Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis.
2014 Aug;21(2):96-103.
Comparison of Group A, B and C Rotaviral Gastroenteritis among Children in Korea: Prevalence and Clinical Features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St Mary's Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. leewb@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Clinical Medical Research Institute, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St Mary's Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study is that the prevalence of rotavirus infection was evaluated by each group and clinical features of group A, B and C rotaviruses infections were described respectively to compare one with another.
METHODS
Between January 2010 and December 2010, we enrolled a group of children below 10 years of age admitted for management of acute diarrhea at the Catholic University of Korea Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital. A total of 310 stool samples documented to be free of common bacterial pathogens were collected from children with diarrhea. The presence of group A, B or C rotavirus is indicated by amplification of DNA segments of the expected lengths after the first and second PCRs.
RESULTS
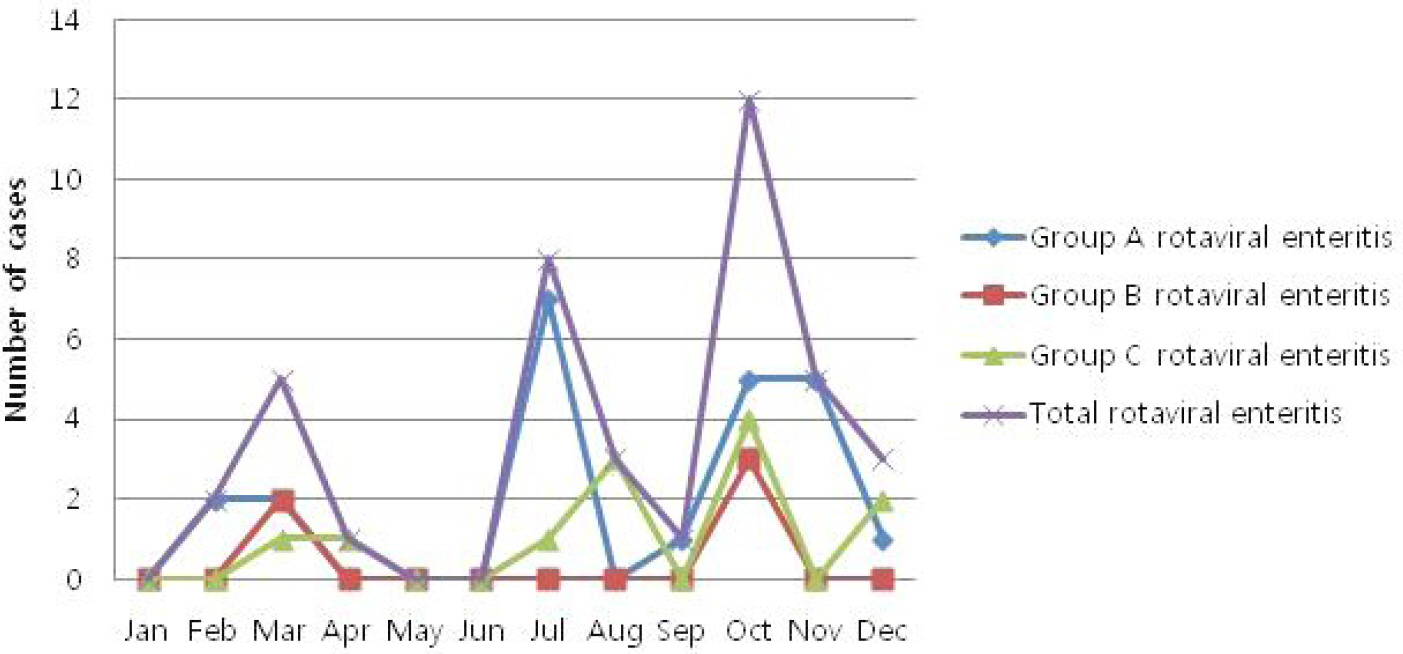
In a total of 310 stool specimens, 40 (12.9%) specimens were positive for rotaviruses. These included 23 (7.4%) positive for group A, 5 (1.6%) for group B and 12 (3.9%) for group C rotaviruses. Group B rotavirus infected patients had significantly less diarrheas per day (group A: P=0.01, group C: P=0.01) and shorter duration of vomiting days (group A: P=0.03, group C: P=0.03) than those with group A and C rotaviruses infection respectively. All the group B rotaviruses had been isolated in March and October. Group C rotavirus infections were prevalent during late summer and early winter and peaked in October.
CONCLUSION
These findings indicate that group B and C rotaviruses are notable causes or the contributing causes of diarrhea among infants and children in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kapikian AZ, Hoshino Y, Chanock RM. Rotaviruses. Knipe D, Howley P, Griffin D, MArtin M, Lamb R, Roizman B, Straus S, editors. Fields virology. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 1787–822.2. Saif LJ, Jiang B. Nongroup A rotaviruses of humans and animals. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1994; 185:339–71.
Article3. Krishnan T, Sen A, Choudhury JS, Das S, Naik TN, Bhattacharya SK. Emergence of adult diarrhoea rotavirus in Calcutta, India. Lancet. 1999; 353:380–1.
Article4. James VL, Lambden PR, Caul EO, Cooke SJ, Clarke IN. Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in the UK. J Med Virol. 1997; 52:86–91.
Article5. Riepenhoff-Talty M, Morse K, Wang CH, Shapiro C, Roberts J, Welter M, et al. Epidemiology of group C rotavirus infection in Western New York women of childbearing age. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35:486–8.
Article6. Steele AD, James VL. Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in South Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:4142–4.
Article7. Iturriza-Gomara M, Clarke I, Desselberger U, Brown D, Thomas D, Gray J. Seroepidemiology of group C rotavirus infection in England and Wales. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004; 19:589–95.
Article8. Maunula L, Svensson L, von Bonsdorff CH. A family outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by group C rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1992; 124:269–78.
Article9. Jiang B, Dennehy PH, Spangenberger S, Gentsch JR, Glass RI. First detection of group C rotavirus in fecal specimens of children with diarrhea in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1995; 172:45–50.
Article10. Cunliffe NA, Dove W, Jiang B, Thinwda Cert BD, Broad-head RL, Molyneux ME, et al. Detection of group C rotavirus in children with acute gastroenteritis in Blantyre, Malawi. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001; 20:1088–90.
Article11. Adah MI, Wade A, Oseto M, Kuzuya M, Taniguchi K. Detection of human group C rotaviruses in Nigeria and sequence analysis of their genes encoding VP4, VP6, and VP7 proteins. J Med Virol. 2002; 66:269–75.
Article12. Sanchez-Fauquier A, Roman E, Colomina J, Wilhelmi I, Glass RI, Jiang B. First detection of group C rotavirus in children with acute diarrhea in Spain. Arch Virol. 2003; 148:399–404.13. Phan TG, Nishimura S, Okame M, Nguyen TA, Khamrin P, Okitsu S, et al. Virus diversity and an outbreak of group C rotavirus among infants and children with diarrhea in Maizuru city, Japan during 2002–2003. J Med Virol. 2004; 74:173–9.
Article14. Rahman M, Banik S, Faruque AS, Taniguchi K, Sack DA, Van Ranst M, et al. Detection and characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:4460–5.
Article15. Steyer A, Poljsak-Prijatelj M, Bufon T, Sedmak M, Vidmar L, Mijovski JZ, et al. First detection of group C rotavirus in patients with gastroenteritis in Slovenia. J Med Virol. 2006; 78:1250–5.
Article16. Estes M, Kapikian A, Knipe D, Howley P. Rotaviruses. Knipe D, Howley P, Griffin D, Lamb R, Martin M, Roizman B, Straus S, editors. editors.Fields virology. 5th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 1917–74.17. Rodriguez WJ, Kim HW, Arrobio JO, Brandt CD, Chanock RM, Kapikian AZ, et al. Clinical features of acute gastroenteritis associated with human reovirus-like agent in infants and young children. J Pediatr. 1977; 91:188–93.
Article18. Rahman M, Hassan ZM, Zafrul H, Saiada F, Banik S, Faruque AS, et al. Sequence analysis and evolution of group B rotaviruses. Virus Res. 2007; 125:219–25.
Article19. Sanekata T, Ahmed MU, Kader A, Taniguchi K, Kobayashi N. Human group B rotavirus infections cause severe diarrhea in children and adults in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:2187–90.
Article20. Gouvea V. PCR detection of rotavirus. Persing DH, Smith TF, Tenover FC, White TJ, editors. editors.Diagnostic molecular microbiology: principles and applications. Washington, DC: American Society for microbiology;2006. p. 383–88.21. Moon S, Humphrey CD, Kim JS, Baek LJ, Song JW, Song KJ, et al. First detection of Group C rotavirus in children with acute gastroenteritis in South Korea. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; 17:244–7.
Article22. Mitui MT, Bozdayi G, Dalgic B, Bostanci I, Nishizono A, Ahmed K. Molecular characterization of a human group C rotavirus detected first in Turkey. Virus Genes. 2009; 39:157–64.
Article23. Castello AA, Arguelles MH, Villegas GA, Olthoff A, Glikmann G. Incidence and prevalence of human group C rotavirus infections in Argentina. J Med Virol. 2002; 67:106–12.
Article24. Kuzuya M, Fujii R, Hamano M, Nishijima M, Ogura H. Detection and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Okayama prefecture, Japan, between 1986 and 2005. J Med Virol. 2007; 79:1219–28.
Article25. Castello AA, Arguelles MH, Rota RP, Humphrey CD, Olthoff A, Gentsch JR, et al. Detection and characterization of group C rotavirus in Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1997–2003. J Med Virol. 2009; 81:1109–16.
Article26. Kuzuya M, Fujii R, Hamano M, Ohata R, Ogura H, Yamada M. Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in Japan based on a blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001; 8:161–5.
Article27. Banyai K, Jiang B, Bogdan A, Horvath B, Jakab F, Meleg E, et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Hungary. J Clin Virol. 2006; 37:317–22.28. Luchs A, Morillo SG, de Oliveira CM, Timenetsky Mdo C. Monitoring of group C rotavirus in children with acute gastroenteritis in Brazil: an emergent epidemiological issue after rotavirus vaccine? J Med Virol. 2011; 83:1631–6.
Article29. Meleg E, Banyai K, Martella V, Jiang B, Kocsis B, Kisfali P, et al. Detection and quantification of group C rotaviruses in communal sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008; 74:3394–9.
Article30. Castello AA, Arguelles MH, Villegas GA, Lopez N, Ghi-ringhelli DP, Semorile L, et al. Characterization of human group C rotavirus in Argentina. J Med Virol. 2000; 62:199–207.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical features of acute noroviral gastroenteritis in children : comparison with rotaviral gastroenteritis
- Comparison of Clinical Features between Noroviral and Rotaviral Gastroenteritis
- Fat Content in Stool of Children with Rotaviral Enteritis
- The Clinial Usefulness C-reactive Protein Levels in Rotavirus and Salmonella Gastroenteritis in Childhood
- Comparison of Clinical Features of Norovirus and Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Hospitalized Children and Norovirus Genotype Analysis