J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Dec;24(6):1227-1229. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1227.
Solitary Metastasis of Bronchogenic Adenocarcinoma to the Internal Auditory Canal: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-HNS, Collage of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. khchang@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1783163
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1227
Abstract
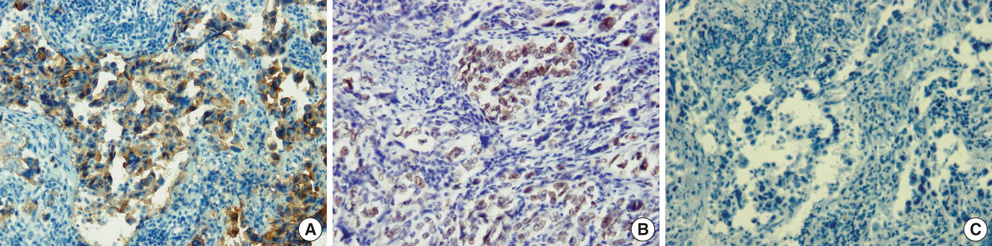
- We report a patient with an isolated metastasis to the internal auditory canal (IAC) of bronchogenic adenocarcinoma. A 58-yr-old man who had received 6-cycle of chemotherapy under diagnosis of non-small cell lung carcinoma (T4N2M0) two years ago was referred to our department with vertigo, right-sided facial paralysis and right-sided hearing loss. A provisional diagnosis of vestibular schwannoma or meningioma involving right IAC was made from magnetic resonance imaging. The patient underwent a translabyrinthine removal of the tumor. Histopathological study of the resected lesion showed a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma compatible with bronchogenic origin. The patient died 9 months after surgery from extensive brain metastasis despite postoperative radiation therapy. In patients with a previous history of treatment of malignancy elsewhere in the body, the possibility of IAC metastasis must be considered when an IAC lesion is detected.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bilateral Internal Auditory Canal Metastasis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Chang-Hee Kim, Jung Eun Shin, Hee Joung Kim, Kye Young Lee
Cancer Res Treat. 2015;47(1):110-114. doi: 10.4143/crt.2013.079.
Reference
-
1. Moffat DA, Saunders JE, McElveen JT Jr, McFerran DJ, Hardy DG. Unusual cerebello-pontine angle tumors. J Laryngol Otol. 1993. 107:1087–1098.2. Belal A Jr. Metastatic tumours of the temporal bone-a histopathological report. J Laryngol Otol. 1985. 99:839–846.3. Gloria-Cruz TI, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Adams GL, Fulton SE. Metastases to temporal bones from primary nonsystemic malignant neoplasms. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000. 126:209–214.
Article4. Yuh WT, Mayr-Yuh NA, Koci TM, Simon JH, Nelson KL, Zyroff J, Jinkins JR. Metastatic lesions involving the cerebellopontine angle. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993. 14:99–106.5. Cureoglu S, Tulunay O, Ferlito A, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Rinaldo A. Otologic manifestations of metastatic tumors to the temporal bone. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004. 124:1117–1123.
Article6. Krainik A, Cyna-Gorse F, Bouccara D, Cazals-Hatem D, Vilgrain V, Denys A, Rey A, Sterkers O, Menu Y. MRI of unusual lesions in the internal auditory canal. Neuroradiology. 2001. 43:52–57.
Article7. Moloy PJ, del Junco R, Porter RW, Brackmann DE. Metastasis from an unknown primary presenting as a tumor in the internal auditory meatus. Am J Otol. 1989. 10:297–300.
Article8. Marques E, Brandis A, Samii M, Tatagiba M. Late metastasis of breast adenocarcinoma into internal auditory canal and cerebellopontine angle: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002. 60:639–642.
Article9. Suryanarayanan R, Dezso A, Ramsden RT, Gillespie JE. Metastatic carcinoma mimicking a facial nerve schwannoma: the role of computerized tomography in diagnosis. J Laryngol Otol. 2005. 119:1010–1012.
Article10. Schrock A, Laffers W, Bootz F. Solitary metastasis of lung carcinoma to the internal auditory canal. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006. 27:214–216.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Solitary Fibrous Tumor in the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Osteoma with Cholesteatoma in the External Auditory Canal
- Is a Solitary Fibrous Tumor in the External Auditory Canal Benign?
- A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ Occurredin the External Auditory Canal
- A Case of Solitary Neurofibroma of the External Auditory Canal