Lab Anim Res.
2014 Jun;30(2):90-93. 10.5625/lar.2014.30.2.90.
No expression of porcine endogenous retrovirus after pig to monkey xenotransplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Institute of Animal Science, Suwon, Korea. imseoki@rda.go.kr
- 2Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Orient Genia Inc., Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1707449
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2014.30.2.90
Abstract
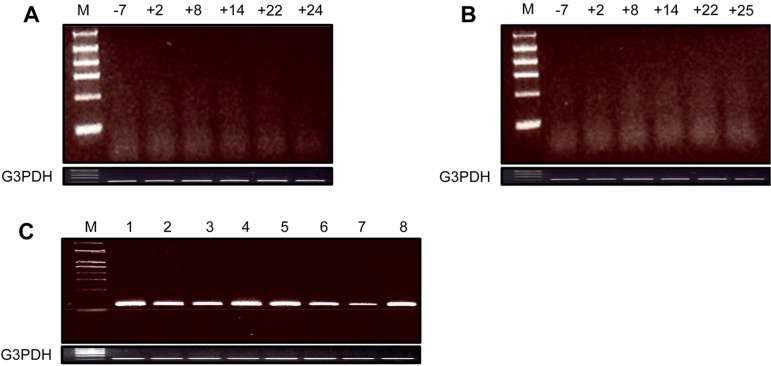
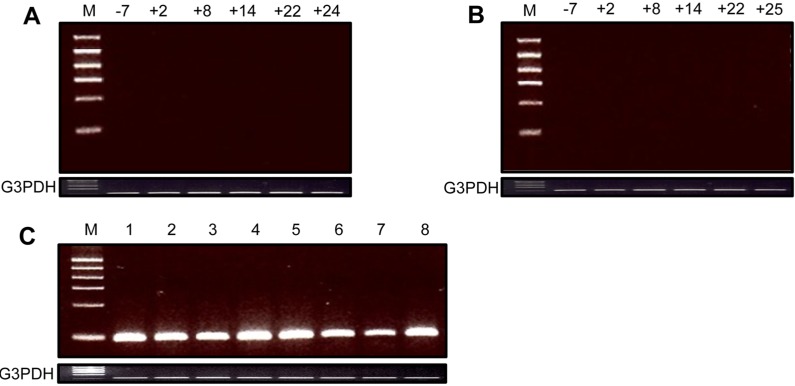
- This study was performed to investigate the expression of two porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) elements, PERV gag and full-length conserved PERV, in blood cells collected periodically from organ-recipient monkeys that underwent pig to non-human primate xenotransplantation. The heart and kidney-respectively acquired from alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase knockout (GT-KO) pigs that survived for24 and 25 days-were xenografted into cynomolgus monkeys. The two PERV elements expressed in the xenografted GT-KO pig organs were not present in the blood cells of the recipient monkeys. In the present study, we deduced that PERVs are not transmitted during GT-KO pig to monkey xenotransplantation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Status of Solid Organ Xenotransplantation
Ik Jin Yun
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2016;30(2):69-76. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.2.69.
Reference
-
1. van der Windt DJ, Bottino R, Kumar G, Wijkstrom M, Hara H, Ezzelarab M, Ekser B, Phelps C, Murase N, Casu A, Ayares D, Lakkis FG, Trucco M, Cooper DK. Clinical islet xenotransplantation: how close are we? Diabetes. 2012; 61(12):3046–3055. PMID: 23172951.2. Dieckhoff B, Petersen B, Kues WA, Kurth R, Niemann H, Denner J. Knockdown of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) expression by PERV-specific shRNA in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation. 2008; 15(1):36–45. PMID: 18333912.
Article3. Hwang S, Oh KB, Kim DH, Woo JS, Shim H, Yun IJ, Park JK, Im GS. Production of α1,3-galactosyltransferase (GalT) double knock-out (-/-) transgenic pigs for xenotransplantation. Korean J Embryo Transf. 2012; 27(1):9–14.4. Irgang M, Sauer IM, Karlas A, Zeilinger K, Gerlach JC, Kurth R, Neuhaus P, Denner J. Porcine endogenous retroviruses: no infection in patients treated with a bioreactor based on porcine liver cells. J Clin Virol. 2003; 28(2):141–154. PMID: 12957184.
Article5. Karlas A, Irgang M, Votteler J, Specke V, Ozel M, Kurth R, Denner J. Characterisation of a human cell-adapted porcine endogenous retrovirus PERV-A/C. Ann Transplant. 2010; 15(2):45–54. PMID: 20657519.6. Kim H, Chee HK, Yang J, Hwang S, Han KH, Kang J, Park JH, Kim JS, Lee SJ, Ock SA, Park MH, Park KS, Byeongchun L, Cho K, Noh J, Park W, Yun IJ, Ahn C. Outcomes of alpha 1,3-GT-knockout porcine heart transplants into a preclinical nonhuman primate model. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45(8):3085–3091. PMID: 24157041.
Article7. Moon HJ, Kim HK, Park SJ, Lee CS, Song DS, Kang BK, Park BK. Comparison of the age-related porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV)expression using duplex RT-PCR. J Vet Sci. 2009; 10(4):317–322. PMID: 19934597.8. Paradis K, Langford G, Long Z, Heneine W, Sandstrom P, Switzer WM, Chapman LE, Lockey C, Onions D, Otto E. The XEN 111 Study Group. Search for cross-species transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus in patients treated with living pig tissue. Science. 1999; 285(5431):1236–1241. PMID: 10455044.
Article9. Quinn G, Wood J, Suling K, Arn S, Sachs DH, Schuurman HJ, Patience C. Genotyping of porcine endogenous retroviruses from a family of miniature swine. J Virol. 2004; 78(1):314–319. PMID: 14671113.
Article10. Ritzhaupt A, Van Der Laan LJ, Salomon DR, Wilson CA. Porcine endogenous retrovirus infects but does not replicate in nonhuman primate primary cells and cell lines. J Virol. 2002; 76(22):11312–11320. PMID: 12388691.
Article11. Wilson CA. Porcine endogenous retroviruses and xenotransplantation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008; 65(21):3399–3412. PMID: 18818871.12. Wood JC, Quinn G, Suling KM, Oldmixon BA, Van Tine BA, Cina R, Arn S, Huang CA, Scobie L, Onions DE, Sachs DH, Schuurman HJ, Fishman JA, Patience C. Identification of exogenous forms of human-tropic porcine endogenous retrovirus in miniature Swine. J Virol. 2004; 78(5):2494–2501. PMID: 14963150.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the age-related porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) expression using duplex RT-PCR
- Analysis of env Subtypes of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus in SNU Miniature Pigs
- Construction of the Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus Envelope Glycoprotein A and B Specific Antibody
- No Evidence of the Productive Replication of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus (PERV) from SNU Miniature Pigs in Human Cell Line
- Analysis of swine leukocyte antigen class I gene profiles and porcine endogenous retrovirus viremia level in a transgenic porcine herd inbred for xenotransplantation research