J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2010 Oct;40(5):244-248. 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.244.
Marginal bony changes in relation to different vertical positions of dental implants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology and Research Institute of Oral Sciences, Gangneung-Wonju National University College of Dentistry, Gangneung, Korea. dentist@gwnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Periodontics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.244
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to radiographically evaluate marginal bony changes in relation to different vertical positions of dental implants.
METHODS
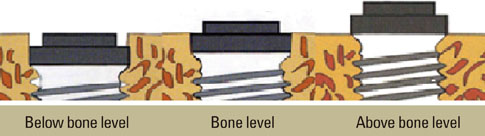
Two hundred implants placed in 107 patients were examined. The implants were classified by the vertical positions of the fixture-abutment connection (microgap): 'bone level,' 'above bone level,' or 'below bone level.' Marginal bone levels were examined in the radiographs taken immediately after fixture insertion, immediately after second-stage surgery, 6 months after prosthesis insertion, and 1 year after prosthesis insertion. Radiographic evaluation was carried out by measuring the distance between the microgap and the most coronal bone-to-implant contact (BIC).
RESULTS
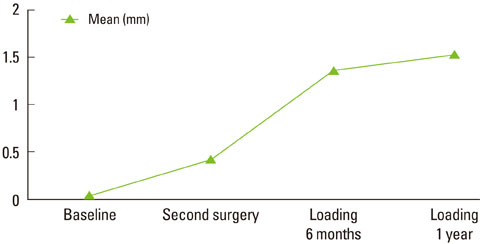
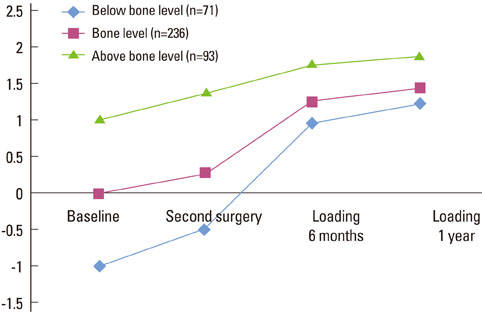
Immediately after fixture insertion, the distance between the microgap and most coronal BIC was 0.06 +/- 0.68 mm; at second surgery, 0.43 +/- 0.83 mm; 6 months after loading, 1.36 +/- 0.56 mm; and 1 year after loading, 1.53 +/- 0.51 mm (mean +/- SD). All bony changes were statistically significant but the difference between the second surgery and the 6-month loading was greater than between other periods. In the 'below bone level' group, the marginal bony change between fixture insertion and 1 year after loading was about 2.25 mm, and in the 'bone level' group, 1.47 mm, and in 'above bone level' group, 0.89 mm. Therefore, the marginal bony change was smaller than other groups in the 'above bone level' group and larger than other groups in the 'below bone level' group.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results demonstrated that marginal bony changes occur during the early phase of healing after implant placement. These changes are dependent on the vertical positions of implants.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Marginal bone level changes in association with different vertical implant positions: a 3-year retrospective study
Yeon-Tae Kim, Gyu-Hyung Lim, Jae-Hong Lee, Seong-Nyum Jeong
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017;47(4):231-239. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2017.47.4.231.Marginal bone loss around crestal or subcrestal dental implants: prospective clinical study
Naser Sargolzaie, Hosein Hoseini Zarch, Hamidreza Arab, Tahereh Koohestani, Mahdiye Fasihi Ramandi
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;48(3):159-166. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.3.159.
Reference
-
1. Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Branemark PI. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981. 10:387–416.
Article2. Jemt T, Lekholm U, Grondahl K. 3-year followup study of early single implant restorations ad modum Branemark. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1990. 10:340–349.3. Cox JF, Zarb GA. The longitudinal clinical efficacy of osseointegrated dental implants: a 3-year report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1987. 2:91–100.4. Albrektsson T, Isidor F. Lang NP, Karring T, editors. Consensus report of session V. Proceedings of the 1st European Workshop on Periodontology. 1993. London: Quintessence;365–369.5. Hermann JS, Cochran DL, Nummikoski PV, Buser D. Crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A radiographic evaluation of unloaded nonsubmerged and submerged implants in the canine mandible. J Periodontol. 1997. 68:1117–1130.
Article6. Quirynen M, van Steenberghe D. Bacterial colonization of the internal part of two-stage implants. An in vivo study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1993. 4:158–161.
Article7. Persson LG, Lekholm U, Leonhardt A, Dahlen G, Lindhe J. Bacterial colonization on internal surfaces of Branemark system implant components. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:90–95.
Article8. Tarnow DP, Cho SC, Wallace SS. The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of inter-implant bone crest. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:546–549.
Article9. Bain CA. Implant installation in the smoking patient. Periodontol 2000. 2003. 33:185–193.
Article10. Hermann JS, Buser D, Schenk RK, Schoolfield JD, Cochran DL. Biologic Width around one- and two-piece titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001. 12:559–571.
Article11. Weber HP, Buser D, Donath K, Fiorellini JP, Doppalapudi V, Paquette DW, et al. Comparison of healed tissues adjacent to submerged and non-submerged unloaded titanium dental implants. A histometric study in beagle dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:11–19.
Article12. Lee DW, Choi YS, Park KH, Kim CS, Moon IS. Effect of microthread on the maintenance of marginal bone level: a 3-year prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. 18:465–470.
Article13. Oh TJ, Yoon J, Misch CE, Wang HL. The causes of early implant bone loss: myth or science? J Periodontol. 2002. 73:322–333.
Article14. Wilderman MN, Pennel BM, King K, Barron JM. Histogenesis of repair following osseous surgery. J Periodontol. 1970. 41:551–565.
Article15. Jung YC, Han CH, Lee KW. A 1-year radiographic evaluation of marginal bone around dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996. 11:811–818.16. Engquist B, Astrand P, Dahlgren S, Engquist E, Feldmann H, Grondahl K. Marginal bone reaction to oral implants: a prospective comparative study of Astra Tech and Branemark System implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:30–37.17. Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. Biological width revisited. J Clin Periodontol. 1996. 23:971–973.18. Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Ericsson I, Marinello CP, Liljenberg B, Thomsen P. The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1991. 2:81–90.
Article19. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Moon IS, Lindhe J. Peri-implant tissues at submerged and non-submerged titanium implants. J Clin Periodontol. 1999. 26:600–607.
Article20. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Wennstrom J, Lindhe J. The peri-implant hard and soft tissues at different implant systems. A comparative study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:212–219.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Marginal bone level changes in association with different vertical implant positions: a 3-year retrospective study
- RADIOGRAGHIC STUDY OF MARGINAL BONE LOSS AROUND OSSEOINTEGRATED IMPLANTS AFTER FUNCTIONAL LOADING
- Comparison of marginal bone loss of dental implants and adjacent teeth in the same interproximal unit: a retrospective study with follow-up over 2 years after prosthesis delivery
- Study on the stress distribution around two types of implants with an internal connection by finite element analysis
- Influence of crown-to-implant ratio on periimplant marginal bone loss in the posterior region: a five-year retrospective study