J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Aug;83(2):92-96. 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.2.92.
The learning curve for laparoscopic totally extraperitoneal herniorrhaphy by moving average
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. srglee@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1820093
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.83.2.92
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Laparoscopic totally extraperitoneal (TEP) herniorrhaphy has been recognized as a treatment option for inguinal hernia. The objective of this study was to clarify the learning curve for laparoscopic TEP herniorrhaphy using the moving average method.
METHODS
A total of 90 patients underwent laparoscopic TEP herniorrhaphy by a single surgeon between March 2009 and March 2011. We analyzed medical records including the demographic data, operating time, hospital stay, and postoperative complications.
RESULTS
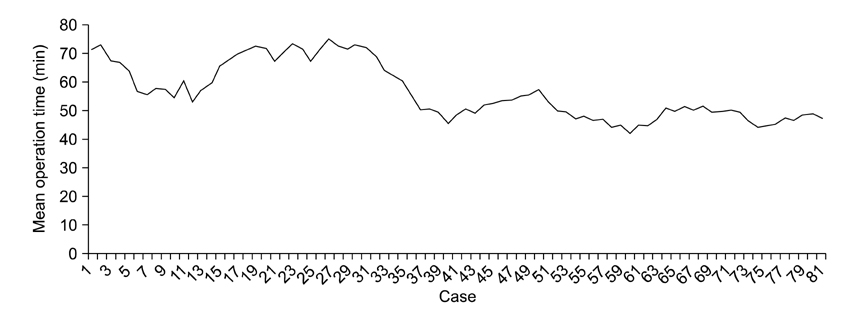
The mean operating time of the initial 30 cases (learning period group) was 66.3 minutes. After the initial 30 cases were performed, the time decreased to 52.8 minutes in the later 60 cases (experienced period group, P = 0.015). This represents the operating time becoming stabilized and then decreasing as the number of performed cases accumulates. Hospital stay was shorter and frequency of pain control, and complication rate were lower in the experienced period, however, there was no statistical significance.
CONCLUSION
We suggest that number of patients needed for the learning curve for laparoscopic TEP herniorrhaphy should be 30 cases. The operating time for laparoscopic TEP herniorrhaphy stabilizes after 40 cases in moving average analysis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belyansky I, Tsirline VB, Klima DA, Walters AL, Lincourt AE, Heniford TB. Prospective, comparative study of postoperative quality of life in TEP, TAPP, and modified Lichtenstein repairs. Ann Surg. 2011. 254:709–714.2. National Health Insurance. The 2010 annals of major operation statistics. 2011. Seoul: National Health Insurance.3. Lichtenstein IL, Shulman AG, Amid PK, Montllor MM. The tension-free hernioplasty. Am J Surg. 1989. 157:188–193.4. Han MS, Lee SM, Choi SI, Joo SH, Hong SW. Comparison of laparoscopic totally extraperitoneal inguinal hernia repair and tension-free herniorrhaphy using perfix(R): short-term follow-up results. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 77:189–194.5. Lal P, Kajla RK, Chander J, Ramteke VK. Laparoscopic total extraperitoneal (TEP) inguinal hernia repair: overcoming the learning curve. Surg Endosc. 2004. 18:642–645.6. Liem MS, van Steensel CJ, Boelhouwer RU, Weidema WF, Clevers GJ, Meijer WS, et al. The learning curve for totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Am J Surg. 1996. 171:281–285.7. Seo K, Choi Y, Choi J, Yoon K. Laparoscopic appendectomy is feasible for inexperienced surgeons in the early days of individual laparoscopic training courses. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 76:23–27.8. Moore MJ, Bennett CL. The Southern Surgeons Club. The learning curve for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am J Surg. 1995. 170:55–59.9. Schlachta CM, Mamazza J, Seshadri PA, Cadeddu M, Gregoire R, Poulin EC. Defining a learning curve for laparoscopic colorectal resections. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001. 44:217–222.10. Choi YY, Kim Z, Hur KY. Learning curve for laparoscopic totally extraperitoneal repair of inguinal hernia. Can J Surg. 2012. 55:33–36.11. Kim KH, Kim MC, Jung GJ, Kim HH. The learning curve in laparoscopy assisted distal gastrectomy (LADG) with systemic lymphadenectomy for early gastric cancer considering the operation time. J Korean Surg Soc. 2006. 70:102–107.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Totally Extraperitoneal Herniorrhaphy by Logarithmic Function
- The Learning Curve of the Beginner Surgeon with Supervisor for Laparoscopic Totally Extraperitoneal Repair
- Totally Laparoscopic Distal Gastrectomy after Learning Curve Completion: Comparison with Laparoscopy-Assisted Distal Gastrectomy
- Factors influencing on difficulty with laparoscopic total extraperitoneal repair according to learning period
- Laparoscopic Extraperitoneal Resection of Urachal Cyst