Korean J Leg Med.
2015 May;39(2):49-52. 10.7580/kjlm.2015.39.2.49.
Sudden Death from Acute Epiglottitis and Epiglottic Abscess in Adult
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. foremed@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1794324
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2015.39.2.49
Abstract
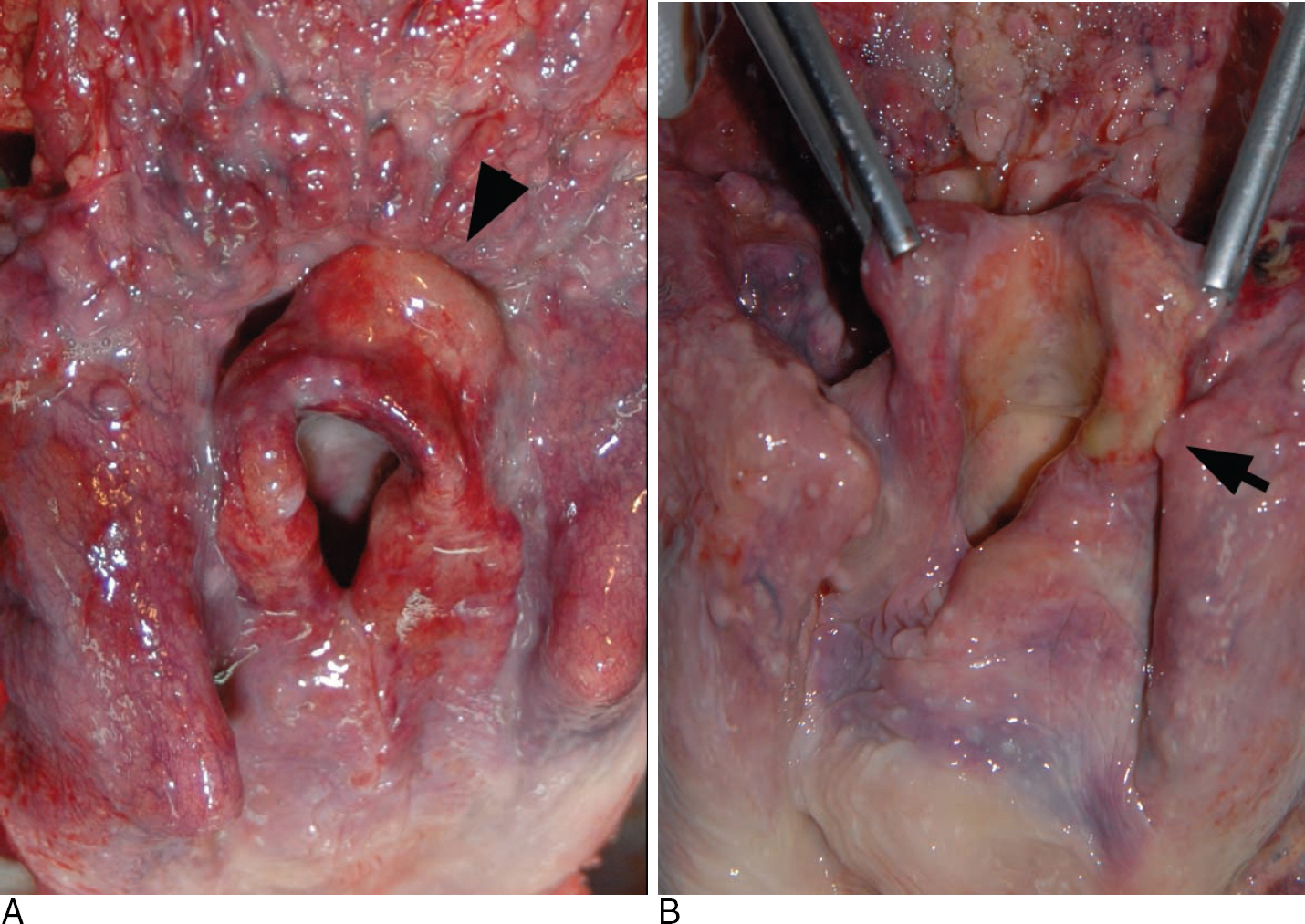
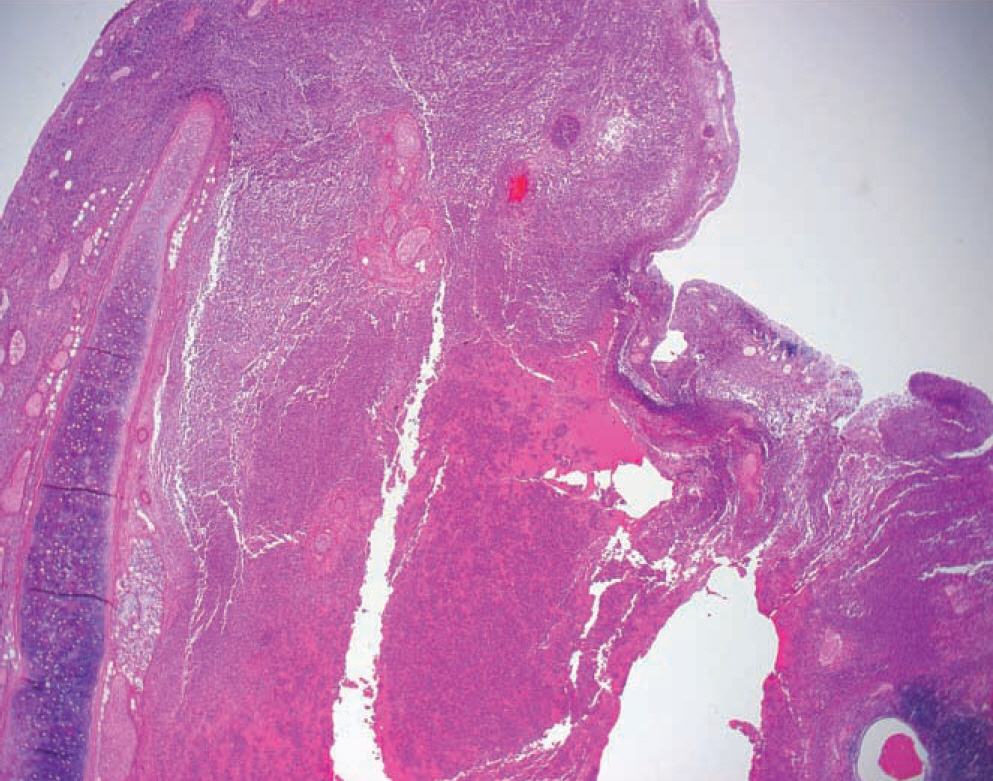
- Acute epiglottitis is an inflammation of the epiglottis and adjacent structures. Although the incidence is extremely rare, acute epiglottitis is a life-threatening medical emergency and can cause sudden respiratory obstruction. Herein, we describe two cases of sudden death from epiglottitis and epiglottic abscess. A 39-year-old man and 66-year-old man died after suffering from shortness of breath. Autopsies revealed diffuse swelling and abscess formation in the epiglottis and neighboring structures. These cases emphasize the medicolegal importance of sudden death from acute epiglottitis and epiglottic abscess in adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berger G, Landau T, Berger S, et al. The rising incidence of adult acute epiglottitis and epiglottic abscess. Am J Otolaryngol. 2003; 24:374–83.
Article2. Isakson M, Hugosson S. Acute epiglottitis: epidemiology and Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype distribution in adults. J Laryngol Otol. 2011; 125:390–3.
Article3. Guldfred LA, Lyhne D, Becker BC. Acute epiglottitis: epidemiology, clinical presentation, management and outcome. J Laryngol Otol. 2008; 122:818–23.
Article4. Harvey M, Quagliotto G, Milne N. Fatal epiglottic abscess after radiotherapy for laryngeal carcinoma. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2012; 33:297–9.
Article5. Stack BC Jr, Ridley MB. Epiglottic abscess. Head Neck. 1995; 17:263–5.
Article6. Hindy J, Novoa R, Slovik Y, et al. Epiglottic abscess as a complication of acute epiglottitis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2013; 34:362–5.
Article7. Shah RK, Stocks C. Epiglottitis in the United States: national trends, variances, prognosis, and management. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120:1256–62.
Article8. Yang KM, Jung NE, Kim JK, et al. Sudden death due to epiglottic abscess. Korean J Leg Med. 2007; 31:89–91.9. Kahn MW, Miovic M, Perez-Cahill D. Epiglottitis in a psychotic, non-English-speaking adult. Psychiatr Serv. 2000; 51:254.
Article10. Kornak JM, Freije JE, Campbell BH. Caustic and thermal epiglottitis in the adult. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 114:310–2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sudden death due to epiglottic abscess
- Three Cases of the Epiglottic Abscess
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- A Case of Empyema and Retropharyngeal Abscess Complicated by Acute Epiglottitis
- Objective Criteria for Radiologic Diagnosis of Epiglottitis in Korean Adults