Korean J Ophthalmol.
2013 Jun;27(3):224-227. 10.3341/kjo.2013.27.3.224.
Silent Giant Cell Arteritis in an Elderly Korean Woman
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. hjm@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1798064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.3.224
Abstract
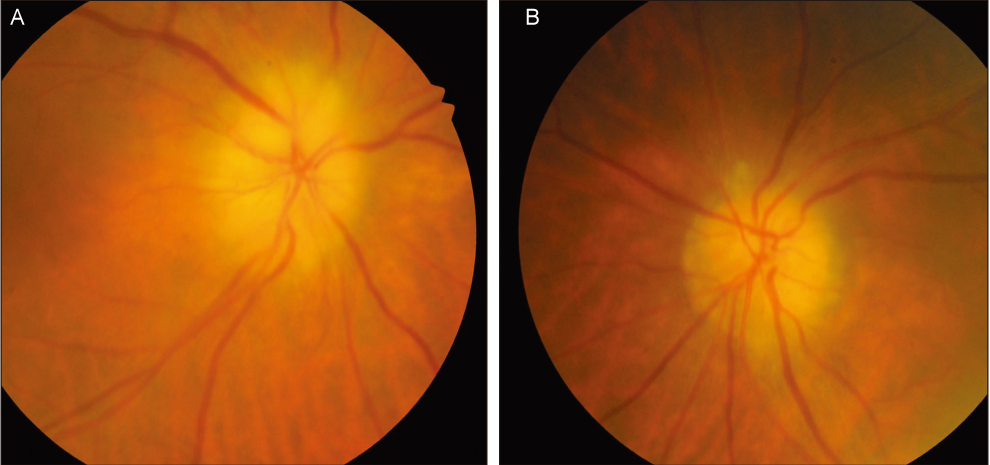
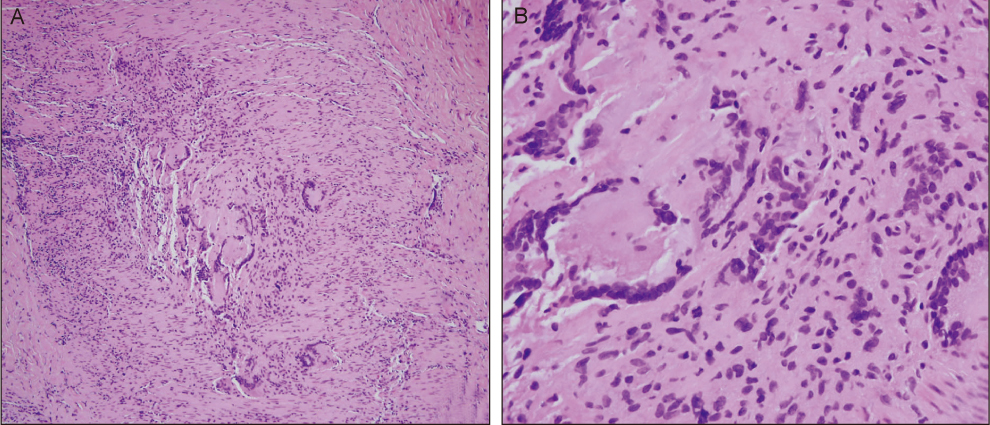
- Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a rare disease among Asians. Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, which accompanies GCA, has not yet been reported in Koreans. Diagnosis of GCA is difficult if typical symptoms other than visual loss are absent. Here, we report a case of an 83-year-old Korean woman presenting with sudden visual loss in both eyes (oculus uterque, OU). Her visual acuities included perception of light in the right eye (oculus dexter, OD) and perception of hand motion in the left eye (oculus sinister, OS). The results of the Hardy-Rand-Rittler test and Ishihara test showed total dyschromatopsia OU. The Goldmann perimetry test revealed a total field defect OD and paracentral island OS. Fundus examination revealed chalky-white disc swelling OU. Other systemic symptoms and signs were unremarkable. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein and platelet count were highly elevated. Temporal artery biopsy revealed multiple lymphocytes and multinucleated giant cells in the arterial media layer. To our knowledge, this is the first report of GCA in a Korean that has been confirmed with temporal artery biopsy. In conclusion, silent GCA can occur in Koreans, and hence, elderly patients presenting with chalky-white disc swelling, and corresponding laboratory findings must be evaluated for GCA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion after Trauma: Report of Two Cases
Joong Sik Koh, Se Joon Woo
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016;57(2):324-329. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.2.324.Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant-Cell Arteritis in Korean Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis and Review of the Literature
Jae-Hwan Choi, Jong Hoon Shin, Jae Ho Jung
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(3):386-392. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.386.Case of Brain Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis
Ho Hyun Park, Seung Heon Kang, Sang Hoon Park, Jae-Sung Park, Bon San Koo
J Rheum Dis. 2016;23(6):396-400. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2016.23.6.396.
Reference
-
1. Rahman W, Rahman FZ. Giant cell (temporal) arteritis: an overview and update. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005. 50:415–428.2. Hayreh SS, Podhajsky PA, Zimmerman B. Occult giant cell arteritis: ocular manifestations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998. 125:521–526.3. Simmons RJ, Cogan DG. Occult temporal arteritis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1962. 68:8–18.4. Ezeonyeji AN, Borg FA, Dasgupta B. Delays in recognition and management of giant cell arteritis: results from a retrospective audit. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. 30:259–262.5. Cullen JF, Chan BM, Wong CF, Chew WC. Giant cell (temporal) arteritis in Singapore: an occult case and the rationale of treatment. Singapore Med J. 2010. 51:73–77.6. Aui-Aree N, Tungsinmunkong K, Hirunpat S, et al. A variety of atypical manifestations in giant cell arteritis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010. 93:629–632.7. Lee JL, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Gershwin ME. The geoepidemiology of temporal (giant cell) arteritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. 35:88–95.8. Liu NH, LaBree LD, Feldon SE, Rao NA. The epidemiology of giant cell arteritis: a 12-year retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 2001. 108:1145–1149.9. Smith CA, Fidler WJ, Pinals RS. The epidemiology of giant cell arteritis: report of a ten-year study in Shelby County, Tennessee. Arthritis Rheum. 1983. 26:1214–1219.10. Kobayashi S, Yano T, Matsumoto Y, et al. Clinical and epidemiologic analysis of giant cell (temporal) arteritis from a nationwide survey in 1998 in Japan: the first government-supported nationwide survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 49:594–598.11. Cullen JF, Chan CM, Chuah KL. Giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis, cranial arteritis) and a case from Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2003. 44:306–308.12. Cheng CK, Lee CC, Huang KH, et al. Giant cell (temporal) arteritis with anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: a biopsy-proven case in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010. 109:550–554.13. Wang X, Hu Z, Lu W, et al. Giant cell arteritis: a rare disease in Asians. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009. 15:48.14. Chen CH, Kung SY, Tsai YY, et al. Temporal arteritis. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005. 68:333–335.15. Kwok AK, Lam DS, Liew CT. Bilateral arteritic central retinal artery occlusion in a Chinese patient. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1998. 26:175–176.16. Pereira LS, Yoon MK, Hwang TN, et al. Giant cell arteritis in Asians: a comparative study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011. 95:214–216.17. Chaudhry IA, Shamsi FA, Elzaridi E, et al. Epidemiology of giant-cell arteritis in an Arab population: a 22-year study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007. 91:715–718.18. Kwon CM, Hong YH, Chun KA, et al. A case of silent giant cell arteritis involving the entire aorta, carotid artery and brachial artery screened by integrated PET/CT. Clin Rheumatol. 2007. 26:1959–1962.19. Kim KH, Yang WI, Choi IJ. Giant cell arteritis of the breast: a case report. Yonsei Med J. 1990. 31:80–84.20. Hayreh SS, Podhajsky PA, Raman R, Zimmerman B. Giant cell arteritis: validity and reliability of various diagnostic criteria. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997. 123:285–296.21. Walvick MD, Walvick MP. Giant cell arteritis: laboratory predictors of a positive temporal artery biopsy. Ophthalmology. 2011. 118:1201–1204.