J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Feb;24(1):77-83. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.77.
Improved Detection of Germline Mutations in Korean VHL Patients by Multiple Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konyang Univeristy Hospital, College of Medical Science Konyang University, Daejon, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. culture.kim@samsung.com
- KMID: 1794410
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.77
Abstract
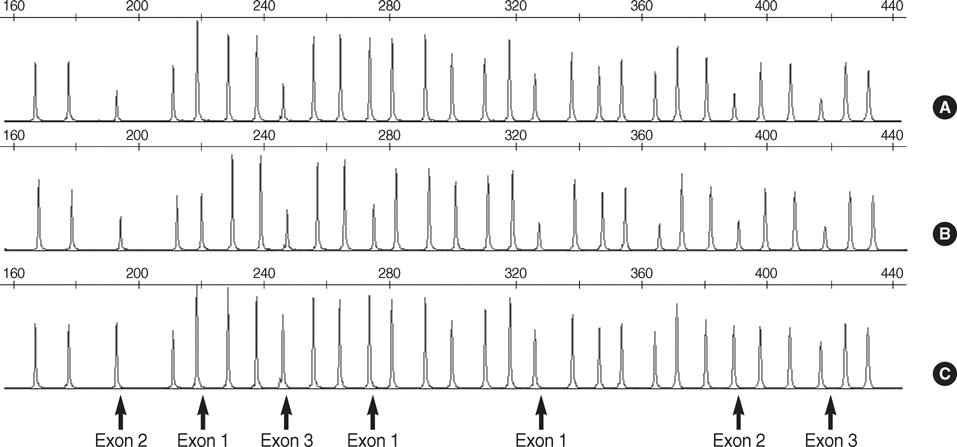
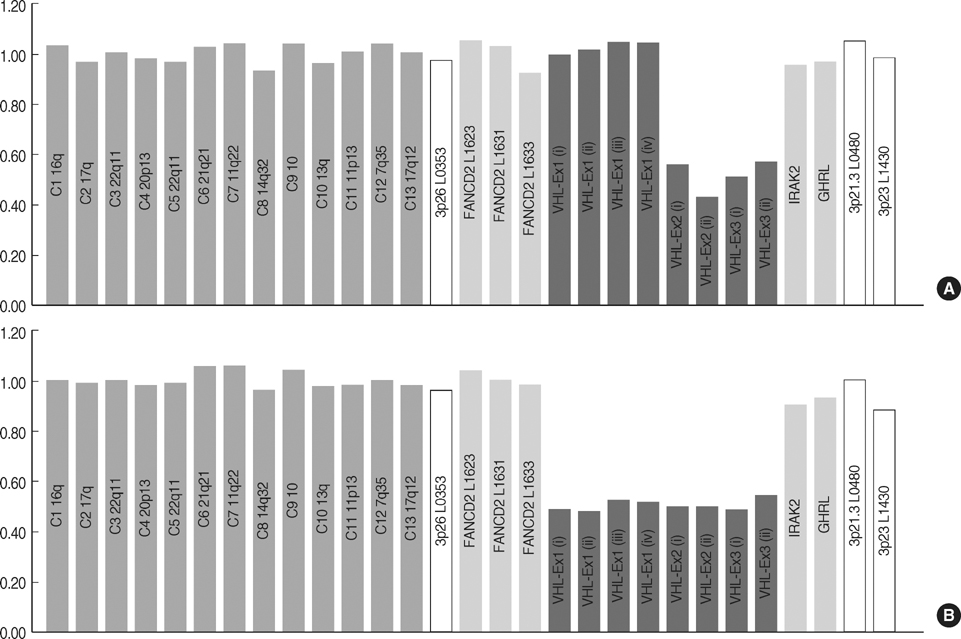
- von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant inherited tumor syndrome characterized by the development of tumors in the eye, brain, spinal cord, inner ear, adrenal gland, pancreas, kidney, and epididymis, associated with germline mutations in the VHL gene. We used sequentially sequencing method and multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) analysis and detected germline mutations in the VHL in 15/15 (100%) of VHL patients fulfilling the clinical criteria. Of the 15 distinct mutations detected, large deletions were detected in 5/15 (33.3%) patients, including 4/15 (26.7%) partial deletions and 1/15 (6.6%) deletion of the entire VHL gene by MLPA and the remainder were point mutations detected by sequencing method, of which five mutations were novel. Using MLPA analysis, we detected large deletions including both partial deletions and complete gene deletion, which has not been reported in Korean VHL patients. In conclusion, sequential application of sequencing method and MLPA analysis might make possible to identify germline mutations in most patients with VHL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
DNA Mutational Analysis/*methods
Female
Gene Deletion
Genetic Predisposition to Disease
*Germ-Line Mutation
Humans
Korea
Male
Middle Aged
*Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques
Phenotype
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Sequence Analysis
Young Adult
von Hippel-Lindau Disease/diagnosis/*genetics
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Genetic Counseling and Long-Term Surveillance Using a Multidisciplinary Approach in von Hippel–Lindau Disease
Sun Joo Yoon, Won Kyung Kwon, Geehay Hong, Ja-Hyun Jang, Byong Chang Jeong, Jae Hyeon Kim, Jong-Won Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(3):352-357. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.3.352.
Reference
-
1. Melmon KL, Rosen SW. Lindau's disease. Review of the literature and study of a large kindred. Am J Med. 1964. 36:595–617.2. Choyke PL, Glenn GM, Walther MM, Patronas NJ, Linehan WM, Zbar B. von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetic, clinical, and imaging features. Radiology. 1995. 194:629–642.
Article3. Choyke PL, Glenn GM, Wagner JP, Lubensky IA, Thakore K, Zbar B, Linehan WM, Walther MM. Epididymal cystadenomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Urology. 1997. 49:926–931.
Article4. Manski TJ, Heffner DK, Glenn GM, Patronas NJ, Pikus AT, Katz D, Lebovics R, Sledjeski K, Choyke PL, Zbar B, Linehan WM, Oldfield EH. Endolymphatic sac tumors. A source of morbid hearing loss in von Hippel-Lindau disease. JAMA. 1997. 277:1461–1466.
Article5. Richard S, David P, Marsot-Dupuch K, Giraud S, Beroud C, Resche F. Central nervous system hemangioblastomas, endolymphatic sac tumors, and von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neurosurg Rev. 2000. 23:1–22. discussion 23-4.
Article6. Maddock IR, Moran A, Maher ER, Teare MD, Norman A, Payne SJ, Whitehouse R, Dodd C, Lavin M, Hartley N, Super M, Evans DG. A genetic register for von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Med Genet. 1996. 33:120–127.
Article7. Maher ER, Iselius L, Yates JR, Littler M, Benjamin C, Harris R, Sampson J, Williams A, Ferguson-Smith MA, Morton N. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: a genetic study. J Med Genet. 1991. 28:443–447.
Article8. Kaelin WG Jr. Molecular basis of the VHL hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002. 2:673–682.
Article9. Seizinger BR, Rouleau GA, Ozelius LJ, Lane AH, Farmer GE, Lamiell JM, Haines J, Yuen JW, Collins D, Majoor-Krakauer D, Bonner T, Mathew C, Rubenstein A, Halperin J, Mcconkie-Rosell A, Green JS, Trofatter JA, Ponder BA, Eierman L, Bowmer MI, Schimke R, Oostra B, Aronin N, Smith DI, Drabkin H, Waziri MH, Hobbs WJ, Martuza RL, Conneally PM, Hsia YE, Gusella JF. Von Hippel-Lindau disease maps to the region of chromosome 3 associated with renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 1998. 332:268–269.
Article10. Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh FM, Orcutt ML, Stackhouse T, Kuzmin I, Modi W, Geil L, Schmidt L, Zhou F, Li H, Wei MH, Chen F, Glenn G, Choyke P, Walter MM, Weng Y, Duan DS, Dean M, Glavac D, Richards FM, Crossey PA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Paslier DL, Chumakov I, Cohen D, Chinault AC, Maher ER, Linehan WM, Zbar B, Lerman MI. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science. 1993. 260:1317–1320.
Article11. Crossey PA, Richards FM, Foster K, Green JS, Prowse A, Latif F, Lerman MI, Zbar B, Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Maher ER. Identification of intragenic mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene and correlation with disease phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1994. 3:1303–1308.12. Whaley JM, Naglich J, Gelbert L, Hsia YE, Lamiell JM, Green JS, Collins D, Neumann HP, Laidlaw J, Li FP, Klein-Szanto AJP, Seizinger BR, Kley N. Germ-line mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor gene are similar to somatic von Hippel-Lindau aberrations in sporadic renal cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 1994. 55:1092–1102.13. Chen F, Kishida T, Yao M, Hustad T, Glavac D, Dean M, Gnarra JR, Orcutt ML, Duh FM, Glenn G. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene: correlations with phenotype. Hum Mutat. 1995. 5:66–75.
Article14. Clinical Research Group for VHL in Japan. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene in Japanese VHL. Hum Mol Genet. 1995. 4:2233–2237.15. Maher ER, Webster AR, Richards FM, Green JS, Crossey PA, Payne SJ, Moore AT. Phenotypic expression in von Hippel-Lindau disease: correlations with germline VHL gene mutations. J Med Genet. 1996. 33:328–332.
Article16. Zbar B, Kishida T, Chen F, Schmidt L, Maher ER, Richards FM, Crossey PA, Webster AR, Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Brauch H, Glavac D, Neumann HP, Tisherman S, Mulvihill JJ, Gross DJ, Shuin T, Whaley J, Seizinger B, Kley N, Olschwang S, Boisson C, Richard S, Lips CH, Linehan WM, Lerman M. Germline mutations in the Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene in families from North America, Europe, and Japan. Hum Mutat. 1996. 8:348–357.
Article17. Kamada M, Suzuki K, Kato Y, Okuda H, Shuin T. von Hippel-Lindau protein promotes the assembly of actin and vinculin and inhibits cell motility. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:4184–4189.18. Stolle C, Glenn G, Zbar B, Humphrey JS, Choyke P, Walther M, Pack S, Hurley K, Andrey C, Klausner R, Linehan WM. Improved detection of germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Hum Mutat. 1998. 12:417–423.
Article19. Rocha JC, Silva RL, Mendonca BB, Marui S, Simpson AJ, Camargo AA. High frequency of novel germline mutations in the VHL gene in the heterogeneous population of Brazil. J Med Genet. 2003. 40:e31.
Article20. Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. 30:e57.
Article21. Sellner LN, Taylor GR. MLPA and MAPH: new techniques for detection of gene deletions. Hum Mutat. 2004. 23:413–419.
Article22. Scarciolla O, Stuppia L, De Angelis MV, Murru S, Palka C, Giuliani R, Pace M, Di Muzio A, Torrente I, Morella A, Grammatico P, Giacanelli M, Rosatelli MC, Uncini A, Dallapiccola B. Spinal muscular atrophy genotyping by gene dosage using multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification. Neurogenetics. 2006. 7:269–276.
Article23. Cybulski C, Krzystolik K, Maher ER, Richard S, Kurzawski G, Gronwald J, Lubinski J. Long polymerase chain reaction in detection of germline deletions in the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene. Hum Genet. 1999. 105:333–336.
Article24. Cybulski C, Krzystolik K, Murgia A, Gorski B, Debniak T, Jakubowska A, Martella M, Kurzawski G, Prost M, Kojder I, Limon J, Nowacki P, Sagan L, Bialas B, Kaluza J, Zdunek M, Omulecka A, Jaskolski D, Kostyk E, Koraszewska-Matuszewska B, Haus O, Janiszewska H, Pecold K, Starzycka M, Slomski R, Cwirko M, Sikorski A, Gliniewicz B, Cyrylowski L, Fiszer-Maliszewska L, Gronwald J, Toloczko-Grabarek A, Zajaczek S, Lubinski J. Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene in patients from Poland: disease presentation in patients with deletions of the entire VHL gene. J Med Genet. 2002. 39:E38.
Article25. Sgambati MT, Stolle C, Choyke PL, Walther MM, Zbar B, Linehan WM, Glenn GM. Mosaicism in von Hippel-Lindau disease: lessons from kindreds with germline mutations identified in offspring with mosaic parents. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. 66:84–91.
Article26. Glavac D, Neumann HP, Wittke C, Jaenig H, Masek O, Streicher T, Pausch F, Engelhardt D, Plate KH, Hofler H, Chen F, Zbar B, Brauch H. Mutations in the VHL tumor suppressor gene and associated lesions in families with von Hippel-Lindau disease from central Europe. Hum Genet. 1996. 98:271–280.27. Maher ER, Yates JR, Harries R, Benjamin C, Harris R, Moore AT, Ferguson-Smith MA. Clinical features and natural history of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Q J Med. 1990. 77:1151–1163.
Article28. Richard S, Campello C, Taillandier L, Parker F, Resche F. French VHL Study Group. Haemangioblastoma of the central nervous system in von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Intern Med. 1998. 243:547–553.
Article29. Gallou C, Joly D, Mejean A, Staroz F, Martin N, Tarlet G, Orfanelli MT, Bouvier R, Droz D, Chretien Y, Marechal JM, Richard S, Junien C, Beroud C. Mutations of the VHL gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: definition of a risk factor for VHL patients to develop an RCC. Hum Mutat. 1999. 13:464–475.
Article30. Gallou C, Chauveau D, Richard S, Joly D, Giraud S, Olschwang S, Martin N, Saquet C, Chretien Y, Mejean A, Correas JM, Benoit G, Colombeau P, Grunfeld JP, Junien C, Beroud C. Genotype-phenotype correlation in von Hippel-Lindau families with renal lesions. Hum Mutat. 2004. 24:215–224.
Article31. Yoshida M, Ashida S, Kondo K, Kobayashi K, Kanno H, Shinohara N, Shitara N, Kishida T, Kawakami S, Baba M, Yamamoto I, Hosaka M, Shuin T, Yao M. Germ-line mutation analysis in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease in Japan: an extended study of 77 families. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000. 91:204–212.
Article32. Friedrich CA. Genotype-phenotype correlation in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. 10:763–767.
Article33. Kang HC, Kim IJ, Park JH, Shin Y, Jang SG, Ahn SA, Park HW, Lim SK, Oh SK, Kim DJ, Lee KW, Choi YS, Park YJ, Lee MR, Kim DW, Park JG. Three novel VHL germline mutations in Korean patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease and pheochromocytomas. Oncol Rep. 2005. 14:879–883.
Article34. Olschwang S, Richard S, Boisson C, Giraud S, Laurent-Puig P, Resche F, Thomas G. Germline mutation profile of the VHL gene in von Hippel-Lindau disease and in sporadic hemangioblastoma. Hum Mutat. 1998. 12:424–430.35. Crossey PA, Eng C, Ginalska-Malinowska M, Lennard TW, Wheeler DC, Ponder BA, Maher ER. Molecular genetic diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau disease in familial pheochromocytoma. J Med Genet. 1995. 32:885–886.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Effectiveness of Copy Number Variation Detection Using Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification in Patients with Lynch Syndrome-Related Cancer
- Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification Analysis Subsequent to Direct DNA Full Sequencing for Identifying ATP7B Mutations and Phenotype Correlations in Children with Wilson Disease
- Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Retinal Capillary Hemangioblastoma in Korean Patients
- Mutational Research of von Hippel-Lindau Gene of Family with von Hippel-Lindau Disease
- Clinical Usefulness of Molecular Diagnosis in Dystrophin Gene Mutations Using the Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) Method