J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Jun;19(3):466-469. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.3.466.
Successful Treatment of Protein-Losing Enteropathy Induced by Intestinal Lymphangiectasia in a Liver Cirrhosis Patient with Octreotide: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Kuri Hospital, Guri, Korea. hands@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1786830
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.3.466
Abstract
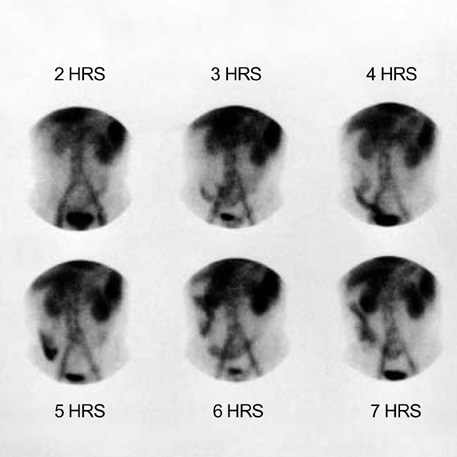
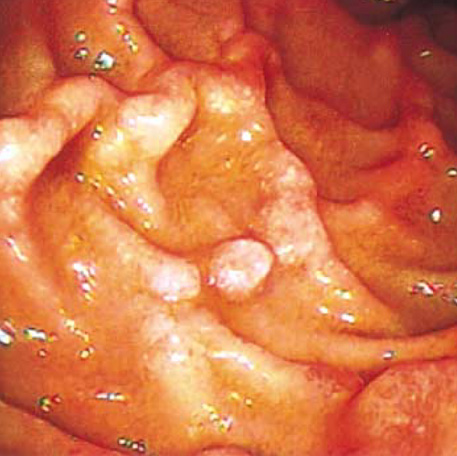
- A 47-yr-old man with hepatitis B virus associated liver cirrhosis was admitted to our hospital with diarrhea and generalized edema and diagnosed as protein-losing enteropathy due to intestinal lymphangiectasia by intestinal biopsy and 99mTc albumin scan. During hospitalization, he received subcutaneous octreotide therapy. After 2 weeks of octreotide therapy, follow-up albumin scan showed no albumin leakage, and the serum albumin level was sustained. We speculate that liver cirrhosis can be a cause of intestinal lymphangiectasia and administration of octreotide should be considered for patients with intestinal lymphangiectasia whose clinical and biochemical abnormalities do not respond to a low-fat diet.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Duodenum/pathology
Female
Hepatitis B/complications
Hepatitis B Virus/metabolism
Human
Intestinal Diseases/*drug therapy/virology
Jejunum/pathology
Liver Cirrhosis/*drug therapy/virology
Lymphangiectasis, Intestinal/*drug therapy/virology
Male
Middle Aged
Octreotide/*pharmacology
Protein-Losing Enteropathies/*drug therapy
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Protein Supplement Effect in Protein-Losing Enteropathy
Hyun Jeong Lee, Mi Yong Rha, Young Yun Cho, Eun Ran Kim, Dong Kyung Chang
Clin Nutr Res. 2012;1(1):94-98. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2012.1.1.94.
Reference
-
1. Sleisenger MH, Fordtran JS. Gastrointestinal disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 1998. 6th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.2. Kuroiwa G, Takayama T, Sato Y, Takahashi Y, Fujita T, Nobuoka A, Kukitsu T, Kato J, Sakamaki S, Niitsu Y. Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia successfully treated with octreotide. J Gastroenterol. 2001. 36:129–132.
Article3. Lee SH, Chang YW, Bak SK, Han JY, Kim JH, Jung YH, Lee BW, Han YS, Dong SH, Kim HJ, Kim BH, Lee JI, Chang R. A case of duodenal lymphangiectasia. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2003. 41:59–63.4. Park GS, Kwak JY, Kim JS, Kwon TC, Jo YJ. A case of primary Intestinal lymphangiectasia. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1999. 19:634–642.5. Bac DJ, Van Hagen PM, Postema PT, ten Bokum AM, Zondervan PE, van Blankenstein M. Octreotide for protein-losing enteropathy with intestinal lymphangiectasia. Lancet. 1995. 345:1639.
Article6. Salvia G, Cascioli CF, Ciccimarra F, Terrin G, Cucchiara S. A case of protein-losing enteropathy caused by intestinal lymphangiectasia in a preterm infant. Pediatrics. 2001. 107:416–417.
Article7. Ballinger AB, Farthing MJ. Octreotide in the treatment of intestinal lymphangiectasia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. 10:699–702.8. Patel AS, DeRidder PH. Endoscopic appearance and significance of functional lymphangiectasia of the duodenal mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990. 36:376–378.
Article9. Mine K, Matsubayashi S, Nakai Y, Nakagawa T. Intestinal lymphangiectasia markedly improved with antiplasmin therapy. Gastroenterology. 1989. 96:1596–1599.
Article10. Lamberts SW, van der Lely AJ, de Herder WW, Hofland LJ. Octreotide. N Engl J Med. 1996. 334:246–254.
Article11. Heresbach D, Raoul JL, Genetet N, Noret P, Siproudhis L, Ramee MP, Bretagne JF, Gosselin M. Immunological study in primary intestinal lymphangiectasia. Digestion. 1994. 55:59–64.
Article12. Dousset B, Legmann P, Soubrane O, Chaussade S, Couturier D, Houssin D, Calmus Y. Protein-losing enteropathy secondary to hepatic venous outflow obstruction after liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 1997. 27:206–210.
Article13. Stanley AJ, Gilmour HM, Ghosh S, Ferguson A, McGilchrist AJ. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt as a treatment for protein-losing enteropathy caused by portal hypertension. Gastroenterology. 1996. 111:1679–1682.
Article14. Garcia-Pagan JC, Escorsell A, Moitinho E, Bosch J. Influence of pharmacological agents on portal hemodynamics: basis for its use in the treatment of portal hypertension. Seminar Liver Dis. 1999. 19:427–438.15. D'Amico G, Pagliaro L, Bosch J. Pharmacological treatment of portal hypertension: an evidence-based approach. Seminar Liver Dis. 1999. 19:475–505.