J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Jun;20(3):502-505. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.502.
A Case of Hypothyroidism and Type 2 Diabetes Associated with Type V Hyperlipoproteinemia and Eruptive Xanthomas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. jrhahm@gshp.gsnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 5Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1778515
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.502
Abstract
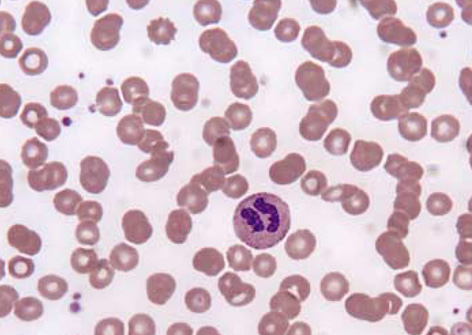
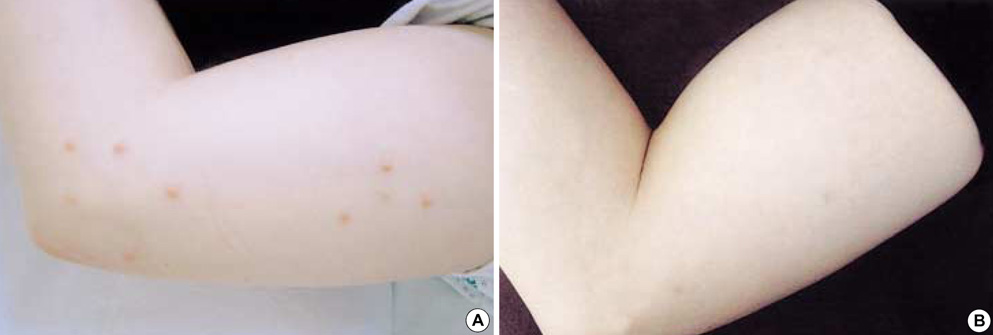
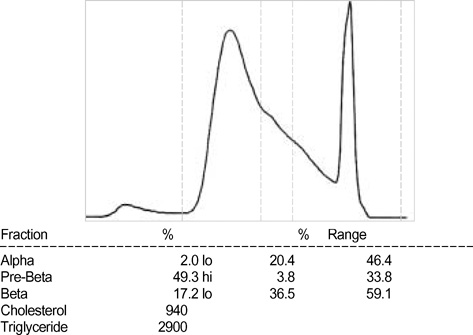
- Primary hypothyroidism and type 2 diabetes are both typically associated with the increased level of triglycerides. To date, there have been only a few case reports of type 2 diabetes patients with both type V hyperlipoproteinemia and eruptive xanthomas, but there have been no reports of hypothyroidism patients associated with eruptive xanthomas. We report here on a case of a 48-yr old female patient who was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and primary hypothyroidism associated with both type V hyperlipoproteinemia and eruptive xanthomas. We found rouleaux formation of RBCs in peripheral blood smear, elevated TSH, and low free T4 level, and dyslipidemia (total cholesterol 18.1 mM/L, triglyceride 61.64 mM/L, HDL 3.0 mM/L, and LDL 2.54 mM/L). She has taken fenofibrate, levothyroxine, and oral hypoglycemic agent for 4 months. After treatment, both TSH level and lipid concentration returned to normal range, and her yellowish skin nodules have also disappeared.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antilipemic Agents/therapeutic use
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/blood/*complications/drug therapy
Erythrocyte Aggregation
Female
Humans
Hyperlipidemia/blood
Hyperlipoproteinemia Type V/blood/*complications/drug therapy
Hypoglycemic Agents/therapeutic use
Hypothyroidism/blood/*complications/drug therapy
Middle Aged
Procetofen/therapeutic use
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Skin Diseases/blood/complications/drug therapy
Thyrotropin/blood/therapeutic use
Thyroxine/blood
Treatment Outcome
Xanthomatosis/blood/*complications/drug therapy
Figure
Reference
-
1. Valdemarsson S, Hansson P, Hedner P, Nilsson-Ehle P. Relations between thyroid function, hepatic and lipoprotein lipase activities, and plasma lipoprotein concentrations. Acta Endocrinol. 1983. 104:50–56.
Article2. Abrams JJ, Grundy SM. Cholesterol metabolism in hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism in man. J Lipid Res. 1981. 22:323–338.
Article3. Mason RL, Hunt HM, Hurxthal L. Blood cholesterol values in hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism: Their significance. N Engl J Med. 1980. 203:1273–1278.4. Bierman EL. Insulin and hypertriglyceridemia. Ir J Med Sci. 1972. 8:303–308.5. Mahley RW, Weisgraber KH, Farese RV Jr. Wilson JD, Foster DW, Kronenberg HM, Larsen PR, editors. Disorders of lipid metabolism. Williams textbook of endocrinology. 1998. 9th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co;1136–1137.6. Chang JH, Lee SH, Lee SJ, Lee JB. A case of type V hyperlipoproteinemia and xanthoma eruptivum associated with diabetes mellitus. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:561–563.7. Lee SY, Lee WS, Chang SE, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. A case of type V hyperlipoproteinemia with xanthoma eruptivum. Korean J Dermatol. 2001. 39:935–937.8. Sordi E, Fargnoli CM, Sordi O, Peris K. Eruptive xanthomas as revealing sign of type V hyperlipoproteinemia in a patient with a psychotic syndrome. Acta Dermatoven APA. 2002. 11.9. Chait A, Brunzell JD. Acquired hyperlipidemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1990. 19:259–278.10. Hansson P, Valdemarsson S, Nilsson-Ehle P. Experimental hyperthyroidism in man: effects on plasma lipoproteins, lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase. Horm Metab Res. 1983. 15:449–452.
Article11. Agdeppa D, Macaron C, Mallik T, Schnuda ND. Plasma high density lipoprotein cholesterol in thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979. 49:726–729.
Article12. Heimberg M, Olubadew JO, Wilcox HG. Plasma lipoproteins and regulation of hepatic metabolism of fatty acids in altered thyroid states. Endocr Rev. 1985. 6:590–607.
Article13. Scarabottolo L, Trezzi E, Roma P, Catapano AL. Experimental hypothyroidism modulates the expression of the low density lipoprotein receptor by the liver. Atherosclerosis. 1986. 59:329–333.
Article14. Parker F. Xanthomas and hyperlipidemias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985. 13:1–30.
Article15. Cruz PD, East C, Bergstresser PR. Dermal, subcutaneous, and tendon xanthomas: diagnostic markers for specific lipoprotein disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988. 19:95–111.
Article16. Brunzell JD, Hazzard WR, Motulsky AG, Bierman EL. Evidence for diabetes mellitus and genetic forms of hypertriglyceridemia as independent entities. Metabolism. 1975. 24:1115–1121.
Article17. Cicha I, Suzuki Y, Tateishi N, Maeda N. Enhancement of red blood cell aggregation by plasma triglycerides. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2001. 24:247–255.18. Brunzell JD, Bierman EL. Chylomicronemia syndrome: Interaction of genetic and acquired hypertriglyceridemia. Med Clin North Am. 1982. 66:455–468.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Type V Hyperlipoproteinemia and Eruptive Xanthomas associated with Diabetes Mellitus
- A Case of Eruptive Xanthoma Associated withType IV Hyperlipoproteinemia and Koebner Phenomenon
- Two Cases of Hyperlipoproteinemia
- Eruptive Xanthoma in a Child with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- A Case of Type IV Hyperlipoproteinemia with Palmar Xanthoma, Tuberous Xanthoma, and Eruptive Xanthoma