Immune Netw.
2014 Feb;14(1):21-29. 10.4110/in.2014.14.1.21.
Insights into the Role of Follicular Helper T Cells in Autoimmunity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Science, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791, Korea. jeminchoi@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute for Natural Sciences, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791, Korea.
- 3Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791, Korea.
- 4Division of Vaccine Discovery, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
- KMID: 1508825
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.1.21
Abstract
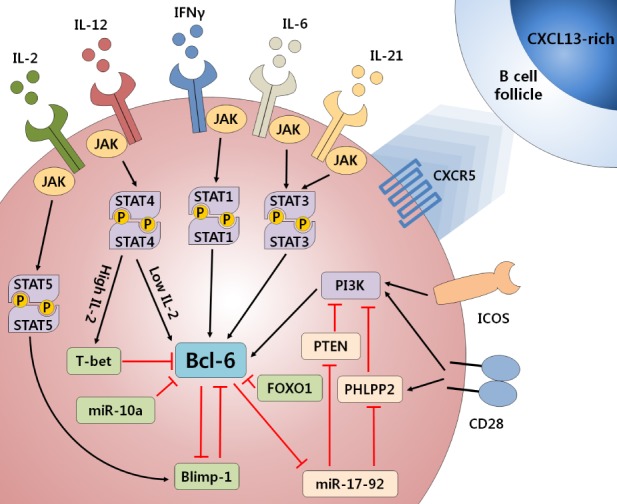
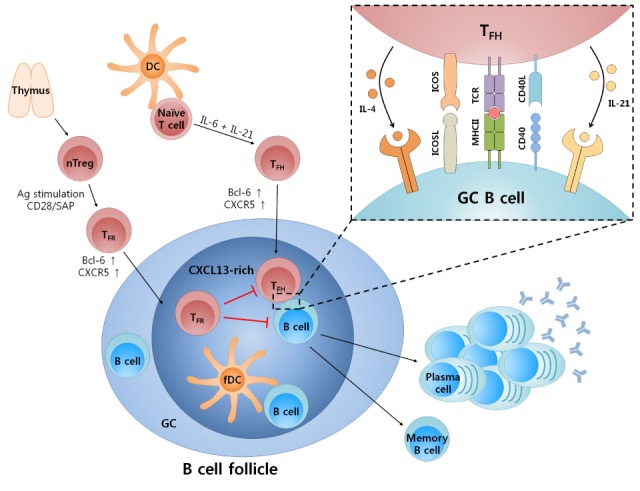
- Follicular helper T (TFH) cells are recently highlighted as their crucial role for humoral immunity to infection as well as their abnormal control to induce autoimmune disease. During an infection, naive T cells are differentiating into TFH cells which mediate memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells in germinal center (GC). TFH cells are characterized by their expression of master regulator, Bcl-6, and chemokine receptor, CXCR5, which are essential for the migration of T cells into the B cell follicle. Within the follicle, crosstalk occurs between B cells and TFH cells, leading to class switch recombination and affinity maturation. Various signaling molecules, including cytokines, surface molecules, and transcription factors are involved in TFH cell differentiation. IL-6 and IL-21 cytokine-mediated STAT signaling pathways, including STAT1 and STAT3, are crucial for inducing Bcl-6 expression and TFH cell differentiation. TFH cells express important surface molecules such as ICOS, PD-1, IL-21, BTLA, SAP and CD40L for mediating the interaction between T and B cells. Recently, two types of microRNA (miRNA) were found to be involved in the regulation of TFH cells. The miR-17-92 cluster induces Bcl-6 and TFH cell differentiation, whereas miR-10a negatively regulates Bcl-6 expression in T cells. In addition, follicular regulatory T (TFR) cells are studied as thymus-derived CXCR5+PD-1+Foxp3+ Treg cells that play a significant role in limiting the GC response. Regulation of TFH cell differentiation and the GC reaction via miRNA and TFR cells could be important regulatory mechanisms for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here, we review recent studies on the various factors that affect TFH cell differentiation, and the role of TFH cells in autoimmune diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmunity*
B-Lymphocytes
CD40 Ligand
Cell Differentiation
Cytokines
Germinal Center
Immune Tolerance
Immunity, Humoral
Interleukin-6
Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic
Memory
MicroRNAs
Negotiating
Plasma Cells
Recombination, Genetic
T-Lymphocytes
T-Lymphocytes, Helper-Inducer*
T-Lymphocytes, Regulatory
Transcription Factors
CD40 Ligand
Cytokines
Interleukin-6
MicroRNAs
Transcription Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Curcumin Elevates TFH Cells and Germinal Center B Cell Response for Antibody Production in Mice
Do-Hyun Kim, Hong-Gyun Lee, Je-Min Choi
Immune Netw. 2019;19(5):. doi: 10.4110/in.2019.19.e35.
Reference
-
1. Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, DiToro D, Yusuf I, Eto D, Barnett B, Dent AL, Craft J, Crotty S. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science. 2009; 325:1006–1010. PMID: 19608860.
Article2. Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Martinez GJ, Yang XO, Tanaka S, Matskevitch TD, Wang YH, Dong C. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science. 2009; 325:1001–1005. PMID: 19628815.
Article3. Yu D, Rao S, Tsai LM, Lee SK, He Y, Sutcliffe EL, Srivastava M, Linterman M, Zheng L, Simpson N, Ellyard JI, Parish IA, Ma CS, Li QJ, Parish CR, Mackay CR, Vinuesa CG. The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2009; 31:457–468. PMID: 19631565.
Article4. Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Hwang D, Yang XO, Kang HS, Ma L, Wang YH, Watowich SS, Jetten AM, Tian Q, Dong C. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity. 2008; 29:138–149. PMID: 18599325.
Article5. Crotty S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH). Annu Rev Immunol. 2011; 29:621–663. PMID: 21314428.
Article6. Qi H, Cannons JL, Klauschen F, Schwartzberg PL, Germain RN. SAP-controlled T-B cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature. 2008; 455:764–769. PMID: 18843362.
Article7. Dong C, Temann UA, Flavell RA. Cutting edge: critical role of inducible costimulator in germinal center reactions. J Immunol. 2001; 166:3659–3662. PMID: 11238604.
Article8. Iwai H, Abe M, Hirose S, Tsushima F, Tezuka K, Akiba H, Yagita H, Okumura K, Kohsaka H, Miyasaka N, Azuma M. Involvement of inducible costimulator-B7 homologous protein costimulatory pathway in murine lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 2003; 171:2848–2854. PMID: 12960306.
Article9. Lu KT, Kanno Y, Cannons JL, Handon R, Bible P, Elkahloun AG, Anderson SM, Wei L, Sun H, O'Shea JJ, Schwartzberg PL. Functional and epigenetic studies reveal multistep differentiation and plasticity of in vitro-generated and in vivo-derived follicular T helper cells. Immunity. 2011; 35:622–632. PMID: 22018472.10. Breitfeld D, Ohl L, Kremmer E, Ellwart J, Sallusto F, Lipp M, Förster R. Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production. J Exp Med. 2000; 192:1545–1552. PMID: 11104797.
Article11. Schaerli P, Willimann K, Lang AB, Lipp M, Loetscher P, Moser B. CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function. J Exp Med. 2000; 192:1553–1562. PMID: 11104798.
Article12. Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:540–550. PMID: 15229479.
Article13. Jacob J, Kelsoe G, Rajewsky K, Weiss U. Intraclonal generation of antibody mutants in germinal centres. Nature. 1991; 354:389–392. PMID: 1956400.
Article14. Berek C, Berger A, Apel M. Maturation of the immune response in germinal centers. Cell. 1991; 67:1121–1129. PMID: 1760840.
Article15. Liu YJ, Malisan F, de Bouteiller O, Guret C, Lebecque S, Banchereau J, Mills FC, Max EE, Martinez-Valdez H. Within germinal centers, isotype switching of immunoglobulin genes occurs after the onset of somatic mutation. Immunity. 1996; 4:241–250. PMID: 8624814.
Article16. Kang SG, Liu WH, Lu P, Jin HY, Lim HW, Shepherd J, Fremgen D, Verdin E, Oldstone MB, Qi H, Teijaro JR, Xiao C. MicroRNAs of the miR-17 approximately 92 family are critical regulators of T(FH) differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2013; 14:849–857. PMID: 23812097.17. Baumjohann D, Kageyama R, Clingan JM, Morar MM, Patel S, de Kouchkovsky D, Bannard O, Bluestone JA, Matloubian M, Ansel KM, Jeker LT. The microRNA cluster miR-17~92 promotes TFH cell differentiation and represses subset-inappropriate gene expression. Nat Immunol. 2013; 14:840–848. PMID: 23812098.18. Takahashi H, Kanno T, Nakayamada S, Hirahara K, Sciumè G, Muljo SA, Kuchen S, Casellas R, Wei L, Kanno Y, O'Shea JJ. TGF-beta and retinoic acid induce the microRNA miR-10a, which targets Bcl-6 and constrains the plasticity of helper T cells. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:587–595. PMID: 22544395.19. Vinuesa CG, Cook MC. The molecular basis of lymphoid architecture and B cell responses: implications for immunodeficiency and immunopathology. Curr Mol Med. 2001; 1:689–725. PMID: 11899257.
Article20. King C, Tangye SG, Mackay CR. T follicular helper (TFH) cells in normal and dysregulated immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008; 26:741–766. PMID: 18173374.
Article21. Chung Y, Tanaka S, Chu F, Nurieva RI, Martinez GJ, Rawal S, Wang YH, Lim H, Reynolds JM, Zhou XH, Fan HM, Liu ZM, Neelapu SS, Dong C. Follicular regulatory T cells expressing Foxp3 and Bcl-6 suppress germinal center reactions. Nat Med. 2011; 17:983–988. PMID: 21785430.
Article22. Fazilleau N, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, Rosen H, McHeyzer-Williams MG. The function of follicular helper T cells is regulated by the strength of T cell antigen receptor binding. Nat Immunol. 2009; 10:375–384. PMID: 19252493.
Article23. Chtanova T, Tangye SG, Newton R, Frank N, Hodge MR, Rolph MS, Mackay CR. T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells. J Immunol. 2004; 173:68–78. PMID: 15210760.
Article24. Choi YS, Kageyama R, Eto D, Escobar TC, Johnston RJ, Monticelli L, Lao C, Crotty S. ICOS receptor instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6. Immunity. 2011; 34:932–946. PMID: 21636296.
Article25. McAdam AJ, Chang TT, Lumelsky AF, Greenfield EA, Boussiotis VA, Duke-Cohan JS, Chernova T, Malenkovich N, Jabs C, Kuchroo VK, Ling V, Collins M, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. Mouse inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS) expression is enhanced by CD28 costimulation and regulates differentiation of CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2000; 165:5035–5040. PMID: 11046032.26. Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC, Eljaschewitsch B, Kraft R, Anagnostopoulos I, Kroczek RA. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature. 1999; 397:263–266. PMID: 9930702.
Article27. Vogelzang A, McGuire HM, Yu D, Sprent J, Mackay CR, King C. A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity. 2008; 29:127–137. PMID: 18602282.
Article28. Gigoux M, Shang J, Pak Y, Xu M, Choe J, Mak TW, Suh WK. Inducible costimulator promotes helper T-cell differentiation through phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:20371–20376. PMID: 19915142.
Article29. Xu H, Li X, Liu D, Li J, Zhang X, Chen X, Hou S, Peng L, Xu C, Liu W, Zhang L, Qi H. Follicular T-helper cell recruitment governed by bystander B cells and ICOS-driven motility. Nature. 2013; 496:523–527. PMID: 23619696.
Article30. Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999; 96:857–868. PMID: 10102273.
Article31. Yuan TL, Cantley LC. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene. 2008; 27:5497–5510. PMID: 18794884.
Article32. Kerdiles YM, Stone EL, Beisner DR, McGargill MA, Ch'en IL, Stockmann C, Katayama CD, Hedrick SM. Foxo transcription factors control regulatory T cell development and function. Immunity. 2010; 33:890–904. PMID: 21167754.
Article33. Oestreich KJ, Mohn SE, Weinmann AS. Molecular mechanisms that control the expression and activity of Bcl-6 in TH1 cells to regulate flexibility with a TFH-like gene profile. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:405–411. PMID: 22406686.
Article34. Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008; 26:57–79. PMID: 17953510.
Article35. Diehl SA, Schmidlin H, Nagasawa M, Blom B, Spits H. IL-6 Triggers IL-21 production by human CD4(+) T cells to drive STAT3-dependent plasma cell differentiation in B cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012; 90:802–811. PMID: 22491065.36. Eddahri F, Denanglaire S, Bureau F, Spolski R, Leonard WJ, Leo O, Andris F. Interleukin-6/STAT3 signaling regulates the ability of naive T cells to acquire B-cell help capacities. Blood. 2009; 113:2426–2433. PMID: 19020307.
Article37. Choi YS, Eto D, Yang JA, Lao C, Crotty S. Cutting edge: STAT1 is required for IL-6-mediated Bcl6 induction for early follicular helper cell differentiation. J Immunol. 2013; 190:3049–3053. PMID: 23447690.
Article38. Eto D, Lao C, DiToro D, Barnett B, Escobar TC, Kageyama R, Yusuf I, Crotty S. IL-21 and IL-6 are critical for different aspects of B cell immunity and redundantly induce optimal follicular helper CD4 T cell (Tfh) differentiation. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e17739. PMID: 21423809.
Article39. Poholek AC, Hansen K, Hernandez SG, Eto D, Chandele A, Weinstein JS, Dong X, Odegard JM, Kaech SM, Dent AL, Crotty S, Craft J. In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell development. J Immunol. 2010; 185:313–326. PMID: 20519643.40. Takeda K, Kaisho T, Yoshida N, Takeda J, Kishimoto T, Akira S. Stat3 activation is responsible for IL-6-dependent T cell proliferation through preventing apoptosis: generation and haracterization of T cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1998; 161:4652–4660. PMID: 9794394.41. Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L, Schluns K, Tian Q, Watowich SS, Jetten AM, Dong C. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T ells. Nature. 2007; 448:480–483. PMID: 17581589.42. Yang Y, Ochando J, Yopp A, Bromberg JS, Ding Y. IL-6 plays a unique role in initiating c-Maf expression during early stage of CD4 T cell activation. J Immunol. 2005; 174:2720–2729. PMID: 15728480.
Article43. Jang E, Cho SH, Park H, Paik DJ, Kim JM, Youn J. A positive feedback loop of IL-21 signaling provoked by homeostatic CD4+CD25- T cell expansion is essential for the development of arthritis in autoimmune K/BxN mice. J Immunol. 2009; 182:4649–4656. PMID: 19342640.44. Ozaki K, Spolski R, Ettinger R, Kim HP, Wang G, Qi CF, Hwu P, Shaffer DJ, Akilesh S, Roopenian DC, Morse HC 3rd, Lipsky PE, Leonard WJ. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J Immunol. 2004; 173:5361–5371. PMID: 15494482.
Article45. Nakayamada S, Kanno Y, Takahashi H, Jankovic D, Lu KT, Johnson TA, Sun HW, Vahedi G, Hakim O, Handon R, Schwartzberg PL, Hager GL, O'Shea JJ. Early Th1 cell differentiation is marked by a Tfh cell-like transition. Immunity. 2011; 35:919–931. PMID: 22195747.
Article46. Lee SK, Silva DG, Martin JL, Pratama A, Hu X, Chang PP, Walters G, Vinuesa CG. Interferon-gamma excess leads to pathogenic accumulation of follicular helper T cells and germinal centers. Immunity. 2012; 37:880–892. PMID: 23159227.47. Zhou G, Ono SJ. Induction of BCL-6 gene expression by interferon-gamma and identification of an IRE in exon I. Exp Mol Pathol. 2005; 78:25–35. PMID: 15596057.48. Dent AL, Shaffer AL, Yu X, Allman D, Staudt LM. Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science. 1997; 276:589–592. PMID: 9110977.
Article49. Klein U, Dalla-Favera R. Germinal centres: role in B-cell physiology and malignancy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8:22–33. PMID: 18097447.
Article50. Ye BH, Cattoretti G, Shen Q, Zhang J, Hawe N, de Waard R, Leung C, Nouri-Shirazi M, Orazi A, Chaganti RS, Rothman P, Stall AM, Pandolfi PP, Dalla-Favera R. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat Genet. 1997; 16:161–170. PMID: 9171827.
Article51. Toyama H, Okada S, Hatano M, Takahashi Y, Takeda N, Ichii H, Takemori T, Kuroda Y, Tokuhisa T. Memory B cells without somatic hypermutation are generated from Bcl6-deficient B cells. Immunity. 2002; 17:329–339. PMID: 12354385.
Article52. Crotty S, Johnston RJ, Schoenberger SP. Effectors and memories: Bcl-6 and Blimp-1 in T and B lymphocyte differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:114–120. PMID: 20084069.
Article53. Haynes NM, Allen CD, Lesley R, Ansel KM, Killeen N, Cyster JG. Role of CXCR5 and CCR7 in follicular Th cell positioning and appearance of a programmed cell death gene-1high germinal center-associated subpopulation. J Immunol. 2007; 179:5099–5108. PMID: 17911595.
Article54. Turner CA Jr, Mack DH, Davis MM. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell. 1994; 77:297–306. PMID: 8168136.
Article55. Martins G, Calame K. Regulation and functions of Blimp-1 in T and B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008; 26:133–169. PMID: 18370921.
Article56. Johnston RJ, Choi YS, Diamond JA, Yang JA, Crotty S. STAT5 is a potent negative regulator of TFH cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 2012; 209:243–250. PMID: 22271576.
Article57. Kwon H, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Kim HP, Oh J, Tunyaplin C, Carotta S, Donovan CE, Goldman ML, Tailor P, Ozato K, Levy DE, Nutt SL, Calame K, Leonard WJ. Analysis of interleukin-21-induced Prdm1 gene regulation reveals functional cooperation of STAT3 and IRF4 transcription factors. Immunity. 2009; 31:941–952. PMID: 20064451.
Article58. Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004; 22:531–562. PMID: 15032588.
Article59. Kanangat S, Blair P, Reddy R, Daheshia M, Godfrey V, Rouse BT, Wilkinson E. Disease in the scurfy (sf) mouse is associated with overexpression of cytokine genes. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26:161–165. PMID: 8566060.
Article60. Clark LB, Appleby MW, Brunkow ME, Wilkinson JE, Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F. Cellular and molecular characterization of the scurfy mouse mutant. J Immunol. 1999; 162:2546–2554. PMID: 10072494.61. Wollenberg I, Agua-Doce A, Hernández A, Almeida C, Oliveira VG, Faro J, Graca L. Regulation of the germinal center reaction by Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2011; 187:4553–4560. PMID: 21984700.62. Linterman MA, Pierson W, Lee SK, Kallies A, Kawamoto S, Rayner TF, Srivastava M, Divekar DP, Beaton L, Hogan JJ, Fagarasan S, Liston A, Smith KG, Vinuesa CG. Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells control the germinal center response. Nat Med. 2011; 17:975–982. PMID: 21785433.63. Sage PT, Francisco LM, Carman CV, Sharpe AH. The receptor PD-1 controls follicular regulatory T cells in the lymph nodes and blood. Nat Immunol. 2013; 14:152–161. PMID: 23242415.
Article64. Cobb BS, Nesterova TB, Thompson E, Hertweck A, O'Connor E, Godwin J, Wilson CB, Brockdorff N, Fisher AG, Smale ST, Merkenschlager M. T cell lineage choice and differentiation in the absence of the RNase III enzyme Dicer. J Exp Med. 2005; 201:1367–1373. PMID: 15867090.
Article65. Muljo SA, Ansel KM, Kanellopoulou C, Livingston DM, Rao A, Rajewsky K. Aberrant T cell differentiation in the absence of Dicer. J Exp Med. 2005; 202:261–269. PMID: 16009718.
Article66. Doria A, Zen M, Canova M, Bettio S, Bassi N, Nalotto L, Rampudda M, Ghirardello A, Iaccarino L. SLE diagnosis and treatment: when early is early. Autoimmun Rev. 2010; 10:55–60. PMID: 20813207.
Article67. Luzina IG, Atamas SP, Storrer CE, daSilva LC, Kelsoe G, Papadimitriou JC, Handwerger BS. Spontaneous formation of germinal centers in autoimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2001; 70:578–584. PMID: 11590194.68. Simpson N, Gatenby PA, Wilson A, Malik S, Fulcher DA, Tangye SG, Manku H, Vyse TJ, Roncador G, Huttley GA, Goodnow CC, Vinuesa CG, Cook MC. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:234–244. PMID: 20039395.
Article69. Daikh DI, Finck BK, Linsley PS, Hollenbaugh D, Wofsy D. Long-term inhibition of murine lupus by brief simultaneous blockade of the B7/CD28 and CD40/gp39 costimulation pathways. J Immunol. 1997; 159:3104–3108. PMID: 9317105.70. Vinuesa CG, Cook MC, Angelucci C, Athanasopoulos V, Rui L, Hill KM, Yu D, Domaschenz H, Whittle B, Lambe T, Roberts IS, Copley RR, Bell JI, Cornall RJ, Goodnow CC. A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature. 2005; 435:452–458. PMID: 15917799.
Article71. Linterman MA, Rigby RJ, Wong RK, Yu D, Brink R, Cannons JL, Schwartzberg PL, Cook MC, Walters GD, Vinuesa CG. Follicular helper T cells are required for systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2009; 206:561–576. PMID: 19221396.
Article72. Bubier JA, Sproule TJ, Foreman O, Spolski R, Shaffer DJ, Morse HC 3rd, Leonard WJ, Roopenian DC. A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:1518–1523. PMID: 19164519.
Article73. Dolff S, Abdulahad WH, Westra J, Doornbos-van der Meer B, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG, Bijl M. Increase in IL-21 producing T-cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13:R157. PMID: 21959034.
Article74. Wong CK, Wong PT, Tam LS, Li EK, Chen DP, Lam CW. Elevated production of B cell chemokine CXCL13 is correlated with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. J Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:45–52. PMID: 19774453.
Article75. Young DA, Hegen M, Ma HL, Whitters MJ, Albert LM, Lowe L, Senices M, Wu PW, Sibley B, Leathurby Y, Brown TP, Nickerson-Nutter C, Keith JC Jr, Collins M. Blockade of the interleukin-21/interleukin-21 receptor pathway ameliorates disease in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:1152–1163. PMID: 17393408.
Article76. Kouskoff V, Korganow AS, Duchatelle V, Degott C, Benoist C, Mathis D. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell. 1996; 87:811–822. PMID: 8945509.
Article77. Victoratos P, Kollias G. Induction of autoantibody-mediated spontaneous arthritis critically depends on follicular dendritic cells. Immunity. 2009; 30:130–142. PMID: 19119026.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Niche of Follicular Helper T Cells in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
- Germinal Center Formation Controlled by Balancing Between Follicular Helper T Cells and Follicular Regulatory T Cells
- The Role of B Cells in Transplantation Rejection
- Follicular Helper T (Tfh) Cells in Autoimmune Diseases and Allograft Rejection
- Regulatory T Cells in B Cell Follicles