Imaging Sci Dent.
2012 Dec;42(4):255-260. 10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255.
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, CSMSS Dental College and Hospital, Aurangabad, India. khamboo1927@gmail.com
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, MGM Dental College and Hospital, Navi Mumbai, India.
- 3Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Vasantdada Patil Dental College and Hospital, Sangli, India.
- KMID: 1806793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255
Abstract
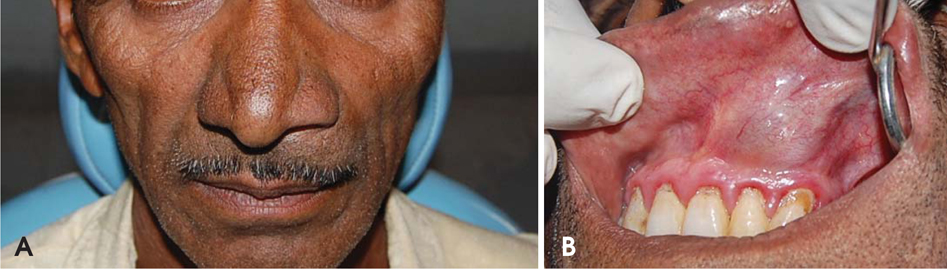
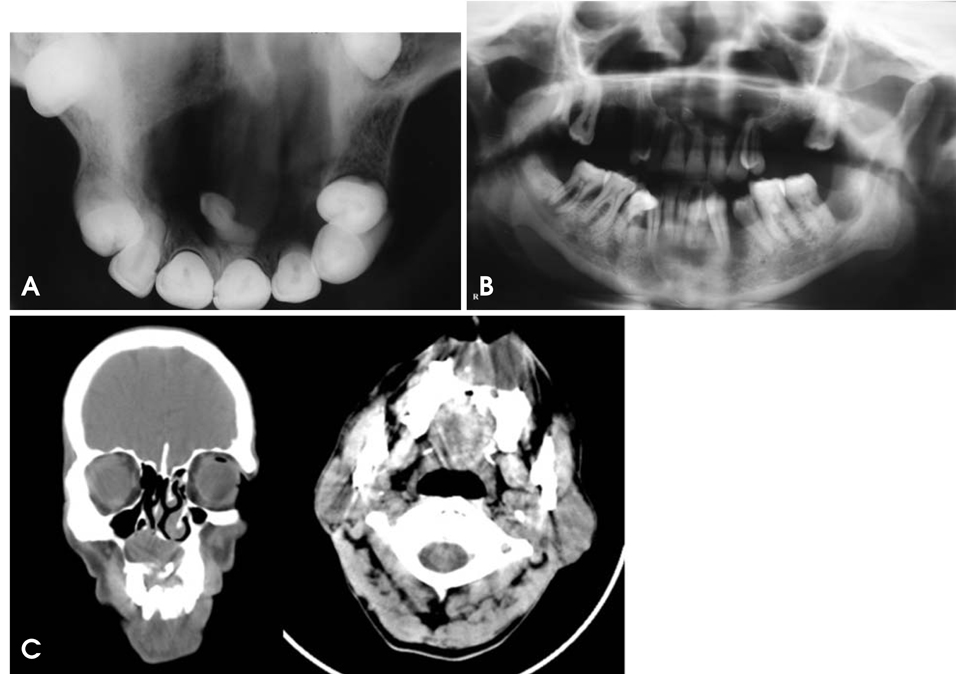
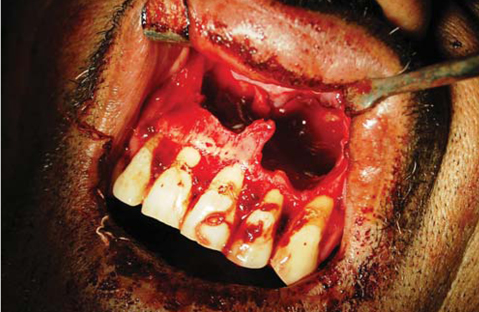
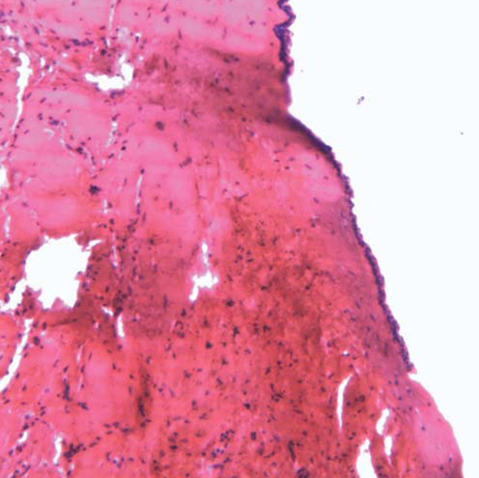
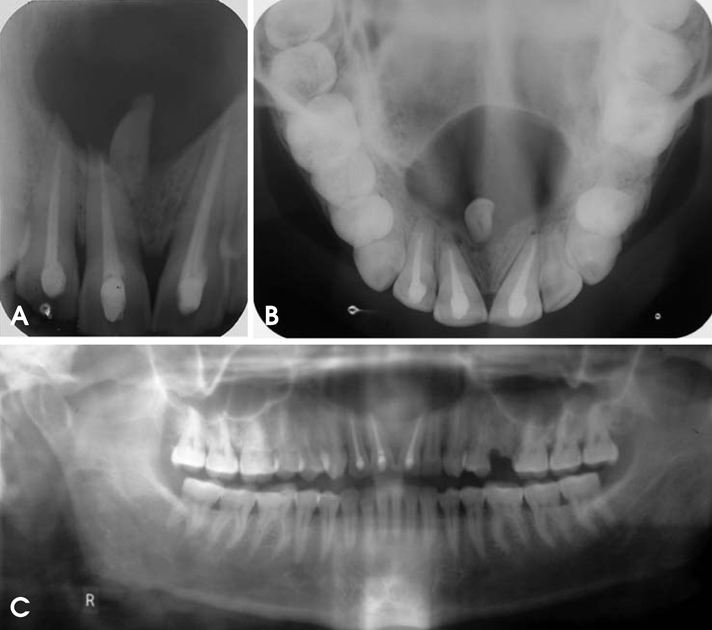
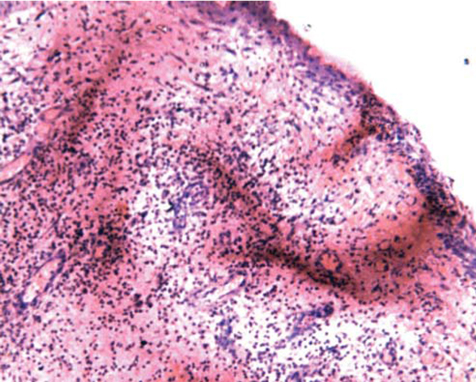
- Dentigerous cysts are the most common developmental cysts of the jaws, most frequently associated with impacted mandibular third molar teeth. Dentigerous cysts around supernumerary teeth, however, account for 5% of all dentigerous cysts, with most developing around a mesiodens in the anterior maxilla. This report describes two cases of a dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens. Both of the patients complained of swelling in the maxillary anterior region. Radiographic examination revealed an impacted mesiodens surrounded by a large corticated radiolucency in both cases. A provisional diagnosis of infected odontogenic cyst was made. The cysts were enucleated with the removal of the mesiodens in the two cases. Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of infected dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens in both cases. The patients remained asymptomatic, and no complications were noted.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buyukkurt MC, Omezli MM, Miloglu O. Dentigerous cyst associated with an ectopic tooth in the maxillary sinus: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. 109:67–71.
Article2. Ko KS, Dover DG, Jordan RC. Bilateral dentigerous cysts - report of an unusual case and review of the literature. J Can Dent Assoc. 1999. 65:49–51.3. von Arx T. Anterior maxillary supernumerary teeth: a clinical and radiographic study. Aust Dent J. 1992. 37:189–195.4. Asaumi JI, Shibata Y, Yanagi Y, Hisatomi M, Matsuzaki H, Konouchi H, et al. Radiographic examination of mesiodens and their associated complications. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2004. 33:125–127.
Article5. Gulses A, Karacayli U, Koymen R. Dentigerous cyst associated with inverted and fused supernumerary teeth in a child: a case report. Oral Health Dent Manag. 2009. 8:38–41.6. Grover SB, Singh P, Venkatachalam VP, Hekha N. Mesiodens presenting as a dentigerous cyst: Case report. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2005. 15:69–72.7. Primosch RE. Anterior supernumerary teeth - assessment and surgical intervention in children. Pediatr Dent. 1981. 3:204–215.8. Hurlen B, Humerfelt D. Characteristics of premaxillary hyperdontia. A radiographic study. Acta Odontol Scand. 1985. 43:75–81.9. Daley TD, Wysocki GP. The small dentigerous cyst. A diagnostic dilemma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. 79:77–81.10. Dinkar AD, Dawasaz AA, Shenoy S. Dentigerous cyst associated with multiple mesiodens: a case report. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2007. 25:56–59.
Article11. Tournas AS, Tewfik MA, Chauvin PJ, Manoukian JJ. Multiple unilateral maxillary dentigerous cysts in a non-syndromic patient: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol Extra. 2006. 1:100–106.
Article12. Dağistan S, Cakur B, Göregen M. A dentigerous cyst containing an ectopic canine tooth below the floor of the maxillary sinus: a case report. J Oral Sci. 2007. 49:249–252.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Long-term Follow-Up Case of Enucleation of Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: Case Report
- Huge Dentigerous Cyst
- Three dimensional evaluation of impacted mesiodens using dental cone beam CT
- A Case of Nasal Septal Abscess Originated from Dentigerous Cyst
- A comparative Ki-67 expression of odontogenic keratocysts(OKCs) with or without impacted tooth