J Korean Med Sci.
2013 May;28(5):725-730. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.5.725.
COMP-Angiopoietin-1 Promotes Cavernous Angiogenesis in a Type 2 Diabetic Rat Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. uropark@gmail.com
- 2Department of Anatomy, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Sexual Medicine Research Center, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1777560
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.5.725
Abstract
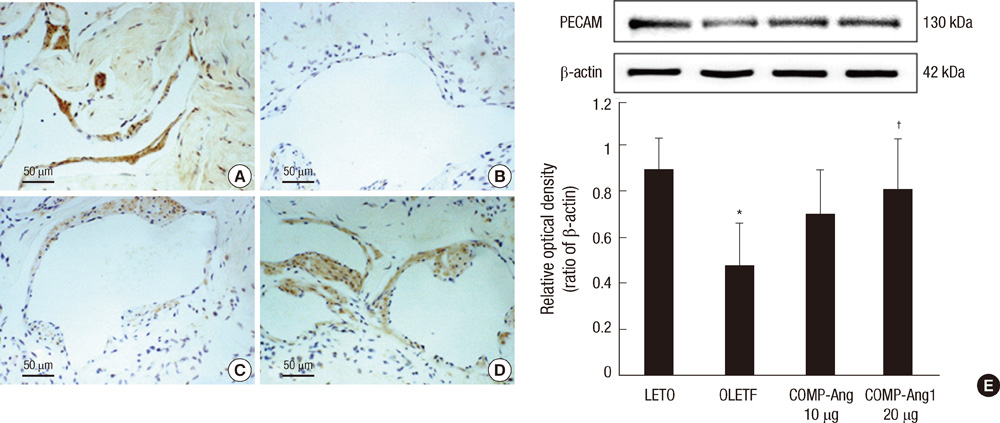
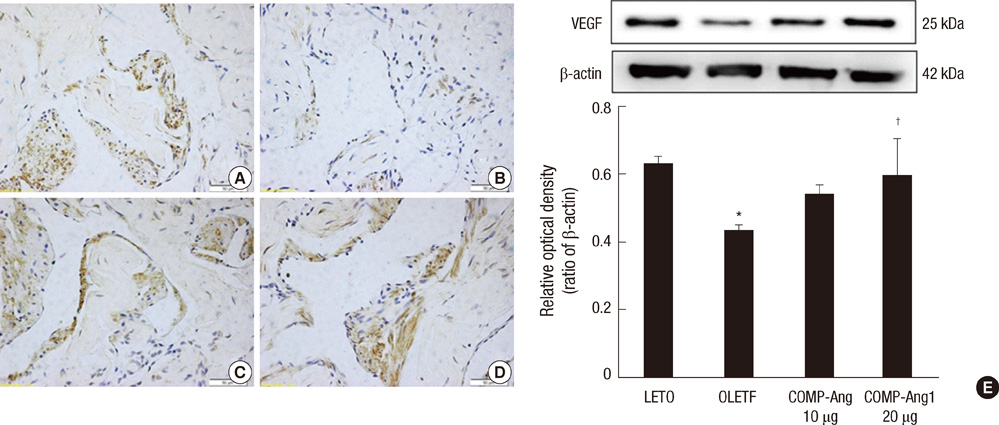
- Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein-angiopoietin-1 (COMP-Ang1) is an angiogenic factor for vascular angiogenesis. The aim was to investigate the effect of an intracavernosal injection of COMP-Ang1 on cavernosal angiogenesis in a diabetic rat model. Male Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats made up the experimental group (1 yr old) and Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka (LETO) rats made up the control group. The experimental group was divided into vehicle only, 10 microg COMP-Ang1, and 20 microg COMP-Ang1. COMP-Ang1 was injected into the corpus cavernosum of the penis. After 4 weeks, the penile tissues of the rats were obtained for immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. The immunoreactivity of PECAM-1 and VEGF was increased in the COMP-Ang1 group compared with the vehicle only group. Moreover, the expression of PECAM-1 and VEGF was notably augmented in the 20 microg Comp Ang-1 group. In the immunoblotting study, the expression of PECAM-1 and VEGF protein was significantly less in the OLEFT rats than in the control LETO rats. However, this expression was restored to control level after intracavernosal injection of COMP-Ang1. These results show that an intracavernosal injection of COMP-Ang1 enhances cavernous angiogenesis by structurally reinforcing the cavernosal endothelium.
MeSH Terms
-
Angiopoietin-1/genetics/*metabolism
Animals
Antigens, CD31/metabolism
Blood Glucose/analysis
Blotting, Western
Body Weight
Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein/genetics/*metabolism
Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental/*pathology
Immunohistochemistry
Male
Neovascularization, Physiologic/*drug effects
Penis/metabolism/pathology
Rats
Rats, Long-Evans
Recombinant Fusion Proteins/biosynthesis/genetics/*pharmacology
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A/metabolism
Angiopoietin-1
Antigens, CD31
Blood Glucose
Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein
Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bacon CG, Mittleman MA, Kawachi I, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Rimm EB. Sexual function in men older than 50 yr of age: results from the health professionals follow-up study. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 139:161–168.2. Heaton JP, Adams MA. Causes of erectile dysfunction. Endocrine. 2004. 23:119–123.3. Jin HR, Kim WJ, Song JS, Piao S, Tumurbaatar M, Shin SH, Choi MJ, Tuvshintur B, Song KM, Kwon MH, et al. Intracavernous delivery of synthetic angiopoietin-1 protein as a novel therapeutic strategy for erectile dysfunction in the type II diabetic db/db mouse. J Sex Med. 2010. 7:3635–3646.4. Xie D, Odronic SI, Wu F, Pippen A, Donatucci CF, Annex BH. Mouse model of erectile dysfunction due to diet-induced diabetes mellitus. Urology. 2007. 70:196–201.5. Luttrell IP, Swee M, Starcher B, Parks WC, Chitaley K. Erectile dysfunction in the type II diabetic db/db mouse: impaired venoocclusion with altered cavernosal vasoreactivity and matrix. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. 294:H2204–H2211.6. Jesmin S, Sakuma I, Salah-Eldin A, Nonomura K, Hattori Y, Kitabatake A. Diminished penile expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors at the insulin-resistant stage of a type II diabetic rat model: a possible cause for erectile dysfunction in diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2003. 31:401–418.7. Shirai M, Yamanaka M, Shiina H, Igawa M, Kawakami T, Ishii N, Lue TF, Fujime M, Dahiya R. Vascular endothelial growth factor restores erectile function through modulation of the insulin-like growth factor system and sex hormone receptors in diabetic rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 341:755–762.8. Dall'Era JE, Meacham RB, Mills JN, Koul S, Carlsen SN, Myers JB, Koul HK. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy using a nonviral gene delivery system improves erectile function in a diabetic rat model. Int J Impot Res. 2008. 20:307–314.9. Thurston G, Suri C, Smith K, McClain J, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD, McDonald DM. Leakage-resistant blood vessels in mice transgenically overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science. 1999. 286:2511–2514.10. Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Acheson A, Compton DL, Jain V, Ryan TE, Bruno J, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996. 87:1161–1169.11. Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell. 1996. 87:1171–1180.12. Cho CH, Kim KE, Byun J, Jang HS, Kim DK, Baluk P, Baffert F, Lee GM, Mochizuki N, Kim J, et al. Long-term and sustained COMP-Ang1 induces long-lasting vascular enlargement and enhanced blood flow. Circ Res. 2005. 97:86–94.13. Cho CH, Kammerer RA, Lee HJ, Steinmetz MO, Ryu YS, Lee SH, Yasunaga K, Kim KT, Kim I, Choi HH, et al. COMP-Ang1: a designed angiopoietin-1 variant with nonleaky angiogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:5547–5552.14. Yagi K, Kim S, Wanibuchi H, Yamashita T, Yamamura Y, Iwao H. Characteristics of diabetes, blood pressure, and cardiac and renal complications in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Hypertension. 1997. 29:728–735.15. Park SH, Kim M, Min K, Park K. Erectile function and cavernosal TGF-beta expression in the OLETF rats. Korean J Androl. 2002. 20:82–86.16. Isner JM, Asahara T. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis as therapeutic strategies for postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:1231–1236.17. Freedman SB, Isner JM. Therapeutic angiogenesis for ischemic cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001. 33:379–393.18. Ryu JK, Shin HY, Song SU, Oh SM, Piao S, Han JY, Park KW, Suh JK. Down-regulation of angiogenic factors and their downstream target molecules affects the deterioration of erectile function in a rat model of hypercholesterolemia. Urology. 2006. 67:1329–1334.19. Lee MC, El-Sakka AI, Graziottin TM, Ho HC, Lin CS, Lue TF. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on a rat model of traumatic arteriogenic erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 2002. 167:761–767.20. Gholami SS, Rogers R, Chang J, Ho HC, Grazziottin T, Lin CS, Lue TF. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor and adeno-associated virus mediated brain derived neurotrophic factor on neurogenic and vasculogenic erectile dysfunction induced by hyperlipidemia. J Urol. 2003. 169:1577–1581.21. Lee RJ, Springer ML, Blanco-Bose WE, Shaw R, Ursell PC, Blau HM. VEGF gene delivery to myocardium: deleterious effects of unregulated expression. Circulation. 2000. 102:898–901.22. Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD. Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science. 1998. 282:468–471.23. Baffert F, Thurston G, Rochon-Duck M, Le T, Brekken R, McDonald DM. Age-related changes in vascular endothelial growth factor dependency and angiopoietin-1-induced plasticity of adult blood vessels. Circ Res. 2004. 94:984–992.24. Ryu JK, Cho CH, Shin HY, Song SU, Oh SM, Lee M, Piao S, Han JY, Kim IH, Koh GY, et al. Combined angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer restores cavernous angiogenesis and erectile function in a rat model of hypercholesterolemia. Mol Ther. 2006. 13:705–715.25. Cho CH, Sung HK, Kim KT, Cheon HG, Oh GT, Hong HJ, Yoo OJ, Koh GY. COMP-angiopoietin-1 promotes wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and blood flow in a diabetic mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. 103:4946–4951.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Improvement of the Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap Viability Using Adenovirus-mediated VEGF and COMP-angiopoietin-1
- The Role of Angiopoietin-1 in Kidney Disease
- COMP-angiopoietin 1 Gene Transfer Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis
- COMP-Angiopoietin-1 Stimulates Synovial Proliferation but Suppresses Osteoclast by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Osteoblast Maturation in Collagen-Induced Arthritis
- Blockade of airway inflammation and hyper-responsiveness by an angiopoietin-1 variant, COMP-Ang1