J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Apr;29(4):599-603. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.599.
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease with Bronchial Asthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1774469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.599
Abstract
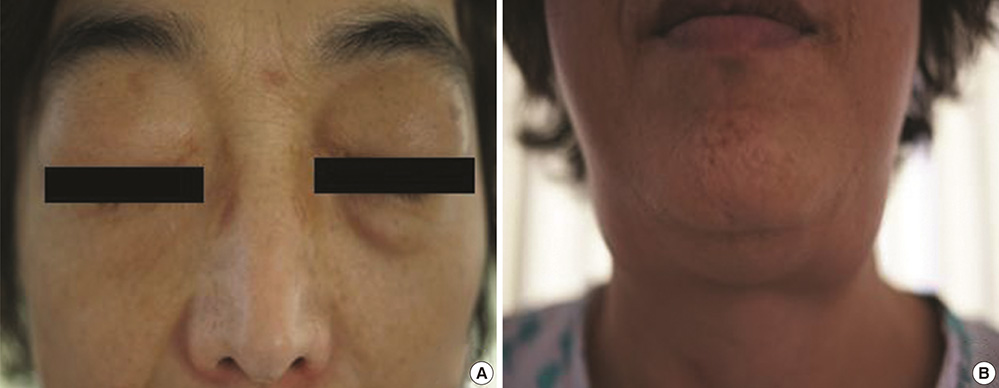
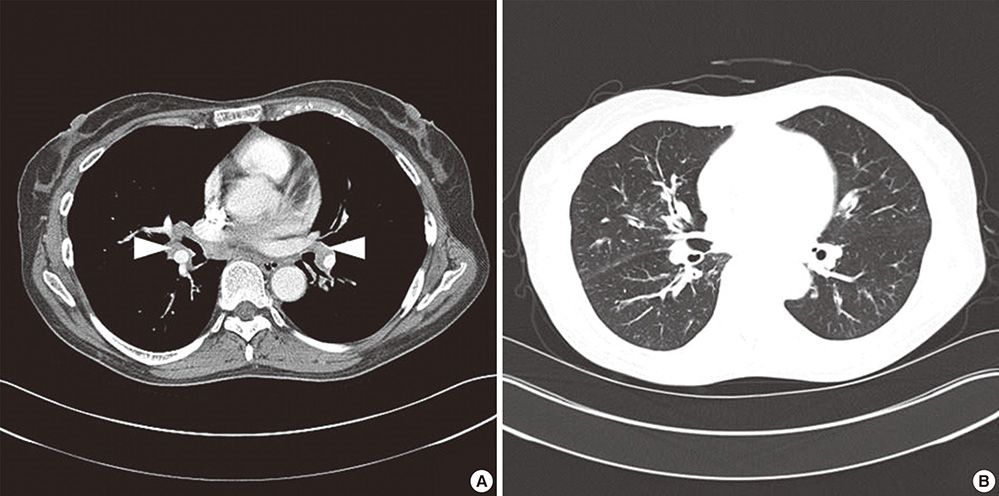
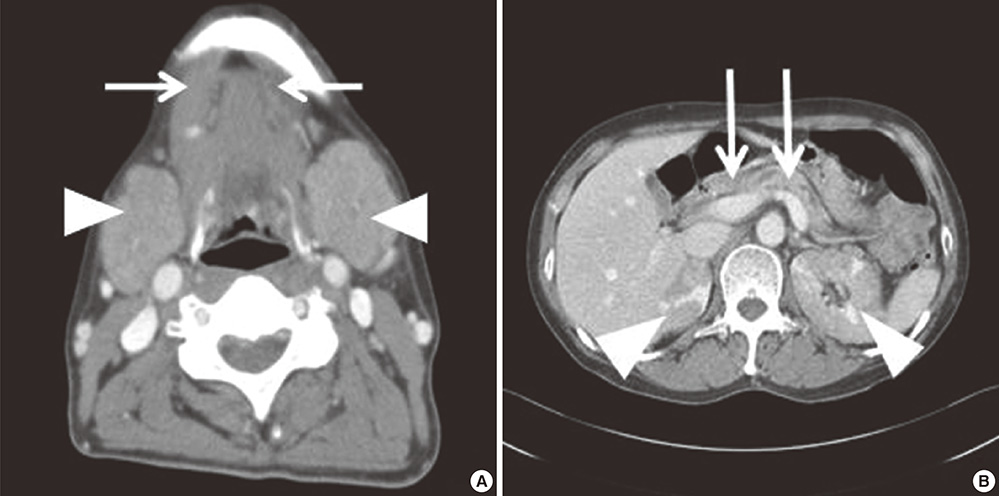
- IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is characterized by a systemic involvement of tumor-like lesions with IgG4-positive plasmacytes. We experienced a case of IgG4-RD developed in a patient with bronchial asthma (BA) and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). A 55-yr-old female patient with BA and CRS complained of both eyes and neck swelling as well as a recurrent upper respiratory infection in recent 1 yr. The serum levels of IgG4, creatinine, and pancreatic enzymes were elevated. A biopsy of the submandibular gland showed an abundant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasmacytes. Her symptoms remarkably improved after the treatment of a systemic steroid that has been maintained without recurrence. We report a rare case of IgG4-RD developed in a patient with BA and CRS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Asthma/complications/*diagnosis
Chronic Disease
Creatinine/blood
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/*blood
Middle Aged
Pancreas/enzymology
Plasma Cells/physiology
Prednisolone/therapeutic use
Republic of Korea
Rhinitis/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Sinusitis/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Submandibular Gland/pathology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Creatinine
Immunoglobulin G
Prednisolone
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.2. Kamisawa T, Egawa N, Nakajima H. Autoimmune pancreatitis is a systemic autoimmune disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:2811–2812.3. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N, Nakajima H. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–984.4. Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Egawa N, Kubota N. Allergic manifestations in autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 21:1136–1139.5. Okazaki K, Uchida K, Koyabu M, Miyoshi H, Takaoka M. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:277–288.6. Okazaki K, Uchida K, Miyoshi H, Ikeura T, Takaoka M, Nishio A. Recent concepts of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011; 41:126–138.7. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.8. Kanari H, Kagami S, Kashiwakuma D, Oya Y, Furuta S, Ikeda K, Suto A, Suzuki K, Hirose K, Watanabe N, et al. Role of Th2 cells in IgG4-related lacrimal gland enlargement. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010; 152:47–53.9. Miyake K, Moriyama M, Aizawa K, Nagano S, Inoue Y, Sadanaga A, Nakashima H, Nakamura S. Peripheral CD4+ T cells showing a Th2 phenotype in a patient with Mikulicz's disease associated with lymphadenopathy and pleural effusion. Mod Rheumatol. 2008; 18:86–90.10. Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada K, Takahira M, Nakanuma Y. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1538–1546.11. Detlefsen S, Sipos B, Zhao J, Drewes AM, Klöppel G. Autoimmune pancreatitis: expression and cellular source of profibrotic cytokines and their receptors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:986–995.12. Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010; 34:1812–1819.13. Ryu JH, Sekiguchi H, Yi ES. Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:180–186.14. Nishimori I, Suda K, Oi I, Ogawa M. Autoimmune pancreatitis. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2000; 97:1355–1363.15. Abraham SC, Leach S, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Murakata LA, Boitnott JK, Albores-Saavedra J, Hruban RH. Eosinophilic pancreatitis and increased eosinophils in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003; 27:334–342.16. Kim YM, Kim YS, Jeon SG, Kim YK. Immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma: more than the Th2 hypothesis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:189–196.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors associated with chronic and recurrent rhinosinusitis in preschool children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- The Effect of Lower Airway Disease on the Severity of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Genetic Factors in Bronchial Asthma
- The Role of Allergy in the Severity of Chronic Rhinosinusitis