Infect Chemother.
2011 Aug;43(4):377-381. 10.3947/ic.2011.43.4.377.
Liver Abscess by Aspergillus and Enterococcus faecium in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. symonlee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1936078
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2011.43.4.377
Abstract
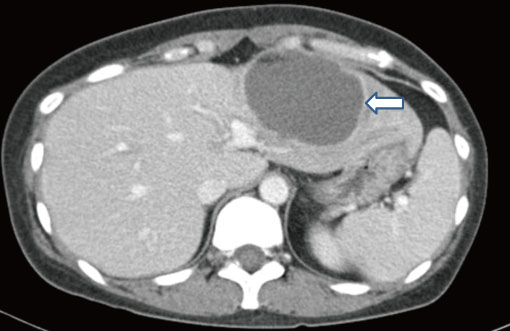
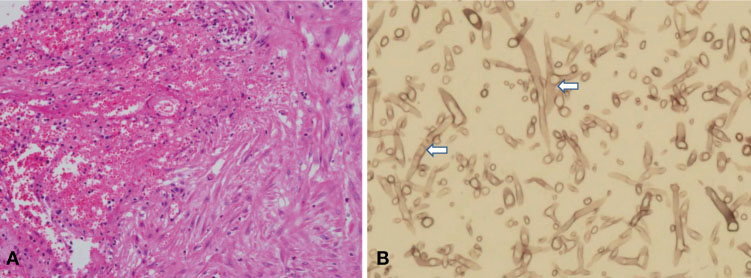
- We report a case of liver abscess caused by Aspergillus and Enterococcus faecium in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. As far as we know, this is the first case of hepatic aspergillosis in Korea. After remission induction chemotherapy, the female patient presented with abdominal pain and was found to have liver abscess. The patient was treated with antibiotics against E. faecium, which was isolated from the abscess drainage. However, the therapeutic response was unsatisfactory and a left lateral sectionectomy of the liver was conducted after 21 days of treatment. The liver tissue showed typical pathologic findings of aspergillosis and voriconazole was administered. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was performed successfully after 4 months. The possibility of aspergillosis should be considered when an immunocompromised patient with hepatic abscess poorly responds to the use of broad spectrum antibiotics.
MeSH Terms
-
Abdominal Pain
Abscess
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus
Drainage
Enterococcus
Enterococcus faecium
Female
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Humans
Immunocompromised Host
Korea
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute
Liver
Liver Abscess
Pyrimidines
Remission Induction
Triazoles
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Pyrimidines
Triazoles
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:358–366.
Article2. Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, Offidani M, Fianchi L, Martino B, Pastore D, Picardi M, Bonini A, Chierichini A, Fanci R, Caramatti C, Invernizzi R, Mattei D, Mitra ME, Melillo L, Aversa F, Van Lint MT, Falcucci P, Valentini CG, Girmenia C, Nosari A. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: the SEIFEM-2004 study. Haematologica. 2006. 91:1068–1075.3. Yamada R, Horikawa K, Ishihara S, Hoshino K, Kawaguchi T, Iyama K, Mitsuya H, Asou N. Successful treatment of Aspergillus liver abscesses in a patient with acute monoblastic leukemia using combination antifungal therapy including micafungin as a key drug. Int J Hematol. 2010. 91:711–715.
Article4. Zhan HX, Lv Y, Zhang Y, Liu C, Wang B, Jiang YY, Liu XM. Hepatic and renal artery rupture due to Aspergillus and Mucor mixed infection after combined liver and kidney transplantation: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2008. 40:1771–1773.
Article5. Rieder J, Lechner M, Lass-Floerl C, Rieger M, Lorenz I, Piza H, Bonatti H. Successful management of Aspergillus liver abscess in a patient with necrotizing fasciitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007. 52:1548–1553.
Article6. Scott CJ, Lambert JS, Taylor CB, Poulton MB. Invasive Aspergillus fumigatus associated with liver and bone involvement in a patient with AIDS. Int J Infect Dis. 2007. 11:550–553.
Article7. van der Velden WJ, Blijlevens NM, Klont RR, Donnelly JP, Verweij PE. Primary hepatic invasive aspergillosis with progression after rituximab therapy for a post transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder. Ann Hematol. 2006. 85:621–623.
Article8. Marotta G, Tozzi M, Sammassimo S, Defina M, Raspadori D, Gozzetti A, Lauria F. Complete resolution of hepatic aspergillosis after non-myeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology. 2005. 10:383–386.
Article9. Lee TY, Yang SS, Chen GH, Hwang WL, Lin YH, Hwang JI. Hepatic abscess caused by Aspergillus fumigatus infection following splenectomy and immunosuppressive therapy. J Formos Med Assoc. 2003. 102:501–505.10. Trachana M, Roilides E, Gompakis N, Kanellopoulou K, Mpantouraki M, Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F. Case report. Hepatic abscesses due to Aspergillus terreus in an immunodeficient child. Mycoses. 2001. 44:415–418.
Article11. Mazza D, Gugenheim J, Toouli J, Mouiel J. Survival of a liver graft recipient treated for an aspergillar liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 1996. 23:831–832.
Article12. Ow C, Maldjian C, Shires GT 3rd, Markisz J, Kazam E. CT, US, and MR imaging of hepatic aspergilloma. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991. 15:852–854.
Article13. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, Pappas PG, Maertens J, Lortholary O, Kauffman CA, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Maschmeyer G, Bille J, Dismukes WE, Herbrecht R, Hope WW, Kibbler CC, Kullberg BJ, Marr KA, Muñoz P, Odds FC, Perfect JR, Restrepo A, Ruhnke M, Segal BH, Sobel JD, Sorrell TC, Viscoli C, Wingard JR, Zaoutis T, Bennett JE. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:1813–1821.
Article14. Leventakos K, Lewis RE, Kontoyiannis DP. Fungal infections in leukemia patients: how do we prevent and treat them? Clin Infect Dis. 2010. 50:405–415.
Article15. Hori A, Kami M, Kishi Y, Machida U, Matsumura T, Kashima T. Clinical significance of extra-pulmonary involvement of invasive aspergillosis: a retrospective autopsy-based study of 107 patients. J Hosp Infect. 2002. 50:175–182.
Article16. Sparrelid E, Hägglund H, Remberger M, Ringdén O, Lönnqvist B, Ljungman P, Andersson J. Bacteraemia during the aplastic phase after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is associated with early death from invasive fungal infection. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998. 22:795–800.
Article17. Maschmeyer G, Haas A, Cornely OA. Invasive aspergillosis: epidemiology, diagnosis and management in immunocompromised patients. Drugs. 2007. 67:1567–1601.18. Marr KA, Leisenring W. Design issues in studies evaluating diagnostic tests for aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 41:Suppl 6. S381–S386.
Article19. Tan YM, Chung AY, Chow PK, Cheow PC, Wong WK, Ooi LL, Soo KC. An appraisal of surgical and percutaneous drainage for pyogenic liver abscesses larger than 5 cm. Ann Surg. 2005. 241:485–490.
Article20. Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Morrison VA, Segal BH, Steinbach WJ, Stevens DA, van Burik JA, Wingard JR, Patterson TF. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:327–360.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Meningitis Treated with Linezolid: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Granulocytic Sarcoma in the Leg Mimicking Hemorrhagic Abscess
- A case of isolated renal aspergillosis in a patient with acute myelocytic leukemia
- Hepatic and Small Bowel Mucormycosis after Chemotherapy in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Bilateral Endogenous Enterococcus Faecalis Endophthalmitis in Liver Abscess