J Korean Acad Periodontol.
2009 Mar;39(1):9-16. 10.5051/jkape.2009.39.1.9.
The effects of hydroxyapatite toothpaste on tooth hypersensitivity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Korea. kyhyuk@khu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Oral Biology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Korea.
- KMID: 1783511
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jkape.2009.39.1.9
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: The present study was performed to evaluate the effect of hydroxyapatite dental paste on tooth hypersensitivity compared to other materials.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
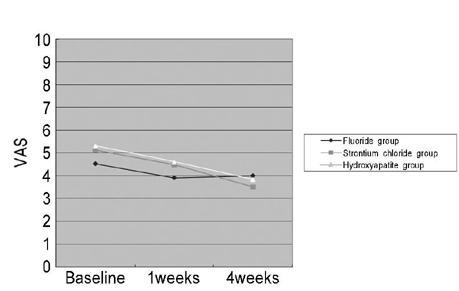
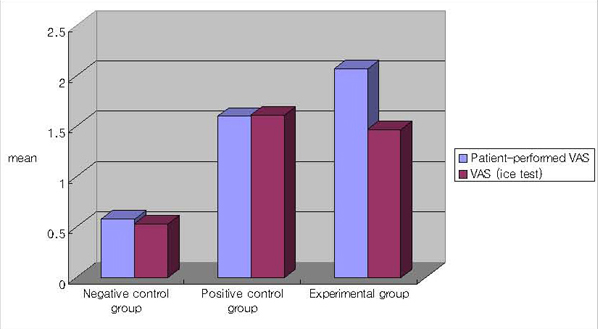
In the general fluoride dental paste, strontium fluoride dental paste and hydroxyapatite dental paste, patient-performed VAS and VAS(ice test) were measured at baseline, 1weeks and 4weeks.
RESULTS
1. In patient-performed VAS, there were significant differences reducing of tooth hypersensitivity between general fluoride toothpaste and hydroxyapatite toothpaste. 2. In operator-performed VAS(ice test), there were significant differences reducing of tooth hypersensitivity among each group, between general fluoride toothpaste and hydroxyapatite toothpaste and between general fluoride toothpaste and strontium fluoride toothpaste.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, hydroxyapatite toothpaste can be applied for control of tooth hypersensitivity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of the whitening effect of toothpastes containing 0.25% hydroxyapatite and 0.75% hydrogen peroxide
Gyeong-Ji Woo, Eun-Kyong Kim, Seong-Hwa Jeong, Keun-Bae Song, Hyo-Jin Goo, Eun-Suk Jeon, Youn-Hee Choi
J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2014;38(1):3-9. doi: 10.11149/jkaoh.2014.38.1.3.
Reference
-
1. Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity: new perspectives on an old problem. Int Dental J. 2002. 52:367–375.
Article2. Dowell P, Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity-A review: Aetiology, symptoms and theories of pain production. J Clin Periodontol. 1983. 10:341–350.
Article3. Bender IB. Pain Conference Summary. J Endodont. 1986. 12:509–517.
Article4. Bamise CT, Olusile AC, Oginni AO. An Analysis of the etiological and predisposing factors related to dentin hypersensitivity. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008. 9:1–9.5. Orchardson R, Gillam DG. Managing dentin hypersensitivity. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006. 137:990–998.
Article6. Addy M. Etiology and clinical implications of dentine hypersensitivity. Dent Clin North Am. 1990. 34:503–514.7. Chabanski MB, Gillam DG, Bulman JS, Newman HN. Prevalence of cervical dentine sensitivity in a population of patients referred to a specialist Periodontology Department. J Clin Periodontol. 1996. 23:989–992.
Article8. Trowbridge HO, Silver DR. A review of current approaches to in-office management of tooth hypersensitivity. Dent Clin North Am. 1990. 34:561–581.9. Berman LH. Dentinal sensation and hypersensitivity-A review of mechanisms and treatment alternatives. J Periodontol. 1984. 56:216–222.
Article10. Addy M, Mostafa P. Dentine hypersensitivity. II. Effects produced by the uptake in vitro of toothpastes onto dentine. J Oral Rehab. 1989. 16:35–48.
Article11. Orchardson R, Peacock JM. Factors affecting nerve excitability and conduction as a basis for desensitizing dentine. Archs Oral Biol. 1994. 39:suppl. 81s–86s.
Article12. Sauro S, Gandolfi MG, Prati C, Mongiorgi R. Oxalate-containing phytocomplexes as dentine desensitisers: An in vitro study. Arch Oral Biol. 2006. 51:655–664.
Article13. Bartold PM. Dentinal hypersensitivity: a review. Aust Dent J. 2006. 51:212–218.
Article14. Tablet WJ, Silverman G, Stolman JM, Fratarcangelo PA. Clinical evaluation of a new treatment for dentinal hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1980. 51:535–540.
Article15. Docimo R, Montesani L, Maturo P, et al. Desensitizing efficacy of a new toothpaste containing 5.5% potassium citrate: A 4-week clinical study. Am J Dent. 2007. 20:209–211.16. Lukomsky EH. Fluorine therapy for exposed dentin and alveolar atrophy. J Dent Res. 1941. 20:649–655.
Article17. Addy M, Dowell P. Dentine hypersensitivity-A review. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of treatment agents. J Clin Periodontol. 1983. 10:351–363.
Article18. Hyot WH, Bibby BG. Use of sodium fluoride for desensitizing dentin. J Am Dent Assoc. 1943. 30:1372–1376.
Article19. Hernandez F, Mohammed C, Shannon I, Volpe A, King W. Clinical study evaluating the desensitizing effect and duration of two commercially available dentifrices. J Periodontol. 1972. 43:367–372.
Article20. Miller JT, Shannon IL, Kilgore WG, Bookman JE. Use of a water-free stannous fluoride-containing gel in the control of dental hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1969. 40:490–491.
Article21. Hiatt WH, Johansen E. Root preparation I. Obturation of dentinal tubules in treatment of root hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1972. 43:373–380.
Article22. Green BL, Green ML, McFall WT. Calcium hydroxide and potassium nitrate as desensitizing agents for hypersensitive root surfaces. J Periodontol. 1977. 48:667–672.
Article23. Braun A, Cichocka A, Semaan E, et al. Root surfaces after ultrasonic instrumentation with a polishing fluid. Quintessence Int. 2007. 38:490–496.24. Fusayama T. Etiology and treatment of sensitive teeth. Quintessence Int. 1988. 19:921–925.25. Zhang Y, Agee K, Pashley DH, Pashley EL. The effects of Pain-Free® desensitizer on dentine permeability and tubule occlusion over time, in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 1998. 25:884–891.
Article26. Gerschman JA, Ruben J, Gebart-Eaglemont J. Low level laser therapy for dentinal tooth hypersensitivity. Aust Dent J. 1994. 39:353–357.
Article27. Renton-Happer P, Midda M. Nd:YAG laser treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity. Br Dent J. 1992. 172:13–16.
Article28. Kim JH, Kim SU, Kwon YH, Lee MS. Clinical evaluation of microcrystalline hydroxyapatite toothpaste in the control of dentin hypersensitivity. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 1984. 14:229–240.29. Hodge HC, Gavett E, Thomas I. The adsorption of strontium at forty degrees by enamel, dentin, bone, and hydroxyapatite as shown by the radioactive isotope. J Biol Chem. 1946. 163:1–6.
Article30. Minkoff S, Axelrod S. Efficacy of strontium chloride in dental hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1987. 58:470–474.
Article31. Zinner DD, Duany LF, Lutz HJ. A new desensitizing dentifrice: preliminary report. J Am Dent Assoc. 1977. 95:982–985.
Article32. Lim SC, Choi JC, Herr Y, Lee MS. Clinical evaluation of microcrystalline hydroxyapatite containing toothpaste in the control of dentin hypersensitivity after periodontal treatment. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 1993. 23:127–134.33. Park JJ, Park JB, Kwon YH, Herr Y, Chung JH. The effect of microcrystalline hydroxyapatite containing toothpaste in the control of tooth hypersensitivity. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2005. 35:577–590.
Article34. Arrais CAG, Micheloni CD, Giannini M, Chan DCN. Occluding effect of dentifrices on dentinal tubules. J Dent. 2003. 31:577–584.
Article35. Paes-leme AF, Santos JCRG, Giannini M, Wada RS. Occlusion of dentin tubules by desensitizing agents. Am J Dent. 2004. 17:368–372.36. Kerns DG, Scheidt MJ, Pashley DH, et al. Dental tubule occlusion and root hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1991. 62:421–428.37. Rimondini I, Baroni C, Carrassi A. Ultrastructure of hypersensitive and non-sensitive dentine: A study on replica models. J Clin Periodontol. 1995. 22:899–902.
Article38. Clark DC, Hanley JA, Geoghegan S, Vinet D. The effectiveness of a fluoride varnish and a desensitizing toothpaste in treating dentinal hypersensitivity. J Periodon Res. 1985. 20:212–219.
Article39. Sowinski J, Ayad F, Petrone M, et al. Comparative investigations of the desensitising efficacy of a new dentifrice. J Clin Periodontol. 2001. 28:1032–1036.
Article40. Prati C, Venturi L, Valdre G, Mongiorgi R. Dentin morphology and permeability after brushing with different toothpastes in the presence and absence of smear layer. J Periodontol. 2002. 73:183–190.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of microcrystalline hydroxyapatite containing toothpaste in the control of tooth hypersensitivity
- The clinical effects of a hydroxyapatite containing toothpaste for dentine hypersensitivity
- Effect of Hydroxyapatite containing dentifrice on teeth hypersensitivity after periodontal therapy
- Comparison of the whitening effect of toothpastes containing 0.25% hydroxyapatite and 0.75% hydrogen peroxide
- Comparison of Coffee Stain Removal Effects of Commercial Whitening Toothpaste in Sound and Demineralized Teeth In Vitro