Korean J Schizophr Res.
2012 Jun;15(1):13-19. 10.16946/kjsr.2012.15.1.13.
How Can We Differentiate Schizoaffective Disorder from Mood Disorder with Psychotic Feature?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Chonbuk National University Hospital & Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Jeonju, Korea. chungyc@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Institute for Medical Science, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Maemsarang Hospital, In-san Medical Foundation, Wanju, Korea.
- KMID: 1790742
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2012.15.1.13
Abstract
- Difficulties surrounding the classification of mixed psychotic and mood symptoms continue to plague psychiatric nosology. Since schizoaffective disorder was first defined in the literature, it has raised a considerable controversy regarding its clinical distinction from schizophrenia and mood disorder, especially mood disorder with psychotic feature. Recently, it seems that more people are diagnosed as mood disorder with psychotic feature rather than schizoaffective disorder when they are showing concurrent psychotic and mood symptoms. This may be due to unwillingness to make severe diagnosis at first and aggressive trend to expand the diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder. Over-diagnosis of mood disorder with psychotic feature would expose the patients to unnecessary mood stabilizer. Therefore, it is critical to make exact diagnosis based on current diagnostic criteria and other relevant study findings. We conducted in-depth review into diagnostic criteria of DSM and ICD-10 for schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic feature and other related studies comparing clinical features between the two disorders. As a result, important points helpful in differentiating the two disorders are highlighted and future suggestions are described.
MeSH Terms
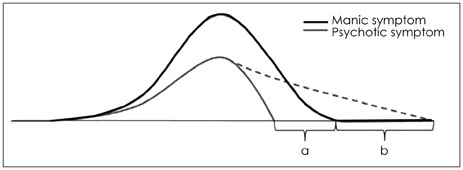
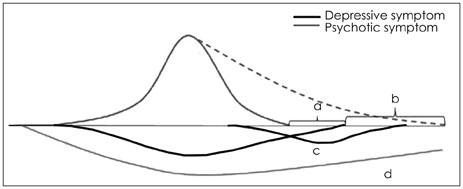
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kasanin K. The acute schizoaffective psychoses. Am J Psychiatry. 1933. 90:97–126.
Article2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 1994. edn 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.3. World Health Organization. International Classification of Disease, edn 10. Clinical description and diagnostic guidelines. 1992. Geneva: World Health Organization.4. Heckers S. Is schizoaffective disorder a useful diagnosis? Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009. 11:332–337.
Article5. Lake CR, Nathaniel H. Schizoaffective disorder merges schizophrenia and bipolar disorders as one disease - there is no schizoaffective disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2007. 20:365–379.
Article6. Vollmer-Larsen A, Jacobsen TB, Hemmingsen R, Parnas J. Schizoaffective disorder - the reliability of its clinical diagnostic use. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006. 113:402–407.
Article7. First M, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, William JB. Structured clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorder. 1998. New York: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute.8. Hirschfeld RM, Cass AR, Holt DC, Carlson CA. Screening for bipolar disorder in patients treated for depression in a family medicine clinic. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2005. 18:233–239.
Article9. Zimmerman M, Ruggero CJ, Chelminski I, Young D. Is Bipolar Disorder Overdiagnosed? J Clin Psychiatry. 2008. 69:935–940.
Article10. Marneros A, Aiskal H. The overlap of affective and schizophrenic spetra. 2007. Cambridge university press.11. Angst J, Felder W, Lohmeyer B. Course of schizoaffective psychoses: Results of a follow-up study. Schizophr Bull. 1980. 6:579–585.
Article12. Fowler RC, McCabe MS, Cadoret RJ, Winokur G. Symptom differences in schizophrenia with good and poor prognosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1972. 123:1239–1243.13. Han OS, Hong JP. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I disorders, Research Version. 2000.14. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Kaplan & Sadock's synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical neuroscience. 2007. 10th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.15. Foulds GA, Bedford A. Hierarchy of classes of personal illness. Psychol Med. 1975. 5:181–192.
Article16. Bleuler E, Brill AA. Textbook of Psychiatry. 1924. 4th Ed. New York, NY: Macmillan Publishing Co Inc.17. Pini S, Queiroz VD, Dell'Osso L, Abelli M, Mastrocinque C, Saettoni M, et al. Cross-sectional similarities and differences between schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and mania or mixed mania with mood-incongruent psychotic features. Eur Psychiatry. 2004. 19:8–14.
Article18. Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic-depressive illness. 1990. New York: Oxford University Press.19. Azorin JM, Akiskal H, Hantouche E. The mood-intability hypothesis in the origin of mood-congruent versus mood-incongruent psychotic distinction in mania:validation in a French National Study of 1090 patients. J Affect Disord. 2006. 96:215–223.
Article20. Black DW, Nasrallah A. Hallucinations and delusions in 1,715 patients with unipolar and bipolar affective disorders. Psychopathology. 1989. 22:28–34.
Article21. Fennig S, Bromet EJ, Karant MT, Ram R, Jandorf L. Mood-congruent versus mood-incongruent psychotic symptoms in first-admission patients with affective disorder. J Affect Disord. 1996. 37:23–29.
Article22. Peralta V, Cuesta MJ. Exploring the borders of the schizoaffective spectrum:a categorical and dimensional approach. J Affect Disord. 2008. 108:71–86.
Article23. Winokur G, Scharfetter C, Angst J. The diagnostic value in assessing mood congruence in delusions and hallucinations and their relationship to the affective state. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1985. 234:299–302.
Article24. Kantor SJ, Glassman AH. Delusional depression:natural history and response to treatment. Br J Psychiatry. 1977. 131:351–360.
Article25. Reichenberg A, Harvey PD, Bowie CR, Moitabai R, Rabinowitz J, Heaton RK, et al. Neuropsychological Function and Dysfunction in Schizophrenia and Psychotic Affective Disorders. Schizophr Bull. 2009. 35:1022–1029.
Article26. Amador XF, Flaum M, Andreasen NC, Strauss DH, Yale SA, Clark SC, et al. Awareness of illness in schizophrenia and schizoaffective and mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994. 51:826–836.
Article27. Fleck DE, DelBello MP, Zimmerman ME, Getz GE, Shear PK, Strakowski SM. Selective attention in schizoaffective disorder: pilot data. Schizophr Res. 2004. 68:109–110.
Article28. Szoke A, Meary A, Trandafir A, Bellivier F, Roy I, Schurhoff F, et al. Executive deficits in psychotic and bipolar disorders e Implications for our understanding of schizoaffective disorder. Eur Psychiatry. 2008. 23:20–25.
Article29. Parnas J, Handest P, Saebye D, Jansson L. Anomalies of subjective experience in schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar illness. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2003. 108:126–133.
Article30. Maj M, Pirozzi R, Formicola AM, Bartoli L, Bucci P. Reliability and validity of the DSM-IV diagnostic category of schizoaffective disorder:Preliminary data. J Affect Disord. 2000. 7:95–98.31. Faraone SV, Blehar M, Pepple J, Moldin SO, Norton J, Nurnberger JI, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and confusability analyses:an application to the Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies. Psychol Med. 1996. 26:401–410.
Article32. Schwartz JE, Fennig S, Tanenberg-Karant M, Carlson G, Craig T, Galambos N, et al. Congruence of Diagnoses 2 Years After a First-Admission Diagnosis of Psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000. 57:593–600.
Article33. Nardi AE, Nascimento I, Freire RC, De-Melo-Neto VL, Valença AM, Dib M, et al. Demographic and clinical features of schizoaffective (schizobipolar) disorder-A 5-year retrospective study. Support for a bipolar spectrum disorder. J Affect Disord. 2005. 89:201–206.
Article34. Veen ND, Selten JS, Schols D, Laan W, Hoek HW, Tweel IVD, et al. Diagnostic stability in a Dutch psychosis incidence cohort. Br J Psychiatry. 2004. 185:460–464.
Article35. Whitty P, Clarke M, McTigue O, Browne S, Kamali M, Larkin C, et al. Diagnostic Stability Four Years After a First Episode of Psychosis. Psychiatr Serv. 2005. 56:1084–1088.
Article36. Benabarre A, Vieta E, Colom F, Marínez-Arán A, Reinares M, Gastó C. Bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia: epidemiologic, clinical and prognostic differences. Eur Psychiatry. 2001. 16:167–172.
Article37. Dell'Osso L, Akiskal HS, Freer P, Barberi M, Placidi GF, Cassano GB. Psychotic and nonpsychotic bipolar mixed states: comparisons with manic and schizoaffective disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1993. 243:75–81.38. Evans JD, Heaton RK, Paulsen JS, McAdams LA, Heaton SC, Jeste DV. Schizoaffective disorder: A form of schizophrenia or affective disorder? J Clin Psychiatry. 1999. 60:874–882.39. Marneros A, Deister A, Rohde A. Psychopathological and social status of patients with affective, schizophrenic and schizoaffective disorders after long-term course. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990. 80:352–358.
Article40. Lenz G, Simhandl C, Thau K, Berner P, Gabriel E. Temporal Stability of Diagnostic Criteria for Functional Psychoses Results from the Vienna Follow-Up Study. Psychopathology. 1991. 24:328–335.
Article41. Cohen LS. Gender-Specific Considerations in the Treatment of Mood Disorders in Women Across the Life Cycle. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003. 64:18–29.42. Ohayon MM, Schatzberg AF. Prevalence of Depressive Episodes with Psychotic Features in the General Population. Am J Psychiatry. 2002. 159:1855–1861.
Article43. Tohen M, Hennen J, Zarate CM, Baldessarini RJ, Strakowski SM, Stoll AL, et al. Two-Year Syndromal and Functional Recovery in 219 Cases of First-Episode Major Affective Disorder With Psychotic Features. Am J Psychiatry. 2000. 157:220.
Article44. Marneros A. The schizoaffective phenomenon: the state of the art. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 2003. 108:29–33.
Article45. Scully PJ, Owens JM, Kinsella A, Waddington JL. Schizophrenia, schizoaffective and bipolar disorder within an epidemiologically complete, homogeneous population in rural Ireland: small area variation in rate. Schizophr Res. 2004. 67:143–155.
Article46. Grant BF, Stinson FS, Hasin DS, Dawson DA, Chou SP, Ruan WJ, et al. Prevalence, correlates, and comorbidity of bipolar I disorder and axis I and II disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. 66:1205–1215.
Article47. Szádóczky E, Papp Z, Vitrai J, Ríhmer Z, Füredi J. The prevalence of major depressive and bipolar disorders in Hungary: Results from a national epidemiologic survey. J Affect Disord. 1998. 50:153–162.48. Gershon ES, Hamovit J, Guroff JJ, Dibble E, Leckman JF, Sceery W, et al. A family study of schizoaffective, bipolar I, bipolar II, unipolar, and normal control probands. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982. 39:1157–1167.
Article49. Gershon ES, DeLisi LE, Hamovit J, Nurnberger JI, Maxwell ME, Schreiber J, et al. A controlled family study of chronic psychoses. Schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988. 45:328–336.50. Maier W, Lichtermann D, Minges J, Hallmayer J, Heun R, Benkert O, et al. Continuity and discontinuity of affective disorders and schizophrenia. Results of a controlled family study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993. 50:871–883.
Article51. Cheniaux E, Landeira-Fernandez J, Telles LL, Lessa JLM, Dias A, Duncan T, et al. Does schizoaffective disorder really exist? A systematic review of the studies that compared schizoaffective disorder with schizophrenia or mood disorders. J Affect Disord. 2008. 106:209–217.
Article52. Hodgkinson CA, Goldman D, Jaeger J, Persaud S, Kane JM, Lipsky RH, et al. Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1): Association with Schizophrenia, Schizoaffective Disorder, and Bipolar Disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. 75:862–872.
Article53. Kane JM. Strategies for making an accurate differential diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010. 71:4–7.
Article54. Marneros A, Deister A, Rohde A. Stability of Diagnoses in Affective, Schizoaffective and Schizophrenic Disorders: Cross-sectional Versus Longitudinal Diagnosis. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1991. 241:187–192.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Schizoaffective Disorder
- Temporal Lobe Volume Measurement in Mood Disorder Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Blonanserin-induced Mood Alteration in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder: Two Cases
- Similarities and Differences between DSM-IV Brief Psychotic Disorder and ICD-10 Acute and Transient Psychotic Disorder
- Clinical Usefulness of Aripiprazole and Lamotrigine in Schizoaffective Presentation of Tuberous Sclerosis