foramen-Influence of flexion-extension movements and of isolated disc collapse. Surg Radiol Anat. 1989; 11:97–102.27). Smith GA, Aspden RM, Porter RW. .:. Measurment of vertebral foraminal dimensions using three demensional computerized tomography. Spine. 1993; 18:629–636.28). De Loubress CG, Bon T, Deburge A, Lassale B, Benoit M. Posterolateral fusion for radicular pain in isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop. 1996; 323:194–201.29). Takahashi K, Kitahara H, Yamagata M, et al. .:. Longterm results of anterior interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1990; 15:1211–1215.
Article30). CH Jeon, YC Kim, NS Jeong. The change of sagittal alignment after anterior interbody fusion with posterior fixation in spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine. Journal of Korea Spine Surg. 2004; 11-3:131–140.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Height Changes of Intervertebral Disc and Neural Foramen after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Lumbar Spine
- The Comparison of Changes in the Dimensions of the Intervertebral Disc and Neural Foramen between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Posterolateral Fusion in the Lumbar Spine
- The Changes of the Dimension of Intervertebral Disc,-Neural Foramen and Spinal Canal after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Lumbar Spine
- Anterior Interbody Fusion for the Spondylolisthesis
- The Change of Segmental Sagittal angle in Low - grade spondylolisthesis after Pedicular Screw Fixation with or without PLIF - PLIF + PLF versus PLF groups -