J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Aug;28(8):1213-1219. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1213.
The Impact of Inosine Triphosphatase Variants on Hemoglobin Level and Sustained Virologic Response of Chronic Hepatitis C in Korean
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. 93cool@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Molecular Medicine, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1793028
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1213
Abstract
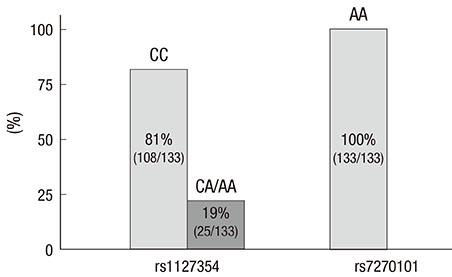
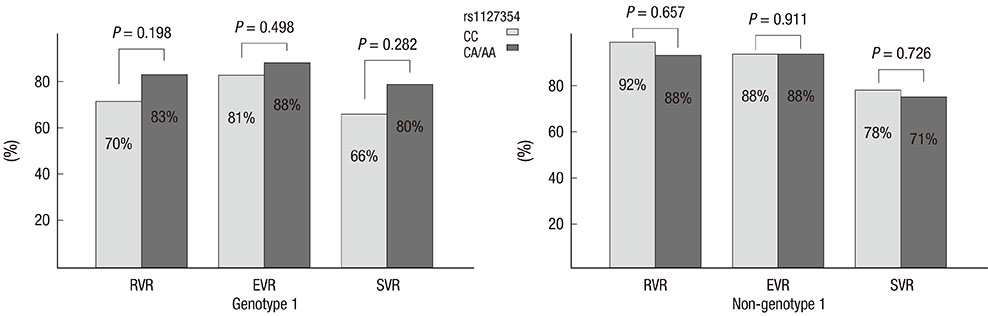
- Two variants of the inosine triphosphatase (ITPA: rs1127354, rs7270101) gene cause ITPA deficiency and protect against the hemolytic toxicity of ribavirin. We investigated the clinical significance of ITPA variants in Korean patients treated with pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) plus ribavirin. Of the 133 patients, 108 were CC and 25 were non-CC at rs1127354 (groups A and B, respectively). On the other hand, at rs7270101 all 133 were AA. The mean values of Hemoglobin (Hgb) after 4, 8, and 12 weeks of treatment in groups A and B were 12.2 and 14.0, 11.8 and 13.2, and 11.5 and 12.9, respectively (P=0.001, 0.036, 0.036). Sustained virologic response (SVR) was achieved in 67.8% (40/59) of genotype 1 patients and in 75% (27/36) of non-genotype 1 patients. Regarding ITPA variants, SVR was achieved by 66% and 80% of genotype 1 (P=0.282), and by 78% and 71% (P=0.726) of non-genotype 1. SVR was not significantly different in groups A and B. In conclusion, non-CC at rs1127354 without involvement of rs7270101 is strongly associated with protection from ribavirin-induced anemia, however, ITPA genotype is not associated with SVR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Alleles
Antiviral Agents/therapeutic use
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Cohort Studies
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Genotype
Hemoglobins/*analysis
Hemolysis
Hepacivirus/genetics
Hepatitis C, Chronic/drug therapy/*genetics
Humans
Interferon-alpha/therapeutic use
Interleukins/genetics
Male
Middle Aged
Polyethylene Glycols/therapeutic use
Pyrophosphatases/*genetics
Recombinant Proteins/therapeutic use
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Ribavirin/therapeutic use
Treatment Outcome
Antiviral Agents
Hemoglobins
Interferon-alpha
Interleukins
Polyethylene Glycols
Pyrophosphatases
Recombinant Proteins
Ribavirin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davis GL, Alter MJ, El-Serag H, Poynard T, Jennings LW. Aging of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected persons in the United States: a multiple cohort model of HCV prevalence and disease progression. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:513–521.2. Wiese M, Grüngreiff K, Güthoff W, Lafrenz M, Oesen U, Porst H. East German Hepatitis C Study Group. Outcome in a hepatitis C (genotype 1b) single source outbreak in Germany: a 25-year multicenter study. J Hepatol. 2005; 43:590–598.3. Massard J, Ratziu V, Thabut D, Moussalli J, Lebray P, Benhamou Y, Poynard T. Natural history and predictors of disease severity in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2006; 44:S19–S24.4. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Gonçales FL Jr, Häussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:975–982.5. Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001; 358:958–965.6. Homma M, Hosono H, Hasegawa Y, Kohda Y. Morphological transformation and phosphatidylserine exposure in erythrocytes treated with ribavirin. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009; 32:1940–1942.7. Sakamoto N, Tanaka Y, Nakagawa M, Yatsuhashi H, Nishiguchi S, Enomoto N, Azuma S, Nishimura-Sakurai Y, Kakinuma S, Nishida N, et al. ITPA gene variant protects against anemia induced by pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin therapy for Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Res. 2010; 40:1063–1071.8. You BC, Kim YS, Kim Hi, Kim SH, Park SS, Seo YR, Kim SG, Lee SW, Kim HS, Jeong SW, et al. A reduced dose of ribavirin does not influence the virologic response during pegylated interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin combination therapy in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012; 18:272–278.9. Jeong SH, Jung YK, Yang JW, Park SJ, Kim JW, Kwon OS, Kim YS, Choi DJ, Kim JH. Efficacy of peginterferon and ribavirin is associated with the IL28B gene in Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012; 18:360–367.10. Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Ge D, Gumbs CE, Urban TJ, Shianna KV, Little LD, Qiu P, Bertelsen AH, Watson M, et al. ITPA gene variants protect against anaemia in patients treated for chronic hepatitis C. Nature. 2010; 464:405–408.11. Thompson AJ, Fellay J, Patel K, Tillmann HL, Naggie S, Ge D, Urban TJ, Shianna KV, Muir AJ, Fried MW, et al. Variants in the ITPA gene protect against ribavirin-induced hemolytic anemia and decrease the need for ribavirin dose reduction. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:1181–1189.12. Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009; 29:74–81.13. D'Souza R, Foster GR. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C. J R Soc Med. 2004; 97:223–225.14. Reichard O, Norkrans G, Frydén A, Braconier JH, Sönnerborg A, Weiland O. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of interferon alpha-2b with and without ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C: the Swedish Study Group. Lancet. 1998; 351:83–87.15. Brok J, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Ribavirin monotherapy for chronic hepatitis C infection: a Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:842–847.16. Krishnan SM, Dixit NM. Ribavirin-induced anemia in hepatitis C virus patients undergoing combination therapy. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011; 7:e1001072.17. Russmann S, Grattagliano I, Portincasa P, Palmieri VO, Palasciano G. Ribavirin-induced anemia: mechanisms, risk factors and related targets for future research. Curr Med Chem. 2006; 13:3351–3357.18. McHutchison JG, Manns M, Patel K, Poynard T, Lindsay KL, Trepo C, Dienstag J, Lee WM, Mak C, Garaud JJ, et al. Adherence to combination therapy enhances sustained response in genotype-1-infected patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:1061–1069.19. Reddy KR, Nelson DR, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin: current role in the optimal clinical management of chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2009; 50:402–411.20. De Franceschi L, Fattovich G, Turrini F, Ayi K, Brugnara C, Manzato F, Noventa F, Stanzial AM, Solero P, Corrocher R. Hemolytic anemia induced by ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: role of membrane oxidative damage. Hepatology. 2000; 31:997–1004.21. Takaki S, Tsubota A, Hosaka T, Akuta N, Someya T, Kobayashi M, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Saitoh S, Arase Y, et al. Factors contributing to ribavirin dose reduction due to anemia during interferon alfa2b and ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:668–673.22. Bierau J, Lindhout M, Bakker JA. Pharmacogenetic significance of inosine triphosphatase. Pharmacogenomics. 2007; 8:1221–1228.23. Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Akuta N, Sezaki H, Hirakawa M, Kawamura Y, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Saito S, Arase Y, et al. Influence of ITPA polymorphisms on decreases of hemoglobin during treatment with pegylated interferon, ribavirin, and telaprevir. Hepatology. 2011; 53:415–421.24. Ochi H, Maekawa T, Abe H, Hayashida Y, Nakano R, Kubo M, Tsunoda T, Hayes CN, Kumada H, Nakamura Y, et al. ITPA polymorphism affects ribavirin-induced anemia and outcomes of therapy: a genome-wide study of Japanese HCV virus patients. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:1190–1197.25. Shiffman ML, Ghany MG, Morgan TR, Wright EC, Everson GT, Lindsay KL, Lok AS, Bonkovsky HL, Di Bisceglie AM, Lee WM, et al. Impact of reducing peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin dose during retreatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:103–112.26. Reddy KR, Shiffman ML, Morgan TR, Zeuzem S, Hadziyannis S, Hamzeh FM, Wright TL, Fried M. Impact of ribavirin dose reductions in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 patients completing peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:124–129.27. Shin HR, Hwang SY, Nam CM. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in Korea: pooled analysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2005; 20:985–988.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Durability of a sustained virologic response in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with peginterferon and ribavirin
- Development and surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with sustained virologic response after antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C
- Clinical Utility of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer in Chronic Liver Diseases
- Antiviral Therapy in Patients after Treatment for Hepatitis C-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Role of vitamin D in chronic hepatitis C