Clin Endosc.
2013 Jan;46(1):102-105. 10.5946/ce.2013.46.1.102.
Giant Brunner's Gland Adenoma of the Proximal Jejunum Presenting as Iron Deficiency Anemia and Mimicking Intussusceptions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Medical Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhj1229@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Hallym University Medical Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1792650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.1.102
Abstract
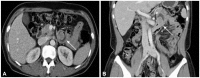
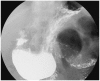
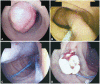
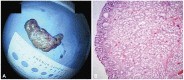
- Brunner's gland adenoma is a rare benign proliferative lesion developing most commonly in the posterior wall of the duodenum. It is usually small in size and asymptomatic. Depending on its size or location, however, the clinical manifestations of this tumor may be variable from nonspecific symptoms to gastrointestinal bleeding or obstruction. Brunner's gland adenoma in the proximal jejunum is extremely rare. We report a very rare case of giant Brunner's gland adenoma developing in the proximal jejunum which presented as iron deficiency anemia and mimicked intussusceptions on radiologic studies.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case Of Huge Brunner's Gland Adenoma With Acute Bleeding Treated By Endoscopic Resection
Pyung Kang Park, Woo-Cho Chung, Kyoung Yong Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Jae Jung Jang, Seungchul Suh
Kosin Med J. 2015;30(2):171-174. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2015.30.2.171.
Reference
-
1. Sleisenger MH, Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger & Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management. 2006. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.2. Hirasaki S, Kubo M, Inoue A, Miyake Y, Oshiro H. Pedunculated Brunner's gland hamartoma of the duodenum causing upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:373–375. PMID: 19140240.
Article3. El Faleh I, Lutz N, Osterheld MC, Reinberg O, Nydegger A. Gastric outlet obstruction by Brunner's gland hyperplasia in an 8-year-old child. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:E21–E24. PMID: 19361619.
Article4. Cruveilhier J. Anatomie Pathologique du Corps Humain. 1835. Paris: Bailliere.5. Krause WJ, Stevens R, Palmiter P. The effect of surgical ablation of Brunner's glands on the proximal duodenal mucosa. Anat Anz. 1988; 166:111–115. PMID: 3189825.6. Stolte M, Schwabe H, Prestele H. Relationship between diseases of the pancreas and hyperplasia of Brunner's glands. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981; 394:75–87. PMID: 7336574.
Article7. Feyrter F. Über wucherungen der brunnerschen drüsen. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1934; 293:509–526.
Article8. Christie AC. Duodenal carcinoma with neoplastic transformation of the underlying Brunner's glands. Br J Cancer. 1953; 7:65–67. PMID: 13051506.
Article9. Fujimaki E, Nakamura S, Sugai T, Takeda Y. Brunner's gland adenoma with a focus of p53-positive atypical glands. J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:155–158. PMID: 10680672.
Article10. Mayoral W, Salcedo JA, Montgomery E, Al-Kawas FH. Biliary obstruction and pancreatitis caused by Brunner's gland hyperplasia of the ampulla of Vater: a case report and review of the literature. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:998–1001. PMID: 11147953.
Article11. Henken EM, Forouhar F. Hamartoma of Brunner's gland causing partial obstruction of the ileum. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1983; 34:73–74. PMID: 6841428.12. Palanivelu C, Rangarajan M, Jategaonkar PA, Annapoorni S, Prasad H. Laparoscopic antrectomy for a proximal duodenal Brunner gland hamartoma. JSLS. 2009; 13:110–115. PMID: 19366555.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Giant Brunner's Gland Hamartoma Presenting as Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
- A Case of a Giant Brunner's Gland Hamartoma Originating from the Pyloric Ring
- Large Hepatocellular Adenoma Presenting with Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Case Report
- A Brunner's Gland Adenoma Removed by Endoscopic Polypectomy
- A Case of Brunner's Gland Hyperplasia with Dysplasia