J Vet Sci.
2013 Jun;14(2):215-222. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.2.215.
Effects of one-time and two-time intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid sodium salt after joint surgery in dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Animal Bone and Joint Research Laboratory, Department of Veterinary Biosciences and Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai 50100, Thailand. korakot.n@cmu.ac.th
- 2Materials Science Research Center, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai 50200, Thailand.
- 3Metta Pet Hospital, Chiang Mai 50000, Thailand.
- KMID: 1705524
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.2.215
Abstract
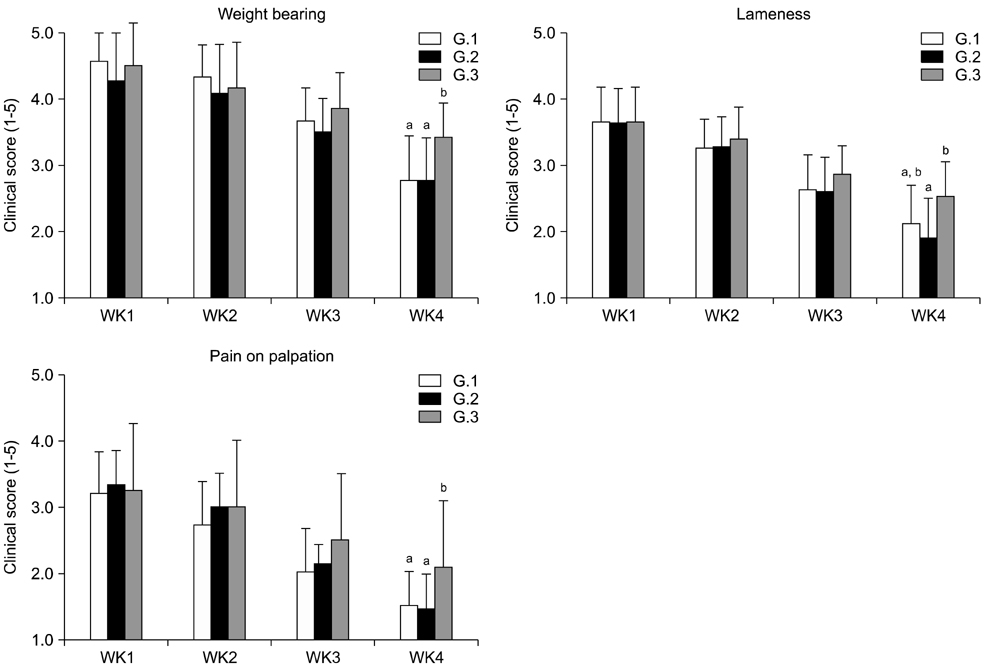
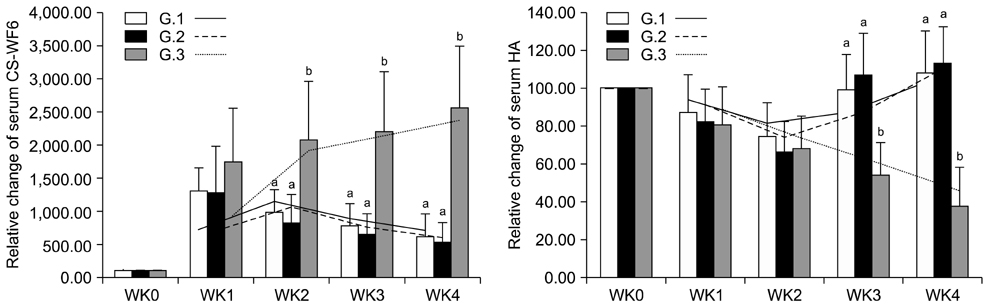
- Thirty-one dogs with patellar luxation (grades 2 and 3) were categorized into three groups. Group 1 (G.1; n = 12) had sodium hyaluronate (SHA) intra-articularly injected into the stifle joint that received surgery. Group 2 (G.2; n = 10) received SHA twice: first after surgery and then 1 week later. Group 3 (G.3; n = 9) served as a control, without injection. Blood was collected before injection and then once a week for 4 weeks after injection for evaluation of chondroitin sulfate (CS-WF6) and hyaluronan (HA). The results revealed significantly (p < 0.05) improved clinical scores by the end of week 4 in G.1 and G.2 relative to G.3; however, there was no significant difference between G.1 and G.2. There was a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in serum CS-WF6 levels beginning at week 2 in G.1 and G.2. At weeks 3 and 4, serum HA in G.1 and G.2 differed from that in G.3 (p < 0.05). No significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed in serum biomarkers between G.1 and G.2. In conclusion, intra-articular injection with SHA after joint surgery may improve homeostasis of the joint, retarding the process of OA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blood Chemical Analysis/veterinary
Chondroitin Sulfates/metabolism
*Dogs
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/veterinary
Female
Hyaluronic Acid/*administration & dosage/metabolism
Injections, Intra-Articular/veterinary
Male
Osteoarthritis, Knee/drug therapy/prevention & control/*veterinary
Stifle/*surgery
Viscosupplements/*administration & dosage
Chondroitin Sulfates
Hyaluronic Acid
Viscosupplements
Figure
Reference
-
1. Altman RD, Moskowitz R. Hyalgan Study Group. Intraarticular sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:2203–2212.2. Berenbaum F, Grifka J, Cazzaniga S, D'Amato M, Giacovelli G, Chevalier X, Rannou F, Rovati LC, Maheu E. A randomised, double-blind, controlled trial comparing two intra-articular hyaluronic acid preparations differing by their molecular weight in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:1454–1460.
Article3. Budsberg SC, Lenz ME, Thonar EJA. Serum and synovial fluid concentrations of keratan sulfate and hyaluronan in dogs with induced stifle joint osteoarthritis following cranial cruciate ligament transection. Am J Vet Res. 2006; 67:429–432.
Article4. Canapp SO, Cross AR, Brown MP, Lewis DD, Hernandez J, Merritt KA, Tran-Son-Tay R. Examination of synovial fluid and serum following intravenous injections of hyaluronan for the treatment of osteoarthritis in dogs. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2005; 18:169–174.
Article5. Coleman PJ, Scott D, Mason RM, Levick JR. Role of hyaluronan chain length in buffering interstitial flow across synovium in rabbits. J Physiol. 2000; 526:425–434.
Article6. Decaria JE, Montero-Odasso M, Wolfe D, Chesworth BM, Petrella RJ. The effect of intra-articular hyaluronic acid treatment on gait velocity in older knee osteoarthritis patients: A randomized, controlled study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012; 55:310–315.
Article7. DeGroot H 3rd, Uzunishvili S, Weir R, Al-omari A, Gomes B. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid is not superior to saline solution injection for ankle arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:2–8.
Article8. Echigo R, Mochizuki M, Nishimura R, Sasaki N. Suppressive effect of hyaluronan on chondrocyte apoptosis in experimentally induced acute osteoarthritis in dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 2006; 68:899–902.
Article9. Foti C, Cisari C, Carda S, Giordan N, Rocco A, Frizziero A, Della Bella G. A prospective observational study of the clinical efficacy and safety of intra-articular sodium hyaluronate in synovial joints with osteoarthritis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2011; 47:407–415.10. Fuller CJ, Barr AR, Sharif M, Dieppe PA. Cross-sectional comparison of synovial fluid biochemical markers in equine osteoarthritis and the correlation of these markers with articular cartilage damage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001; 9:49–55.
Article11. Ghosh P, Guidolin D. Potential mechanism of action of intra-articular hyaluronan therapy in osteoarthritis: are the effects molecular weight dependent? Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 32:10–37.
Article12. Girish KS, Kemparaju K, Nagaraju S, Vishwanath BS. Hyaluronidase inhibitors: a biological and therapeutic perspective. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16:2261–2288.
Article13. Hellström LE, Carlsson C, Boucher JF, Michanek P. Intra-articular injections with high molecular weight sodium hyaluronate as a therapy for canine arthritis. Vet Rec. 2003; 153:89–90.
Article14. Huang TL, Chang CC, Lee CH, Chen SC, Lai CH, Tsai CL. Intra-articular injections of sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan®) in osteoarthritis of the knee. a randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial in the Asian population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011; 12:221.
Article15. Jazrawi LM, Rosen J. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid: potential treatment of younger patients with knee injury and/or post-traumatic arthritis. Phys Sportsmed. 2011; 39:107–113.
Article16. Kolarz G, Kotz R, Hochmayer I. Long-term benefits and repeated treatment cycles of intra-articular sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 32:310–319.
Article17. Kuroki K, Cook JL, Kreeger JM. Mechanisms of action and potential uses of hyaluronan in dogs with osteoarthritis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2002; 221:944–950.
Article18. Marshall KW, Manolopoulos V, Mancer K, Staples J, Damyanovich A. Amelioration of disease severity by intraarticular hylan therapy in bilateral canine osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2000; 18:416–425.
Article19. Moore AR, Willoughby DA. Hyaluronan as a drug delivery system for diclofenac: a hypothesis for mode of action. Int J Tissue React. 1995; 17:153–156.20. Moreland LW. Intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis: mechanisms of action. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5:54–67.21. Nganvongpanit K, Pothacharoen P, Chaochird P, Klunklin K, Warrit K, Settakorn J, Pattamapaspong N, Luevitoonvechkij S, Arpornchayanon O, Kongtawelert P, Pruksakorn D. Prospective evaluation of serum biomarker levels and cartilage repair by autologous chondrocyte transplantation and subchondral drilling in a canine model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:R78.
Article22. Ozturk C, Atamaz F, Hepguler S, Argin M, Arkun R. The safety and efficacy of intraarticular hyaluronan with/without corticosteroid in knee osteoarthritis: 1-year, single-blind, randomized study. Rheumatol Int. 2006; 26:314–319.
Article23. de la Peña E, Sala S, Rovira JC, Schmidt RF, Belmonte C. Elastoviscous substances with analgesic effects on joint pain reduce stretch-activated ion channel activity in vitro. Pain. 2002; 99:501–508.
Article24. Plickert HD, Bondzio A, Einspanier R, Tichy A, Brunnberg L. Hyaluronic acid concentrations in synovial fluid of dogs with different stages of osteoarthritis. Res Vet Sci. 2013; 94:728–734.
Article25. Pothacharoen P, Teekachunhatean S, Louthrenoo W, Yingsung W, Ong-Chai S, Hardingham T, Kongtawelert P. Raised chondroitin sulfate epitopes and hyaluronan in serum from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14:299–301.
Article26. Pozo MA, Balazs EA, Belmonte C. Reduction of sensory responses to passive movements of inflamed knee joints by hylan, a hyaluronan derivative. Exp Brain Res. 1997; 116:3–9.
Article27. Pruksakorn D, Rojanasthien S, Pothacharoen P, Luevitoonvechkij S, Wongtreratanachai P, Ong-Chai S, Kongtawelert P. Chondroitin sulfate epitope (WF6) and hyaluronic acid as serum markers of cartilage degeneration in patients following anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Sci Med Sport. 2009; 12:445–448.
Article28. Pullman-Mooar S, Mooar P, Sieck M, Clayburne G, Schumacher HR. Are there distinctive inflammatory flares after hylan g-f 20 intraarticular injections. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:2611–2614.29. Sakugawa H, Nakayoshi T, Kobashigawa K, Yamashiro T, Maeshiro T, Miyagi S, Shiroma J, Toyama A, Nakayoshi T, Kinjo F, Saito A. Clinical usefulness of biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:255–259.
Article30. Smith GN Jr, Mickler EA, Myers SL, Brandt KD. Effect of intraarticular hyaluronan injection on synovial fluid hyaluronan in the early stage of canine post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:1341–1346.31. Smith MM, Ghosh P. The synthesis of hyaluronic acid by human synovial fibroblasts is influenced by the nature of the hyaluronate in the extracellular environment. Rheumatol Int. 1987; 7:113–122.
Article32. Sun SF, Hsu CW, Sun HP, Chou YJ, Li HJ, Wang JL. The effect of three weekly intra-articular injections of hyaluronate on pain, function, and balance in patients with unilateral ankle arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:1720–1726.
Article33. Tiderius CJ, Olsson LE, Nyquist F, Dahlberg L. Cartilage glycosaminoglycan loss in the acute phase after an anterior cruciate ligament injury: delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage and synovial fluid analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:120–127.
Article34. Wenz W, Breusch SJ, Graf J, Stratmann U. Ultrastructural findings after intraarticular application of hyaluronan in a canine model of arthropathy. J Orthop Res. 2000; 18:604–612.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Effect of sodium hyaluronate in treating temporomandibular joint disorders
- The Effect of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid and Steroid Injection in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- The Effect of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid in Facet Syndrome of the Lumbar Spine
- Efficacy of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Early Stage Ankle Osteoarthritis