J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Aug;27(8):876-882. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.876.
Direct Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on the Korean National Diabetes Program
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. lkw65@ajou.ac.kr
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1714198
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.876
Abstract
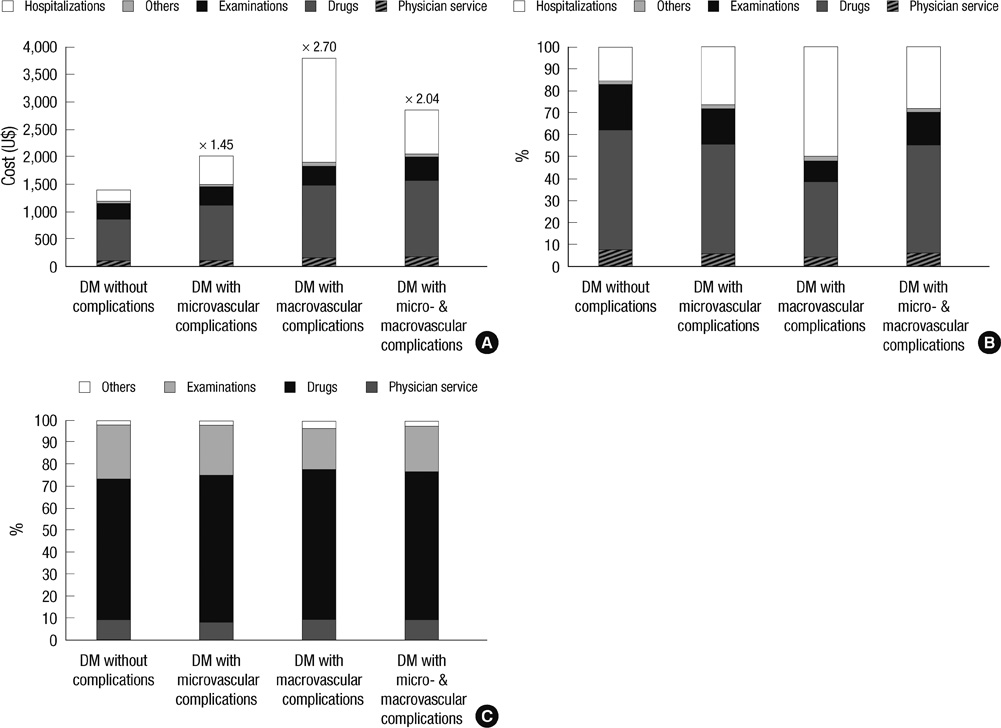
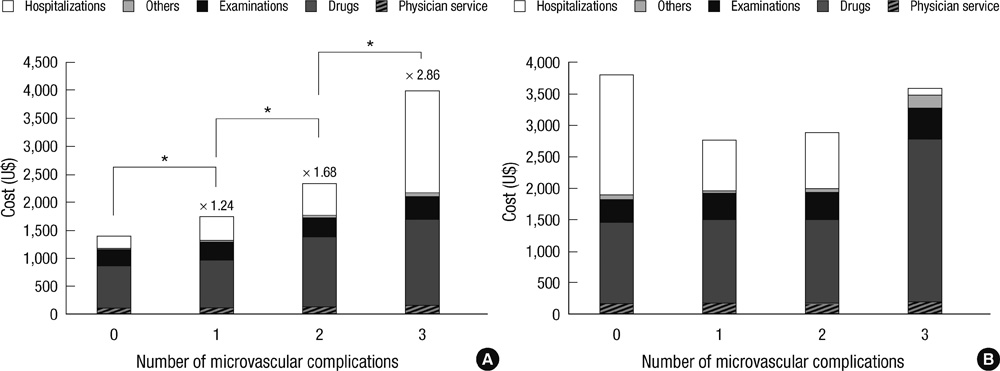
- We analyzed the direct medical costs for Korean patients with type 2 diabetes according to the type of complications and the number of microvascular complications. We analyzed costs for type 2 diabetes and associated complications in 3,125 patients. These data were obtained from the Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP), a large, ongoing, prospective cohort study that began in 2005. The cost data were prospectively collected, using an electronic database, for the KNDP cohort at six hospitals. The costs were analyzed according to complications for 1 yr from enrollment in the study. Among 3,125 patients, 918 patients had no vascular complications; 1,883 had microvascular complications only; 51 had macrovascular complications only; and 273 had both complications. The annual direct medical costs for a patient with only macrovascular, only microvascular, or both macrovascular and microvascular complications were 2.7, 1.5, and 2.0 times higher than the medical costs of patients without complications. Annual direct medical costs per patient increased with the number of microvascular complications in patients without macrovascular complications. The economic costs for type 2 diabetes are attributable largely to the management of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Proper management of diabetes and prevention of related complications are important for reducing medical costs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Trends in adherence to dietary recommendations among Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Kyong Park
Nutr Res Pract. 2015;9(6):658-666. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2015.9.6.658.Glucose Control in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Recent Updates
Sang Youl Rhee
J Neurocrit Care. 2018;11(2):81-85. doi: 10.18700/jnc.180067.
Reference
-
1. Bjork S. The cost of diabetes and diabetes care. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001. 54:S13–S18.2. Rekkedal G. WHO world health report 1997. Tidsskr Sykepl. 1997. 85:37–39.3. King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998. 21:1414–1431.4. Abegunde DO, Mathers CD, Adam T, Ortegon M, Strong K. The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2007. 370:1929–1938.5. Huse DM, Oster G, Killen AR, Lacey MJ, Colditz GA. The economic costs of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 1989. 262:2708–2713.6. Brown JB, Pedula KL, Bakst AW. The progressive cost of complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 1999. 159:1873–1880.7. Williams R, Van Gaal L, Lucioni C. Assessing the impact of complications on the costs of Type II diabetes. Diabetologia. 2002. 45:S13–S17.8. American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. In 2007. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:596–615.9. Massi-Benedetti M. The cost of diabetes Type II in Europe: the CODE-2 Study. Diabetologia. 2002. 45:S1–S4.10. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006. 368:1681–1688.11. Unwin N, Mbanya JC, Ramachandran A, Roglic G, Shaw J, Soltèsz G, Whiting D, Zgibor J, Zhang P, Zimmet P. Diabetes Atlas fourth edition committee. The IDF Diabetes Atlas 2010. accessed on 23 December 2010. Available from http://www.diabetesatlas.org/content/wp-data.12. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(KCDC). The Fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-3),2009. 2010. Seoul: KCDC.13. Rhee SY, Chon S, Kwon MK, Park IB, Ahn KJ, Kim IJ, Kim SH, Lee HW, Koh KS, Kim DM, et al. Prevalence of chronic complications in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the Korean national diabetes program. Diabetes Metab J. 2011. 35:504–512.14. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:S15–S35.15. Morsanutto A, Berto P, Lopatriello S, Gelisio R, Voinovich D, Cippo PP, Mantovani LG. Major complications have an impact on total annual medical cost of diabetes: results of a database analysis. J Diabetes Complications. 2006. 20:163–169.16. Brandle M, Zhou H, Smith BR, Marriott D, Burke R, Tabaei BP, Brown MB, Herman WH. The direct medical cost of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:2300–2304.17. Oliva J, Lobo F, Molina B, Monereo S. Direct health care costs of diabetic patients in Spain. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2616–2621.18. European Diabetes Policy Group 1999. A desktop guide to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1999. 16:716–730.19. Kapur A. Economic analysis of diabetes care. Indian J Med Res. 2007. 125:473–482.20. Beaglehole R, Epping-Jordan J, Patel V, Chopra M, Ebrahim S, Kidd M, Haines A. Improving the prevention and management of chronic disease in low-income and middle-income countries: a priority for primary health care. Lancet. 2008. 372:940–949.21. Kim KS, Choi CH, Lee DY, Kim EJ. Epidemiological study on diabetes mellitus among rural Koreans. Korean Diabetes J. 1972. 1:17–24.22. Park Y, Lee H, Koh CS, Min H, Yoo K, Kim Y, Shin Y. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in Yonchon County, South Korea. Diabetes Care. 1995. 18:545–548.23. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:226–231.24. Hu D, Fu P, Xie J, Chen CS, Yu D, Whelton PK, He J, Gu D. Increasing prevalence and low awareness, treatment and control of diabetes mellitus among Chinese adults: the InterASIA study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008. 81:250–257.25. Ramachandran A, Mary S, Yamuna A, Murugesan N, Snehalatha C. High prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors associated with urbanization in India. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:893–898.26. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:2016–2020.27. Koster I, von Ferber L, Ihle P, Schubert I, Hauner H. The cost burden of diabetes mellitus: the evidence from Germany--the CoDiM study. Diabetologia. 2006. 49:1498–1504.28. Esteghamati A, Khalilzadeh O, Anvari M, Meysamie A, Abbasi M, Forouzanfar M, Alaeddini F. The economic costs of diabetes: a populationbased study in Tehran, Iran. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:1520–1527.29. Tharkar S, Devarajan A, Kumpatla S, Viswanathan V. The socioeconomics of diabetes from a developing country: a population based cost of illness study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010. 89:334–340.30. Wang W, McGreevey WP, Fu C, Zhan S, Luan R, Chen W, Xu B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in China: a preventable economic burden. Am J Manag Care. 2009. 15:593–601.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics and Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Medical Insurance Coverage for Diabetes Education
- Costs of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- An Analysis of Medical Costs of Diabetic Patients in a University Hospital (1996~2005)
- Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetic Patients in the Tertiary Hospital