A Proposal of New Reference System for the Standard Axial, Sagittal, Coronal Planes of Brain Based on the Serially-Sectioned Images
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. dissect@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Department of Electrical Engineering, Seoul National University College of Engineering, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Graduate School of Advanced Imaging Science, Multimedia & Film, Chungang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Neuroscience Research Institute, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713844
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.135
Abstract
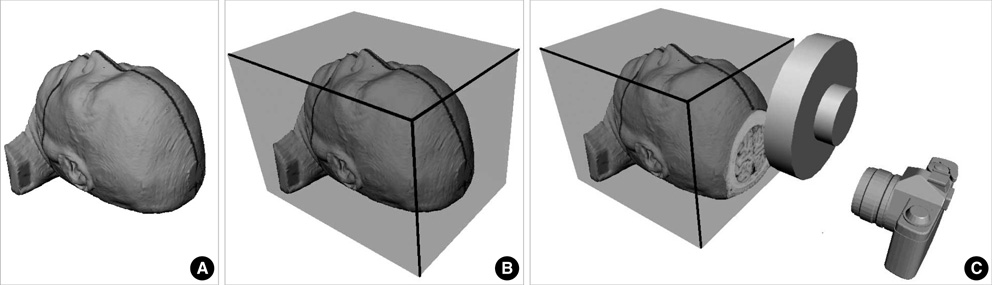
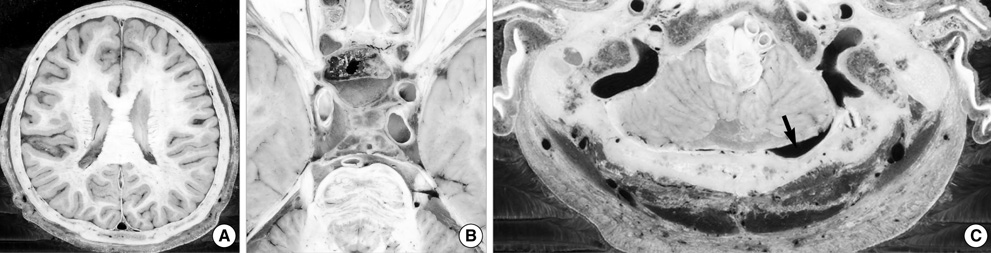
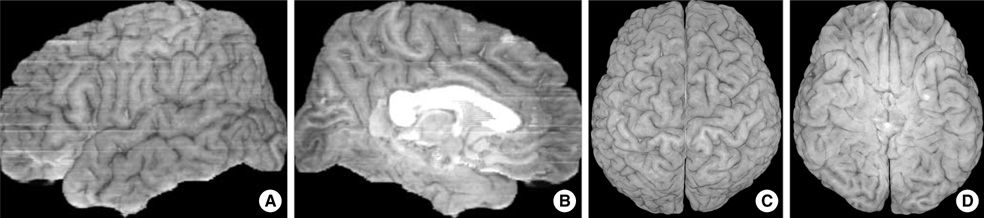
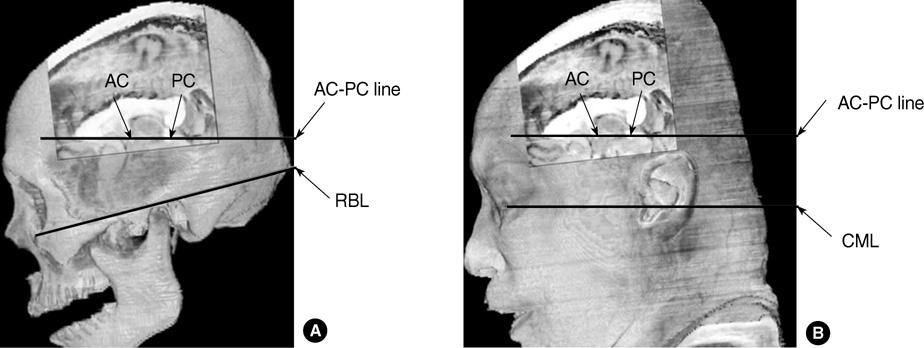
- Sectional anatomy of human brain is useful to examine the diseased brain as well as normal brain. However, intracerebral reference points for the axial, sagittal, and coronal planes of brain have not been standardized in anatomical sections or radiological images. We made 2,343 serially-sectioned images of a cadaver head with 0.1 mm intervals, 0.1 mm pixel size, and 48 bit color and obtained axial, sagittal, and coronal images based on the proposed reference system. This reference system consists of one principal reference point and two ancillary reference points. The two ancillary reference points are the anterior commissure and the posterior commissure. And the principal reference point is the midpoint of two ancillary reference points. It resides in the center of whole brain. From the principal reference point, Cartesian coordinate of x, y, z could be made to be the standard axial, sagittal, and coronal planes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Segmentation of Cerebral Gyri in the Sectioned Images by Referring to Volume Model
Jin Seo Park, Min Suk Chung, Je-Geun Chi, Hyo Seok Park, Dong Sun Shin
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(12):1710-1715. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1710.Advanced Sectioned Images of a Cadaver Head with Voxel Size of 0.04 mm
Beom Sun Chung, Miran Han, Donghwan Har, Jin Seo Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(34):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e218.Rise of the Visible Monkey: Sectioned Images of Rhesus Monkey
Beom Sun Chung, Chang-Yeop Jeon, Jae-Won Huh, Kang-Jin Jeong, Donghwan Har, Kyu-Sung Kwack, Jin Seo Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(8):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e66.Anterior Commissure - Posterior Commissure Revisited
Sang-Han Choi, Je-Geun Chi, Young-Bo Kim, Zang-Hee Cho
Korean J Radiol. 2013;14(4):653-661. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.653.
Reference
-
1. Staubesand J. Sobotta Atlas of Human Anatomy. 1990. Vol l. Baltimore-Munich: Urban & Schwarzenberg.2. Rohen JW, Yokochi C. Color Atlas of Anatomy. 1998. 2nd ed. New York: Igaku-Shoin.3. Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2006. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.4. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH, Park HS. Visible Korean Human: Improved serially sectioned images of the whole body. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005. 24:352–360.5. Park JS, Jung Y-W, Lee JW, Shin DS, Chung MS, Riemer M, Handels H. Generating useful images for medical applications from the Visible Korean Human. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008. 92:257–266.
Article6. Spitzer VM, Ackerman MJ, Scherzinger AL, Whitlock D. The Visible Human male: a technical report. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1996. 3:118–130.
Article7. Zhang SX, Heng PA, Liu ZJ. Chinese visible human project. Clin Anat. 2006. 19:204–215.
Article8. Yuan Y, Qi L, Luo S. The reconstruction and application of virtual Chinese human female. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008. 92:249–256.
Article9. Dimitrova A, Weber J, Redies C, Kindsvater K, Maschke M, Kolb FP, Forsting M, Diener HC, Timmann D. MRI atlas of the human cerebellar nuclei. Neuroimage. 2002. 17:240–255.
Article10. Sandor T, Tieman J, Ong HT, Moss MB, Jolesz F, Albert M. Comparison of the precision of two standardized co-ordinate systems for the quantitation of brain anatomy: preliminary results. Neuroradiology. 1994. 36:499–503.
Article11. Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W. Atlas of Stereotaxy of the Human Brain. 1977. 2nd ed. Stuttgart: Thieme.12. Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain: 3-Dimensional Proportional System: An Approach to Cerebral Imaging. 1988. Stuttgart: Thieme.13. Nowinski WL. Modified Talairach landmarks. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001. 143:1045–1057.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serially Sectioned and Segmented Images of the Mouse for Learning Mouse Anatomy
- A Novel Human Brainstem Map Based on True-Color Sectioned Images
- Manufacture of the Serially Sectioned Images of the Whole Body (Third Report: Methods for Manufacture of the Segmented Images, Coronal Segmented Images, and Sagittal Segmented Images)
- Manufacture of the Serially Sectioned Images of the Whole Body (First Report: Methods for Embedding and Serial Sectioning)
- MR Imaging in Meniscal Injury of Knee Joint : ROC Analysis of Diagnositic Performance According to Imaging Planes and Window Widths