Korean J Lab Med.
2009 Feb;29(1):59-65. 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.1.59.
An Experience of the Use of Anti-HBc and Anti-HBs for Blood Donor Screening Tests at a Tertiary Hospital Blood Center in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. limyoung@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1781595
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.1.59
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to report the first experience of using tests of antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc) and antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) for the selection of blood donors in a tertiary hospital blood center in Korea.
METHODS
From January 2005 to December 2007, the data of all eligible donors according to the Korean Blood Regulation Law were analyzed. Anti-HBc testing was performed in all donors, but anti-HBs was tested only in anti-HBc seropositive donors. Anti-HBs negative but anti-HBc positive donors were regarded as ineligible for blood donation. Cost for donor testing was calculated based on Korean health insurance payment schedule from 2005 to 2007.
RESULTS
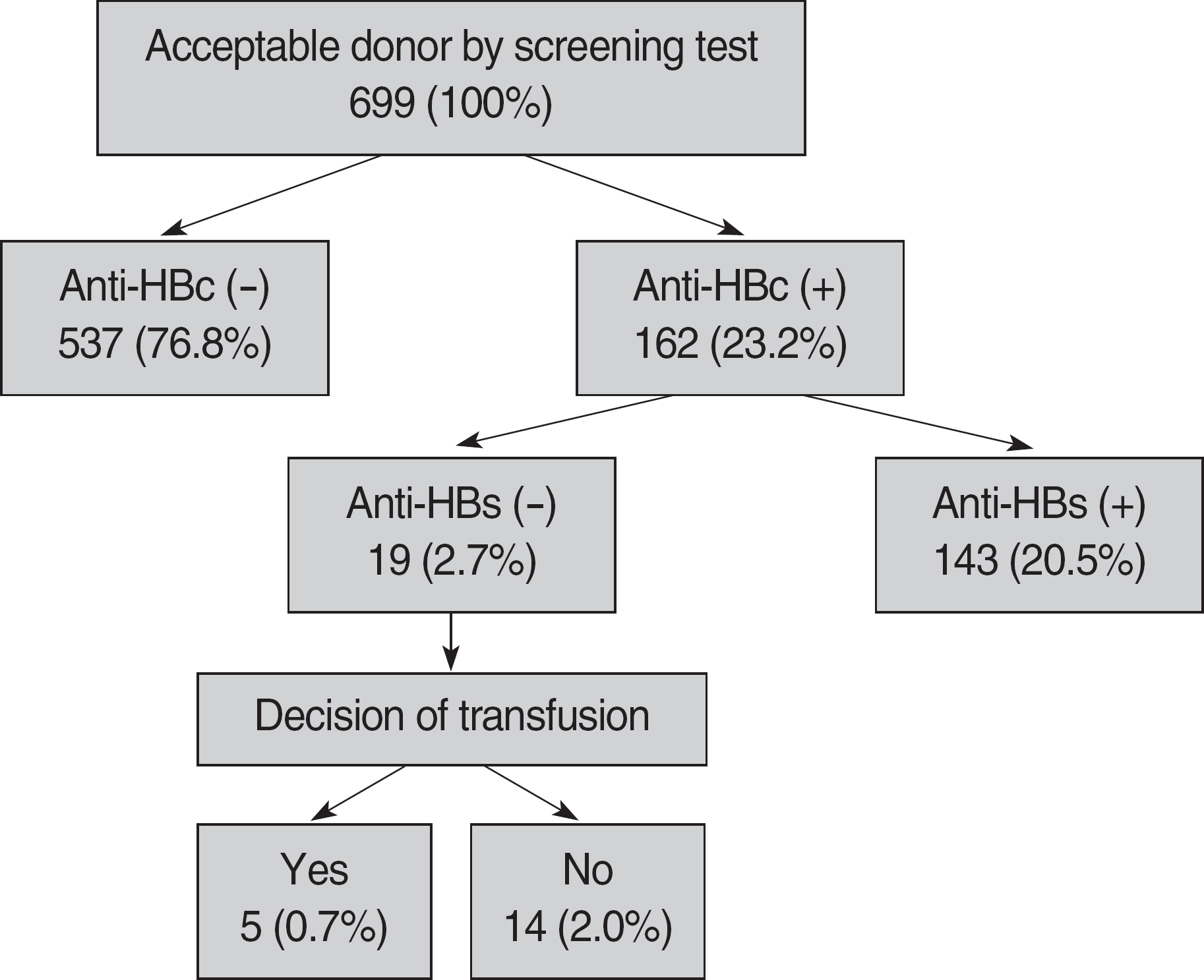
The seroprevalence of anti-HBc in blood donors was 23.2% (162/699) and increased with increasing age. The proportion of ineligible donors for blood collection was 2.7% (19/699) of total donors and 11.6% (19/162) of anti-HBc seropositive donors. The cost of testing for anti-HBc and anti-HBs was estimated to be about 40% of the total screening cost.
CONCLUSIONS
Although additional donor screening tests for anti-HBc and anti-HBs requires increased cost and relatively small number of donors are additionally excluded by these tests, they are considered to be helpful for the safety of blood products, because our blood center has characteristics with small number of donors and relatively high percentage of donors in the age group of thirties and older.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prophylaxis for Hepatitis B Core Antibody-Positive Donors after Liver Transplantation
Hee-Yeon Kim, Jong-Young Choi
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2010;24(2):73-79. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.2.73.
Reference
-
1.Blumberg BS., Gerstley BJ., Hungerford DA., London WT., Sutnick AI. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967. 66:924–31.
Article2.Okochi K., Murakami S. Observations on Australia antigen in Japanese. Vox Sang. 1968. 15:374–85.
Article3.Prince AM. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968. 60:814–21.
Article4.Menitove JE. Hepatitis. Anderson KC, Ness PM, editors. Scientific basis of transfusion medicine. Pennsylvania: W.B. Saunders Company;1994. p. 620–36.5.Jung BC., Lee SH., Kim DS., Kim SI. Prevalence of HBsAg and anti-HCV among Korean blood donors. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1994. 5:143–50. (정보찬, 이선호, 김두성, 김상인. 한국헌혈자에서의B형, C형간염표지자양성율. 대한수혈학회지 1994;5: 143-50.).6.Oh DJ., Hwang YS., Choi JM., Min TH. A study on ALT levels in hepatitis marker positive donors – Anti-HBc positive rate in blood donors. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1997. 8:9–17. (오덕자, 황유성, 최중문, 민태희. 공혈자의간염표지자양성율및양성군의ALT 평균수치-HBs항원및항체음성공혈자의HBc항체양성률. 대한수혈학회지1997 1997;8: 9-17.).7.Oh HB., Cho YJ., Hwang YS., Kim DS., Kim SI. Detection rate of hepatitis B virus DNA among blood donors showing HBsAg positivity or negativity and relatedness with other hepatitis B viral marker. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1997. 8:249–61. (오흥범, 조연정, 황유성, 김두성, 김상인. HBsAg 양성 및 음성 헌혈자의 HBV DNA 검출율과 각종간염표지자와의관련성. 대한수혈학회지 1997;8: 249-61.).8.Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III), 2005 – Summary -. Final report of project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea. 2006. 200–1. (한국보건사회연구원. 국민건강 영양조사 제3기 (2005) -총괄-. 보건복지부 용역과제 최종보고서. 2006:200–1. ).9.Schreiber GB., Busch MP., Kleinman SH., Korelitz JJ. The risk of transfusion-transmitted viral infections. The Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study. N Engl J Med. 1996. 334:1685–90.10.Song EY., Yoon YM., Choi YS., Seo DH. The frequency of occult infection to Hepatitis B virus in Korean. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28(S2):S384. (송은영, 윤여민, 최영숙, 서동희. 한국인에서 B형간염바이러스의잠재감염빈도. 대한진단검사의학회지 2008;28(부록 2): S384.).11.Carman WF., Korula J., Wallace L., MacPhee R., Mimms L., Decker R. Fulminant reactivation of hepatitis B due to envelope protein mutant that escaped detection by monoclonal HBsAg ELISA. Lancet. 1995. 345:1406–7.
Article12.Jongerius JM., Wester M., Cuypers HT., van Oostendorp WR., Lelie PN., van der Poel CL, et al. New hepatitis B virus mutant form in a blood donor that is undetectable in several hepatitis B surface antigen screening assays. Transfusion. 1998. 38:56–9.
Article13.Sung H., Oh HB., Hwang BK., Sohn MJ. Necessity of anti-HBc and anti-HBs screening in Korean blood donation program – study using LG anti-HBc and LG anti-HBs ELISA kit and HBV nucleic acid amplification test -. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2001. 12:1–10. (성흥섭, 오흥범, 황병갑, 손미진. 국내 헌혈혈액에 대한 항-HBc 및 항-HBs 검사의필요성 – LG Anti-HBc ELISA, LG Anti-HBs ELISA 키트 및 HBV 핵산증폭검사를이용한연구. 대한수혈학회지 2001;12: 1-10.).14.Comanor L., Holland P. Hepatitis B virus blood screening: unfinished agendas. Vox Sang. 2006. 91:1–12.
Article15.Yugi H., Mizui M., Tanaka J., Yoshizawa H. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening strategy to ensure the safety of blood for transfusion through a combination of immunological testing and nucleic acid amplification testing – Japanese experience. J Clin Virol. 2006. 36(S1):S56–64.
Article16.Joo KR., Bang SJ., Song BC., Youn KH., Joo YH., Yang S, et al. Hepatitis B viral markers of Korean adults in the late 1990s: Survey data of 70,347 health screenees. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 33:642–52. (주광로, 방성조, 송병철, 윤광희, 주연호, 양수현등. 1990년대후반한국성인의 B형 간염바이러스표지자보유양상: 건강검진수검자 70,347명의성적조사. 대한소화기학회지 1999;33: 642-52.).17.Lim YA., Kwon SY., Park KU. Current analysis and long term prospects for supply and demand of blood and blood components. Final report of Korea Health project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A051019). 2005:10–1. (임영애, 권소영, 박경운. 혈액수급현황분석 및 중장기 전망. 보건복지부 보건의료기술인프라개발사업최종보고서 (A051019),. 2005. 10-1.).18.Hollinger FB., Liang TJ. Hepatitis B virus. Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2001. p. 2992–6.19.Levicnik-Stezinar S., Rahne-Potokar U., Candotti D., Lelie N., Allain JP. Anti-HBs positive occult hepatitis B virus carrier blood infectious in two transfusion recipients. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:1022–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of HBV DNA in Packed Red Blood Cells
- A Study on ALT levels in Hepatitis Marker Positive Donors -Anti-HBc Positive Rate in Blood Donors-
- Necessity of Anti-HBc and Anti-HBs Screening in Korean Blood Donation Program: Study using LG Anti-HBc and LG Anti-HBs ELISA Kit and HBV Nucleic Acid Amplification Test
- Detection Rate of Hepatitis B Virus DNA among Blood Donors showing HBsAg Positivity or Negativity and relatedness with other hepatitis B viral markers
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Kits for Hepatitis B Developed by LG Chemical Ltd