J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Dec;25(12):1792-1797. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1792.
Desmopressin is an Effective Treatment for Mixed Nocturia with Nocturnal Polyuria and Decreased Nocturnal Bladder Capacity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Integrative Bioscience and Biotechnology, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ksleedr@skku.edu
- 8Department of Urology, College of Medicine Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1792905
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1792
Abstract
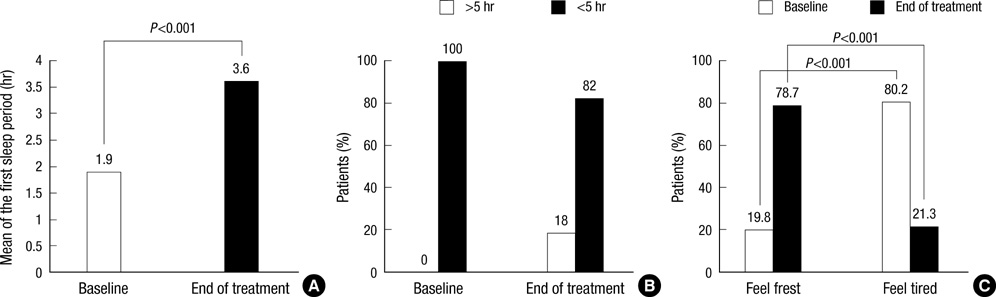
- To investigate the efficacy and safety of desmopressin in patients with mixed nocturia, Patients aged > or =18 yr with mixed nocturia (> or =2 voids/night and a nocturnal polyuria index [NPi] >33% and a nocturnal bladder capacity index [NBCi] >1) were recruited. The optimum dose of oral desmopressin was determined during a 3-week dose-titration period and the determined dose was maintained for 4 weeks. The efficacy was assessed by the frequency-volume charts and the sleep questionnaire. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a 50% or greater reduction in the number of nocturnal voids (NV) compared with baseline. Among 103 patients enrolled, 94 (79 men and 15 women) were included in the analysis. The proportion of patients with a 50% or greater reduction in NV was 68 (72%). The mean number of NV decreased significantly (3.20 to 1.34) and the mean nocturnal urine volume, nocturia index, NPi, and NBCi decreased significantly. The mean duration of sleep until the first NV was prolonged from 118.4+/-44.1 to 220.3+/-90.7 min (P<0.001). The overall impression of patients about their quality of sleep improved. Adverse events occurred in 6 patients, including one asymptomatic hyponatremia. Desmopressin is an effective and well-tolerated treatment for mixed nocturia.
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Oral
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Antidiuretic Agents/*administration & dosage
Deamino Arginine Vasopressin/*administration & dosage
Drug Administration Schedule
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Nocturia/complications/*drug therapy
Polyuria/complications/*drug therapy
Prospective Studies
Questionnaires
Sleep/drug effects/physiology
Urinary Bladder/*physiopathology
Urodynamics/physiology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Van Kerrebroeck PE. Experience with the long-term use of desmopressin for nocturnal enuresis in children and adolescents. BJU Int. 2002. 89:420–425.
Article2. Malmsten UG, Milsom I, Molander U, Norlén LJ. Urinary incontinence and lower urinary tract symptoms: an epidemiological study of men aged 45 to 99 years. J Urol. 1997. 158:1733–1737.
Article3. Irwin DE, Milsom I, Hunskaar S, Reilly K, Kopp Z, Herschorn S, Coyne K, Kelleher C, Hampel C, Artibani W, Abrams P. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: results of the EPIC study. Eur Urol. 2006. 50:1306–1314.
Article4. Choo MS, Ku JH, Park CH, Lee YS, Lee KS, Lee JG, Park WH. Prevalence of nocturia in a Korean population aged 40 to 89 years. Neurourol Urodyn. 2008. 27:60–64.
Article5. Asplund R, Aberg H. Health of the elderly with regard to sleep and nocturnal micturition. Scand J Prim Health Care. 1992. 10:98–104.
Article6. Asplund R, Sundberg B, Bengtsson P. Oral desmopressin for nocturnal polyuria in elderly subjects: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized exploratory study. BJU Int. 1999. 83:591–595.
Article7. Bing MH, Moller LA, Jennum P, Mortensen S, Skovgaard LT, Lose G. Prevalence and bother of nocturia, and causes of sleep interruption in a Danish population of men and women aged 60-80 years. BJU Int. 2006. 98:599–604.
Article8. Chen FY, Dai YT, Liu CK, Yu HJ, Liu CY, Chen TH. Perception of nocturia and medical consulting behavior among community-dwelling women. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2007. 18:431–436.
Article9. Weiss JP, Blaivas JG, Stember DS, Brooks MM. Nocturia in adults: etiology and classification. Neurourol Urodyn. 1998. 17:467–472.
Article10. Marinkovic SP, Gillen LM, Stanton SL. Managing nocturia. BMJ. 2004. 328:1063–1066.
Article11. Van Kerrebroeck P, Abrams P, Chaikin D, Donovan J, Fonda D, Jackson S, Jennum P, Johnson T, Lose G, Mattiasson A, Robertson G, Weiss J. The standardisation of terminology in nocturia: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002. 21:179–183.
Article12. Asplund R, Sundberg B, Bengtsson P. Desmopressin for the treatment of nocturnal polyuria in the elderly: a dose titration study. Br J Urol. 1998. 82:642–646.
Article13. Belmaker RH, Bleich A. The use of desmopressin in adult enuresis. Mil Med. 1986. 151:660–662.
Article14. Vilhardt H. Basic pharmacology of desmopressin. A review. Drug Invest. 1990. 2:Suppl 5. 2–8.15. Mattiasson A, Abrams P, Van Kerrebroeck P, Walter S, Weiss J. Efficacy of desmopressin in the treatment of nocturia: a double-blind placebo-controlled study in men. BJU Int. 2002. 89:855–862.
Article16. Nam SG, Moon DG, Kim JJ. Efficacy of desmopressin in treatment of adult nocturia. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:49–55.17. Weiss JP, Blaivas JG. Nocturia. Curr Urol Rep. 2003. 4:362–366.
Article18. Kim ET, Lee SI, Lee KS. The etiology and classification of nocturia in adults. Korean J Urol. 2001. 42:1075–1079.19. Weiss JP. Nocturia: "do the math". J Urol. 2006. 175:S16–S18.
Article20. Kirkland JL, Lye M, Levy DW, Banerjee AK. Patterns of urine flow and electrolyte excretion in healthy elderly people. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983. 287:1665–1667.
Article21. Nadal M. Secretory rhythm of vasopressin in healthy subjects with inversed sleepwake cycle: evidence for the existence of an intrinsic regulation. Eur J Endocrinol. 1996. 134:174–176.
Article22. Rembratt A, Norgaard JP, Andersson KE. Desmopressin in elderly patients with nocturia: short-term safety and effects on urine output, sleep and voiding patterns. BJU Int. 2003. 91:642–646.
Article23. Iwasaki H, Koyama Y, Tanaka Y, Kawauchi A, Jodo E, Kayama Y, Miki T. Modulation by desmopressin of neuronal activity in brainstem micturition center. Urology. 2004. 63:994–998.
Article24. Blok C, Coolsaet BL, Mansour M, Razzouk A. Dynamics of the ureterovesical junction: interaction between diuresis and detrusor instability at the ureterovesical junction in pigs. J Urol. 1986. 136:1123–1126.
Article25. Van Kerrebroeck P, Rezapour M, Cortesse A, Thüroff J, Riis A, Nørgaard JP. Desmopressin in the treatment of nocturia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Urol. 2007. 52:221–229.
Article26. Thomas S. Some effects of changes of posture on water and electrolyte excretion by the human kidney. J Physiol. 1957. 139:337–352.27. Bae JH, Oh MM, Shim KS, Cheon J, Lee JG, Kim JJ, Moon DG. The effects of long-term administration of oral desmopressin on the baseline secretion of antidiuretic hormone and serum sodium concentration for the treatment of nocturia: a circadian study. J Urol. 2007. 178:200–203.
Article28. Weatherall M. The risk of hyponatremia in older adults using desmopressin for nocturia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004. 23:302–305.
Article29. Rittig S, Jensen AR, Jensen KT, Pedersen EB. Effect of food intake on the pharmacokinetics and antidiuretic activity of oral desmopressin (DDAVP) in hydrated normal subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1998. 48:235–241.
Article30. Lethagen S, Frick K, Sterner G. Antidiuretic effect of desmopressin given in hemostatic dosages to healthy volunteers. Am J Hematol. 1998. 57:153–159.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age Related Change of Nocturia in Women
- Age Related Changes of Voiding Patterns in Women with Overactive Bladder
- Changes of Voiding Patterns with Age in Normal Adult Males
- Study on Persistent Nocturia after Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Effectiveness of Desmopressin in Persistent Nocturia with Nocturnal Polyuria
- Pharmacotherapy for female nocturia