J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Sep;25(9):1364-1367. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1364.
A Case of Multicentric Castleman's Disease Having Lung Lesion Successfully Treated with Humanized Anti-interleukin-6 Receptor Antibody, Tocilizumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, National Defense Medical College, Saitama, Japan. hiromedic@yahoo.co.jp
- KMID: 1785918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1364
Abstract
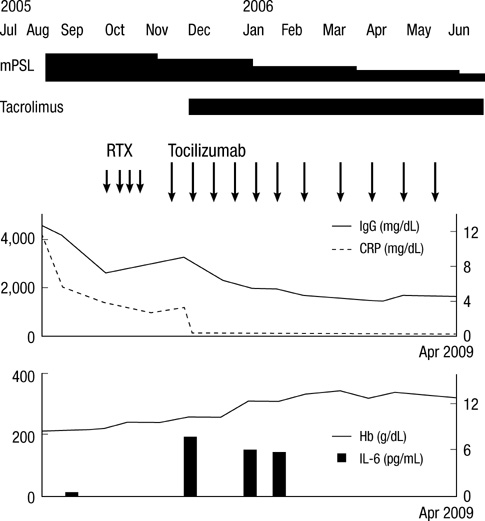
- This report presents the case of a patient demonstrating multicentric Castleman's disease (MCD) with a lung lesion that was successfully treated with an anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab in combination with corticosteroid and tacrolimus. A 43-yr-old female with abnormal shadows on a chest X-ray was referred to the hospital for further examination. She was diagnosed as having MCD based on the characteristic pathology of inguinal lymph node, lung lesions, laboratory data, and undifferentiated arthritis. Corticosteroid and rituximab therapy did not fully ameliorate the symptoms; thus, the therapeutic regimen was changed to include tocilizumab, oral corticosteroid and tacrolimus. This regimen resulted in clinical remission and the dose of tocilizumab and corticosteroid could be tapered. Tocilizumab in combination with corticosteroid and tacrolimus may therefore be a beneficial treatment regimen for lung lesions associated with MCD.
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Cortex Hormones/therapeutic use
Adult
Antibodies, Monoclonal/*therapeutic use
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Giant Lymph Node Hyperplasia/*diagnosis/drug therapy/radiography
Humans
Immunosuppressive Agents/therapeutic use
Lung Diseases, Interstitial/*drug therapy/pathology
Lymph Nodes/pathology
Receptors, Interleukin-6/antagonists & inhibitors
Tacrolimus/therapeutic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
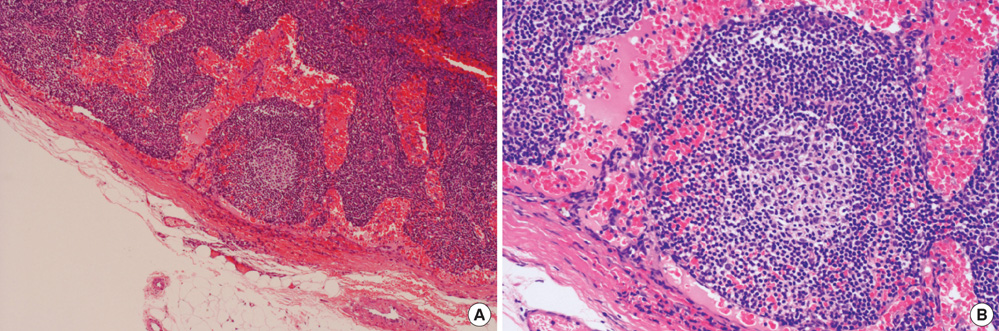
Figure
Reference
-
1. Castleman B, Iverson L, Menendez VP. Localized mediastinal lymph node hyperplasia resembling thymoma. Cancer. 1956. 9:822–830.2. Frizzera G, Peterson BA, Bayrd ED, Goldman A. A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic features of Castleman's disease: clinical findings and clinicopathologic correlations in 15 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1985. 3:1202–1216.
Article3. Keller AR, Hochholzer L, Castleman B. Hyaline-vascular and plasmacell types of giant lymph node hyperplasia of the mediastinum and other locations. Cancer. 1972. 29:670–683.
Article4. Nishimoto N, Sasai M, Shima Y, Nakagawa M, Matsumoto T, Shirai T, Kishimoto T, Yoshizaki K. Improvement in Castleman's disease by humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody therapy. Blood. 2000. 95:56–61.
Article5. Peterson BA, Frizzera G. Multicentric Castleman's disease. Semin Oncol. 1993. 20:636–647.6. Nishimoto N, Kanakura Y, Aozasa K, Johkoh T, Nakamura M, Nakano S, Nakano N, Ikeda Y, Sasaki T, Nishioka K, Hara M, Taguchi H, Kimura Y, Kato Y, Asaoku H, Kumagai S, Kodama F, Nakahara H, Hagihara K, Yoshizaki K, Kishimoto T. Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease. Blood. 2005. 106:2627–2632.
Article7. Akahane D, Kimura Y, Sumi M, Sashida G, Gotoh A, Miyazawa K, Ohyashiki K. Effectiveness of long term administration of humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) for multicentric Castleman's disease with pulmonary involvement. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2006. 47:748–752.8. Yoshizaki K, Matsuda T, Nishimoto N, Kuritani T, Taeho L, Aozasa K, Nakahata T, Kawai H, Tagoh H, Komori T, Kishimoto S, Hirano T, Kishimoto T. Pathogenic significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2) in Castleman's disease. Blood. 1989. 74:1360–1367.
Article9. Johkoh T, Muller NL, Ichikado K, Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Honda O, Tomiyama N, Naitoh H, Nakamura H, Yamamoto S. Intrathoracic multicentric Castleman disease: CT findings in 12 patients. Radiology. 1998. 209:477–481.
Article10. Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, d'Agay MF, Clauvel JP, Raphael M, Degos L, Sigaux F. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood. 1995. 86:1276–1280.11. Bower M, Powles T, Williams S, Davis TN, Atkins M, Montoto S, Orkin C, Webb A, Fisher M, Nelson M, Gazzard B, Stebbing J, Kelleher P. Brief communication: rituximab in HIV-associated multicentric Castleman disease. Ann Intern Med. 2007. 147:836–839.
Article12. Ohno N, Fujiyama S, Ooi M, Haraguchi K, Tokunaga M, Uozumi K, Tsubouchi H. Effectiveness of humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) for Castleman's disease mainly with pulmonary involvement. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. 96:988–990.
Article13. Yoo SA, Park BH, Park GS, Koh HS, Lee MS, Ryu SH, Miyazawa K, Park SH, Cho CS, Kim WU. Calcineurin is expressed and plays a critical role in inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 2006. 177:2681–2690.
Article14. Garcia JE, Lopez AM, de Cabo MR, Rodriguez FM, Losada JP, Sarmiento RG, Lopez AJ, Arellano JL. Cyclosporin A decreases human macrophage interleukin-6 synthesis at post-transcriptional level. Mediators Inflamm. 1999. 8:253–259.15. Cockfield SM, Ramassar V, Halloran PF. Regulation of IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in vivo. Effects of cycloheximide and cyclosporine in normal and lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. J Immunol. 1993. 150:342–352.16. Pham LV, Tamayo AT, Yoshimura LC, Lin-Lee YC, Ford RJ. Constitutive NF-kappaB and NFAT activation in aggressive B-cell lymphomas synergistically activates the CD154 gene and maintains lymphoma cell survival. Blood. 2005. 106:3940–3947.17. Miltenyi Z, Toth J, Gonda A, Tar I, Remenyik E, Illes A. Successful immunomodulatory therapy in castleman disease with paraneoplastic pemphigus vulgaris. Pathol Oncol Res. 2008. 15:375–381.
Article18. Tsujimura S, Saito K, Nakayamada S, Nakano K, Tanaka Y. Clinical relevance of the expression of P-glycoprotein on peripheral blood lymphocytes to steroid resistance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:1676–1683.
Article19. Tanaka Y, Tsujimura S. Multi-drug resistance in the treatments of autoimmune diseases. Jpn J Clin Immunol. 2006. 29:319–324.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tocilizumab-induced Transaminitis in a Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient with Macrophage Activation Syndrome
- A Case of Sepsis Caused by Cellulitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment
- Human Herpesvirus-8 Positive Multicentric Castleman’s Disease with Complete Response after Rituximab Monotherapy: A Case Report
- A Case of Multicentric Castleman's Disease Presenting with Follicular Bronchiolitis
- A Case of Kaposi's Sarcoma Associated with Castleman's Disease