J Vet Sci.
2013 Mar;14(1):7-14. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.1.7.
Quantitation of meloxicam in the plasma of koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) by improved high performance liquid chromatography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Veterinary Science, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. merran.govendir@sydney.edu.au
- 2Discipline of Pharmacology, Bosch Institute, Sydney Medical School, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia.
- KMID: 1482807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.1.7
Abstract
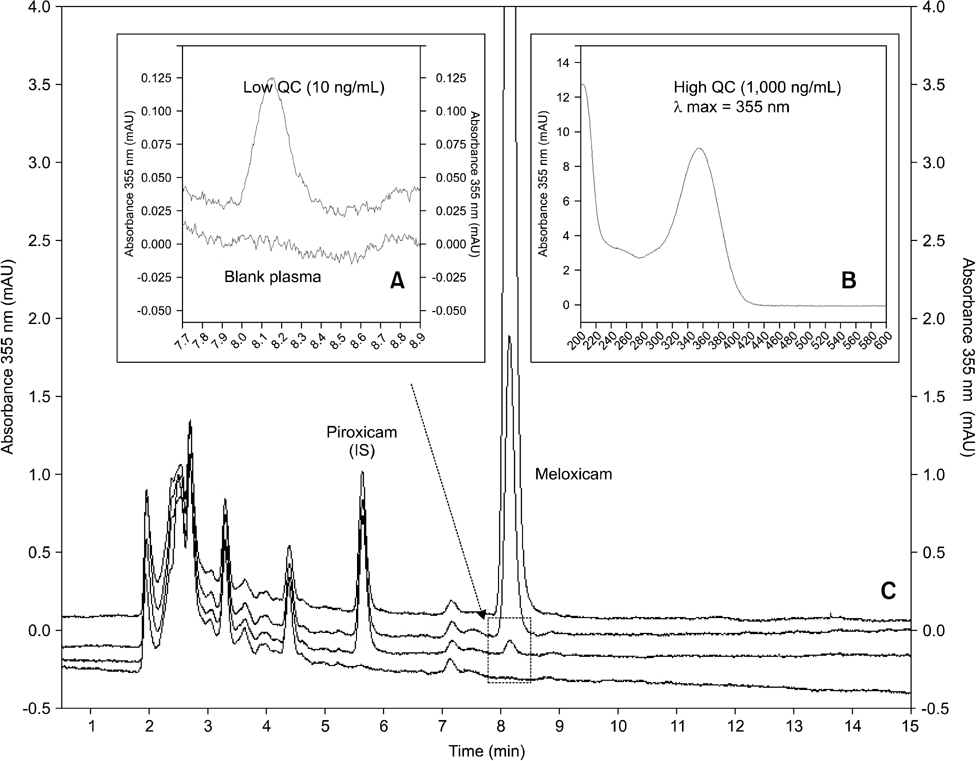
- An improved method to determine meloxicam (MEL) concentrations in koala plasma using reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography equipped with a photo diode array detector was developed and validated. A plasma sample clean-up step was carried out with hydrophilic-lipophilic copolymer solid phase extraction cartridges. MEL was separated from an endogenous interference using an isocratic mobile phase [acetonitrile and 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 2.15), 45:55 (v:v)] on a Nova-Pak C18 4-microm (300 x 3.9 mm) column. Retention times for MEL and piroxicam were 8.03 and 5.56 min, respectively. Peak area ratios of MEL to the internal standard (IS) were used for regression analysis of the calibration curve, which was linear from 10 to 1,000 ng/mL (r2 > 0.9998). Average absolute recovery rates were 91% and 96% for MEL and the IS, respectively. This method had sufficient sensitivity (lower quantitation limit of 10 ng/mL), precision, accuracy, and selectivity for routine analysis of MEL in koala plasma using 250-microL sample volumes. Our technique clearly resolved the MEL peak from the complex koala plasma matrix and accurately measured MEL concentrations in small plasma volumes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/*blood
Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid/methods/*veterinary
Molecular Structure
Phascolarctidae/*blood
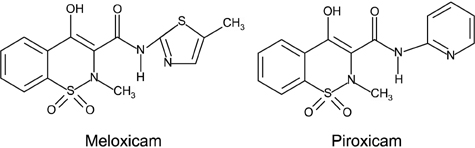
Piroxicam/chemistry
Quality Control
Reproducibility of Results
Sensitivity and Specificity
Thiazines/*blood
Thiazoles/*blood
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Thiazines
Thiazoles
Piroxicam
Figure
Reference
-
1. Altiokka G, Atkosar Z, Tuncel M. Pulse polarographic determination of meloxicam. Pharmazie. 2001. 56:184–185.2. Bae JW, Kim MJ, Jang CG, Lee SY. Determination of meloxicam in human plasma using a HPLC method with UV detection and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. 859:69–73.
Article3. Baert K, De Backer P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of three non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in five bird species. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003. 134:25–33.
Article4. Basu SK, Mandal S. Spectrophotometric methods for the estimation of meloxicam in dosage forms. Asian J Chem. 2009. 21:5184–5188.5. Bebawy LI. Stability-indicating method for the determination of meloxicam and tetracaine hydrochloride in the presence of their degradation products. Spectrosc Lett. 1998. 31:797–820.
Article6. Busch U, Schmid J, Heinzel G, Schmaus H, Baierl J, Huber C, Roth W. Pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in animals and the relevance to humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998. 26:576–584.7. Curry SL, Cogar SM, Cook JL. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: a review. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2005. 41:298–309.
Article8. Dasandi B, Shivaprakash , Saroj H, Bhat KM. LC determination and pharmacokinetics of meloxicam. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002. 28:999–1004.
Article9. European Medicines Agency. European Public Assessment Report (EPAR), Metacam, EPAR Summary for the Public. 2006. London: EMA;1–2.10. García MS, Sánchez-Pedreño C, Albero MI, Martí J. Spectrophotometric methods for determining meloxicam in pharmaceuticals using batch and flow-injection procedures. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000. 9:311–316.
Article11. Gates BJ, Nguyen TT, Setter SM, Davies NM. Meloxicam: a reappraisal of pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005. 6:2117–2140.
Article12. Griffith JE, Higgins DP, Li KM, Krockenberger MB, Govendir M. Absorption of enrofloxacin and marbofloxacin after oral and subcutaneous administration in diseased koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus). J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010. 33:595–604.
Article13. Hassan EM. Spectrophotometric and fluorimetric methods for the determination of meloxicam in dosage forms. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002. 27:771–777.
Article14. Hunter RP, Isaza R. Concepts and issues with interspecies scaling in zoological pharmacology. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2008. 39:517–526.
Article15. International Conference of Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology. 1996. 1st ed. Rockville: ICH;1–10.16. Ji HY, Lee HW, Kim YH, Jeong DW, Lee HS. Simultaneous determination of piroxicam, meloxicam and tenoxicam in human plasma by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. 826:214–219.
Article17. Joseph-Charles J, Bertucat M. Determination of meloxicam in tablet formulations by ultraviolet spectrophotometry and high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Lett. 1999. 32:2051–2059.
Article18. Kimble B, Black L, Gilchrist S, Gillett A, Jobbins S, Li K, Govendir M. Plasma pharmacokinetics of meloxicam after oral, subcutaneous and intravenous administration in the koala. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2012. 35:Suppl 3. 72–73.19. Kirchgessner MS. Meloxicam. J Exot Pet Med. 2006. 15:281–283.
Article20. Li KM, Rivory LP, Clarke SJ. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) techniques for sample preparation in clinical and pharmaceutical analysis: a brief overview. Curr Pharm Anal. 2006. 2:95–102.
Article21. Li KM, Thompson MR, McGregor IS. Rapid quantitation of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in serum by micro-disc solid-phase extraction with high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet absorbance detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004. 804:319–326.
Article22. Luger P, Daneck K, Engel W, Trummlitz G, Wagner K. Structure and physicochemical properties of meloxicam, a new NSAID. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1996. 4:175–187.
Article23. Naidoo V, Wolter K, Cromarty AD, Bartels P, Bekker L, McGaw L, Taggart MA, Cuthbert R, Swan GE. The pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in vultures. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2008. 31:128–134.
Article24. Nemutlu E, Kir S. Method development and validation for the analysis of meloxicam in tablets by CZE. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003. 31:393–400.
Article25. Ouarezki R, Guermouche MH. Liquid chromatographic determination of meloxicam in serum after solid phase extraction. Chem Pap. 2010. 64:429–433.
Article26. Pye GW. Shoulder dysplasia in koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) at San Diego Zoo. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2009. 40:453–457.27. Schattenkirchner M. Meloxicam: a selective COX-2 inhibitor non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1997. 6:321–334.28. Shukla M, Singh G, Sindhura BG, Telang AG, Rao GS, Malik JK. Comparative plasma pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in sheep and goats following intravenous administration. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007. 145:528–532.
Article29. Starek M, Krzek J. A review of analytical techniques for determination of oxicams, nimesulide and nabumetone. Talanta. 2009. 77:925–942.
Article30. Stupans I, Jones B, McKinnon RA. Xenobiotic metabolism in Australian marsupials. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2001. 128:367–376.
Article31. Toutain PL, Reymond N, Laroute V, Garcia P, Popot MA, Bonnaire Y, Hirsch A, Narbe R. Pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in plasma and urine of horses. Am J Vet Res. 2004. 65:1542–1547.
Article32. Tsai RS, Carrupt PA, Tayar NE, Giroud Y, Andrade P, Testa B, Brée F, Tillement JP. Physicochemical and structural properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oxicams. Helv Chim Acta. 1993. 76:842–854.
Article33. Velpandian T, Jaiswal J, Bhardwaj RK, Gupta SK. Development and validation of a new high-performance liquid chromatographic estimation method of meloxicam in biological samples. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000. 738:431–436.
Article34. Vignaduzzo SE, Castellano PM, Kaufman TS. Method development and validation for the simultaneous determination of meloxicam and pridinol mesylate using RP-HPLC and its application in drug formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008. 46:219–225.
Article35. Wang CY, Wang ZX, Guan J, Hu XY. Voltametric determination of meloxicam in pharmaceutical formulation and human serum at glassy carbon electrode modified by cysteic acid formed by electrochemical oxidation of L-cysteine. Sensors. 2006. 6:1139–1152.
Article36. White NA, Kunst ND. Lee AK, Handasyde KA, Sanson GD, editors. Aspects of the ecology of the koala in south eastern Queensland. Biology of the Koala. 1991. Sydney: Surrey Beatty in Association with World Koala Research Corporation;109–116.37. Wiesner JL, de Jager AD, Sutherland FCW, Hundt HKL, Swart KJ, Hundt AF, Els J. Sensitive and rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of meloxicam in human plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003. 785:115–121.
Article38. Yuan Y, Chen X, Zhong D. Determination of meloxicam in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry following transdermal administration. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. 852:650–654.
Article39. Zawilla NH, Abdul-Azim Mohammad M, El kousy NM, El-Moghazy Aly SM. Determination of meloxicam in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003. 32:1135–1144.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circadian variation of plasma histamine in healthy volunteers measured by high-performance liquid chromatography
- A Simple and Sensitive Assay for Cefepime in Human Plasma Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Efficient Isolation of Dihydrophaseic acid 3′-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside from Nelumbo nucifera Seeds Using High-performance Countercurrent Chromatography and Reverse-phased High-performance Liquid Chromatography
- Comparison of High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Total Homocysteine in Human Plasma
- Simultaneous Determination of Glutamate, Glycine, and Alanine in Human Plasma Using Precolumn Derivatization with 6-Aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography