Lab Anim Res.
2014 Dec;30(4):174-180. 10.5625/lar.2014.30.4.174.
Protective effects of pine bark extract against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. toxkim@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1737419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2014.30.4.174
Abstract
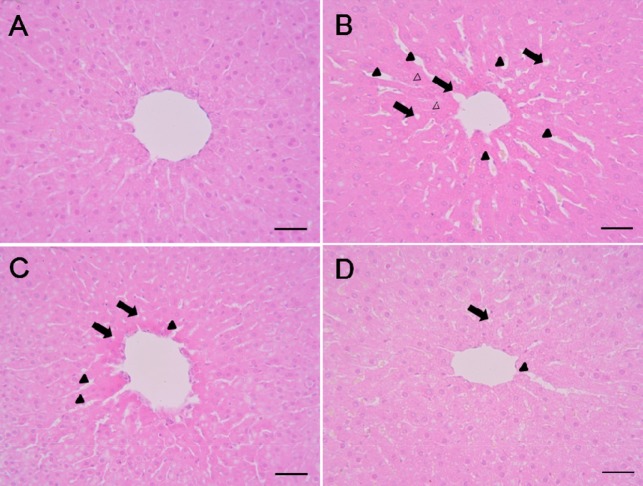
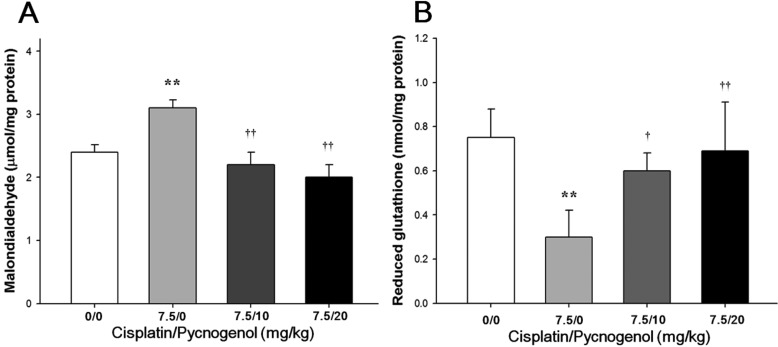
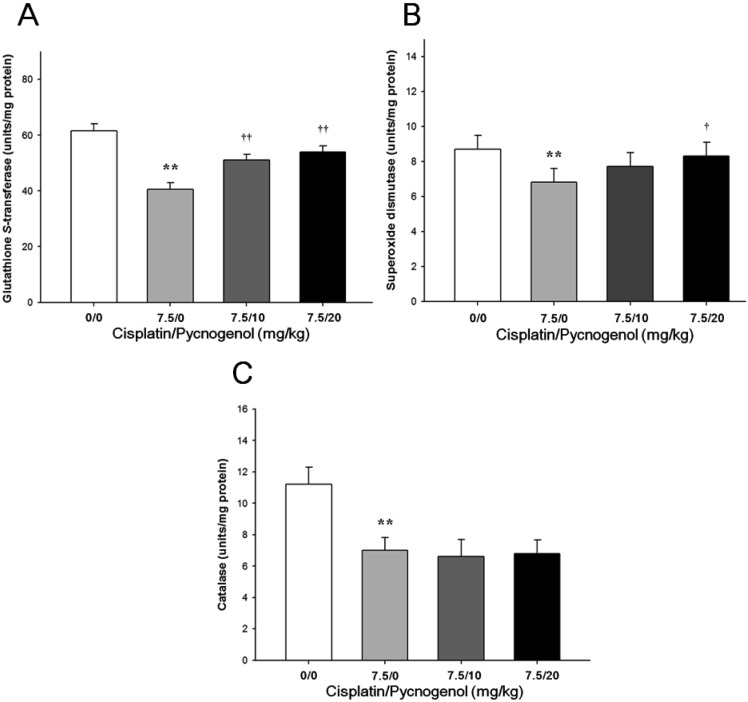
- We investigated the protective effects of pine bark extract (pycnogenol(R), PYC) against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Twenty-four male rats were divided into the following four groups: (1) vehicle control, (2) cisplatin (7.5 mg/kg), (3) cisplatin & PYC 10 (10 mg/kg/day), and (4) cisplatin & PYC 20 (20 mg/kg/day). A single intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity, as evidenced by an increase in serum aminotransferase and histopathological alterations, including degeneration/necrosis of hepatocytes, vacuolation, and sinusoidal dilation. In addition, an increase in the malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration and a decrease in the reduced glutathione (GSH) content and catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione S-transferase (GST) activities were observed in the cisplatin-treated rat hepatic tissues. In contrast, PYC treatment effectively prevented cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity, including the elevation of aminotransferase and histopathological lesions, in a dosedependent manner. Moreover, PYC treatment also induced antioxidant activity by decreasing MDA level and increasing GSH content and SOD and GST activities in liver tissues. These results indicate that PYC has a protective effect against acute hepatotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats, and that the protective effects of PYC may be due to inhibiting lipid peroxidation and increasing antioxidant activity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wiltshaw E, Kroner T. Phase two study of cis-dichlorodimmine-platinum (II) in advanced adenocarcinoma of the ovary. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976; 60:55–60. PMID: 1000519.2. Jordan P, Carmo-Fonseca M. Molecular mechanisms involved in cisplatin cytotoxicity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000; 57:1229–1235. PMID: 11028915.
Article3. Crown JP. The platinum agents: a role in breast cancer treatment? Semin Oncol. 2001; 28:28–37. PMID: 11301372.
Article4. Pinedo HM, Schornagel JH. Platinum and Other Metal Coordination Compounds in Cancer Chemotherapy. New York: Plenum;1996.5. Yang D, Wang AH. Structural studies of interactions between anticancer platinum drugs and DNA. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996; 66(1):81–111. PMID: 9107133.
Article6. Rybak LP, Husain K, Whitworth C, Somani SM. Dose dependent protection by lipoic acid against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats: antioxidant defense system. Toxicol Sci. 1999; 47(2):195–202. PMID: 10220857.
Article7. Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Somani S. Application of antioxidants and other agents to prevent cisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope. 1999; 109(11):1740–1744. PMID: 10569399.8. Teranishi M, Nakashima T, Wakabayashi T. Effects of alpha-tocopherol on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Hear Res. 2001; 151:60–70.9. Cavalli F, Tschopp L, Sonntag RW, Zimmermann A. Cisplatin-induced hepatic toxicity. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978; 62:2125–2126. PMID: 751721.10. Pollera CF, Ameglio F, Nardi M, Vitelli G, Marolla P. Cisplatin-induced hepatic toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1987; 5:318–319. PMID: 3806175.
Article11. Cersosimo RJ. Hepatotoxicity associated with cisplatin chemotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993; 27(4):438–441. PMID: 8477119.
Article12. Lu Y, Cederbaum AI. Cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity is enhanced by elevated expression of cytochrome P450 2E1. Toxicol Sci. 2006; 89(2):515–523. PMID: 16251482.
Article13. Liu J, Liu Y, Habeebu SS, Klaassen CD. Metallothionein (MT)-null mice are sensitive to cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998; 149(2):24–41. PMID: 9512723.
Article14. Naziroglu M, Karaoðlu A, Aksoy AO. Selenium and high dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin-induced oxidative damage to renal, liver and lens tissues in rats. Toxicology. 2004; 195(2-3):221–230. PMID: 14751677.
Article15. Packer L, Rimbach G, Virgili F. Antioxidant activity and biologic properties of a procyanidin-rich extract from pine (Pinus maritima) bark, pycnogenol. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999; 27(5-6):704–724. PMID: 10490291.
Article16. Guo Q, Zhao B, Packer L. Electron spin resonance study of free radicals formed from a procyanidin-rich pine (Pinus maritima) bark extract, pycnogenol. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999; 27(11-12):1308–1312. PMID: 10641725.
Article17. Rohdewald P. A review of the French maritime pine bark extract (Pycnogenol), a herbal medication with a diverse clinical pharmacology. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 40(4):158–168. PMID: 11996210.
Article18. Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB 3rd. Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003; 17(1):24–38. PMID: 12616644.
Article19. Yang YS, Ahn TH, Lee JC, Moon CJ, Kim SH, Jun W, Park SC, Kim HC, Kim JC. Protective effects of Pycnogenol on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008; 46(1):380–387. PMID: 17900780.
Article20. Ateşşahin A, Karahan I, Türk G, Gür S, Yilmaz S, Ceribaşi AO. Protective role of lycopene on cisplatin-induced changes in sperm characteristics, testicular damage and oxidative stress in rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2006; 21(1):42–47. PMID: 15979841.
Article21. Kim SH, Lee IC, Lim JH, Moon C, Bae CS, Kim SH, Shin DH, Park SC, Kim HC, Kim JC. Protective effects of pine bark extract on developmental toxicity of cyclophosphamide in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012; 50(2):109–115. PMID: 22036974.
Article22. Maritim A, Dene BA, Sanders RA, Watkins JB 3rd. Effects of pycnogenol treatment on oxidative stress in streptozotocininduced diabetic rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003; 17(3):193–199. PMID: 12815616.
Article23. Berton TR, Conti CJ, Mitchell DL, Aldaz CM, Lubet RA, Fischer SM. The effect of vitamin E acetate on ultraviolet-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 1998; 23(3):175–184. PMID: 9833778.
Article24. Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979; 582(1):67–78. PMID: 760819.
Article25. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193(1):265–275. PMID: 14907713.
Article26. Halliwell B. Oxidative stress and cancer: have we moved forward? Biochem J. 2007; 401(1):1–11. PMID: 17150040.
Article27. Grimm T, Schäfer A, Högger P. Antioxidant activity and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases by metabolites of maritime pine bark extract (pycnogenol). Free Radic Biol Med. 2004; 36(6):811–822. PMID: 14990359.
Article28. Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Genovesi D, Ledda A, Vinciguerra G, Ricci A, Pellegrini L, Gizzi G, Ippolito E, Dugall M, Cacchio M, Di Renzo A, Stuard S. Pycnogenol may alleviate adverse effects in oncologic treatment. Panminerva Med. 2008; 50(3):227–234. PMID: 18927527.29. Skeel RT, Ganz PA. Handbook of Cancer Chemotherapy. 8th Ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer;1999.30. Kim JC, Kim KH, Chung MK. Testicular cytotoxicity of DA-125, a new anthracycline anticancer agent, in rats. Reprod Toxicol. 1999; 13(5):391–397. PMID: 10560588.
Article31. Liao Y, Lu X, Lu C, Li G, Jin Y, Tang H. Selection of agents for prevention of cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Res. 2008; 57(2):125–131. PMID: 18282716.
Article32. Devaraj S, Vega-López S, Kaul N, Schönlau F, Rohdewald P, Jialal I. Supplementation with a pine bark extract rich in polyphenols increases plasma antioxidant capacity and alters the plasma lipoprotein profile. Lipids. 2002; 37(10):931–934. PMID: 12530550.
Article33. Zimmerman HJ, Seeff LB. Enzymes in hepatic disease: In Diagnostic Enzymology. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger;1970.34. Cersosimo RJ. Hepatotoxicity associated with cisplatin chemotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993; 27(4):438–441. PMID: 8477119.
Article35. Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007; 39(1):44–84. PMID: 16978905.
Article36. Quiles JL, Huertas JR, Battino M, Mataix J, Ramírez-Tortosa MC. Antioxidant nutrients and adriamycin toxicity. Toxicology. 2002; 180(10):79–95. PMID: 12324201.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Protective Effects of Alpinia katsumadai Extract Against Oxidative Stress
- The mechanism of mesna in protection from cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in female rats
- The Effect of Glehnia Littoralis on Alpha-amanitin Induced Hepatotoxicity in a Murine Model
- Cichorium intybus L. extract ameliorates testicular oxidative stress induced by lead acetate in male rats
- Cisplatin-induced Kidney Dysfunction and Perspectives on Improving Treatment Strategies