J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Feb;22(1):70-73. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.70.
Clinical Experience of an Iontophoresis Based Glucose Measuring System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. kimys@khmc.or.kr
- 2Research Institute of Endocrinology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713232
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.70
Abstract
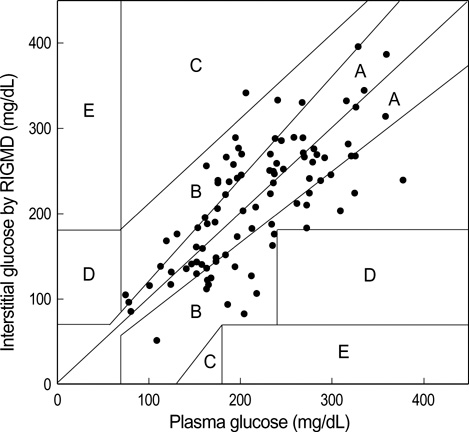
- Currently finger pricking is the common method of blood glucose measurement in patients with diabetes mellitus. However, diabetes patients have proven to be reluctant to check their glucose profiles regularly because of the discomfort associated with this technique. Recently, a non-invasive and continuous Reverse Iontophoresis based Glucose Monitoring Device (RIGMD) was developed in Korea. The study was conducted during the period November 2003-January 2004 on 19 in-patients. Glucose measurements were performed using RIGMD between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Concurrent plasma glucose levels were checked hourly and subsequently compared with RIGMD data. The mean error of RIGMD measurements was -3.45+/-52.99 mg/dL with a mean absolute relative error of 20+/-15.16%. Measurements obtained by RIGMD were correlated with plasma glucose levels (correlation coefficient; 0.784 (p<0.05)) and this correlation was independent of time of data collection. However, after excluding confounding variables this correlation coefficient exhibited a tendency to increase. 98.9% of the results were clinically acceptable by Clarke error grid analysis. We concluded that RIGMD does not have the reliability and accuracy required to wholly replace conventional methods. However, further technical advancements that reduce its shortcomings would make this device useful for the management of diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Artificial Pancreas: A Concise Review
Sang Youl Rhee, Seoung Woo Han, Jeong-Taek Woo
J Korean Diabetes. 2017;18(3):141-149. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2017.18.3.141.
Reference
-
1. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.2. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. UKPDS 34. Lancet. 1998. 352:854–865.3. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. UKPDS 33. Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.4. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:S33–S50.5. Harris MI. Health care and health status and outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:754–758.
Article6. Rhee SY, Kim YS, Oh S, Choi WH, Park JE, Jeong WJ. Diabcare Asia 2001-Korea: Country report on outcome data and analysis. Korean J Intern Med. 2005. 20:48–54.7. Rao G, Guy RH, Glikfeld P, LaCourse WR, Leung L, Tamada J, Potts RO, Azimi N. Reverse iontophoresis: Noninvasive glucose monitoring in vivo in humans. Pharm Res. 1995. 12:1869–1873.8. Tamada JA, Bohannon NJ, Potts RO. Measurement of glucose in diabetic subjects using noninvasive transdermal extraction. Nat Med. 1995. 1:1198–1201.
Article9. Clarke WL, Cox D, Gonder-Frederick LA, Carter W, Pohl SL. Evaluating clinical accuracy of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care. 1987. 10:622–628.
Article10. Rao G, Glikfeld P, Guy RH. Reverse iontophoresis: Development of a noninvasive approach for glucose monitoring. Pharm Res. 1993. 10:1751–1755.11. Garg SK, Potts RO, Ackerman NR, Fermi SJ, Tamada JA, Chase HP. Correlation of fingerstick blood glucose measurements with Glucowatch biographer glucose results in young subjects with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:1708–1714.
Article12. Tamada JA, Garg S, Jovanovic L, Pitzer KR, Fermi S, Potts RO. Noninvasive glucose monitoring: Comprehensive clinical results. Cygnus research team. JAMA. 1999. 282:1839–1844.13. Tierney MJ, Garg S, Ackerman NR, Fermi SJ, Kennedy J, Lopatin M. Effect of acetaminophen on the accuracy of glucose measurements obtained with the Glucowatch biographer. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2000. 2:199–207.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Experience of the Reverse Iontophoresis Based Glucose Measuring System: Glucall(TM)
- Clinical Experience of the Reverse Iontopheresis Based Glucose Measuring System: GlucallTM
- Dermatological Applications of Iontophoresis
- Treatment of idiopathic hyperhidrosis by iontophoresis
- Treatment of musculoskeletal diseases by iontophoresis