J Korean Fract Soc.
2009 Oct;22(4):246-251. 10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.246.
The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. cyh143@freechal.com
- KMID: 1469990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.246
Abstract
- PURPOSE
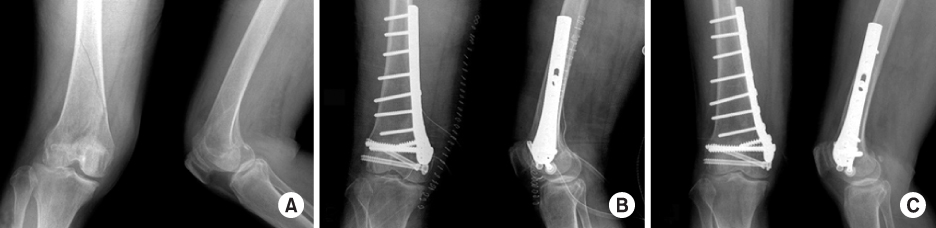
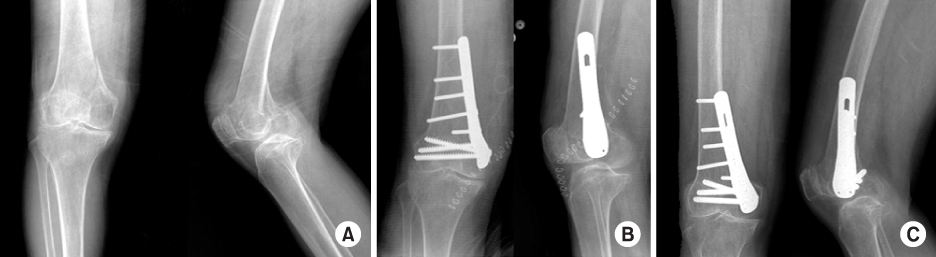
To evaluate clinical and radiological results of surgical treatment of distal femur medial condyle fracture using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study reviewed the results of 9 cases of distal femur medial condyle fracture treated with lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach from December 2005 to June 2007, after a follow up of more than 12 months. There were 2 males and 7 females with a mean age of 63.1 (57~72) years. The clinical results were evaluated using the Schatzker's criteria, and the radiographic results were evaluated using the bone union time. RESULTS: Using the Schatzker's criteria, 7 cases of the 9 patients (78%) showed exellent results. The mean time for bone union was 13.4 (11~15) weeks. There were 3 cases of pain on full weight bearing same as previous operative state by degenerative osteoarthritis. There weren't complications as joint stiffness, infection, varus & rotational deformity, malunion, nonunion, and metal failure. CONCLUSION: Plate fixation using medial approach provides the proper anatomical reduction and stronger fixation, and outcome good results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
Se-Ang Jang, Young-Soo Byun, In-Ho Han, Dongju Shin
J Korean Fract Soc. 2016;29(3):206-212. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.206.
Reference
-
1. Borgen D, Sprague BL. Treatment of distal femoral fractures with early weight-bearing. A preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; 111:156–162.2. Butt MS, Krikler SJ, Ali MS. Displaced fractures of the distal femur in elderly patients. Operative versus non-operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:110–114.3. Chiron HS, Trémoulet J, Casey P, Müller M. Fractures of the distal third of the femur treated by internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974; 100:160–170.
Article4. Giles JB, DeLee JC, Heckman JD, Keever JE. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur treated with a supracondylar plate and lag screw. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982; 64:864–870.
Article5. Hahn SH, Yang BK, Yi SR, Chung SW, Lee JO. Treatment of the distal femoral fracture with anatomical bone plate. J Korean Soc Fract. 2000; 13:258–266.
Article6. Healy WL, Brooker AF Jr. Distal femoral fractures. Comparison of open and closed methods of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 174:166–171.7. Höntzsch D. Distal femoral fracture--Clinical possibilities. Kongressbd Dtsch Ges Chir Kongr. 2001; 118:371–374.8. Johnson KD, Hicken G. Distal femoral fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987; 18:115–132.
Article9. Kwon H, Kim DW, Sohn CS, et al. Metal failure after plate fixation for femur fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1997; 10:371–378.
Article10. Mize RD. Surgical management of comlex fractures of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (240):77–86.11. Moon ES, Lee KB, Jeong JW. Anatomical plate fixation for distal femur fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999; 12:294–300.
Article12. Ostermann PA, Neumann K, Ekkernkamp A, Muhr G. Long term results of unicondylar fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 1994; 8:142–146.
Article13. Ostrum RF, Geel C. Indirect reduction and internal fixation of supracondylar femur fractures without bone graft. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:278–284.
Article14. Schatzker J. Fractures of the distal femur revisited. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 347:43–56.
Article15. Schatzker J, Home G, Waddell J. The Toronto experience with the supracondylar fracture of the femur, 1966-72. Injury. 1974; 6:113–128.
Article16. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; 138:77–83.
Article17. Schatzker J, Tile M. The rationale of operative fracture care. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlg;1996. p. 395.18. Shewring DJ, Meggitt BF. Fractures of the distal femur treated with the AO dynamic condylar screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:122–125.
Article19. Siliski JM, Mahring M, Hofer HP. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur. Treatment by internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:95–114.
Article20. Stewart MJ, Sisk TD, Walace SL Jr. Fractures of the distal third of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg. 1966; 48:784–807.
Article21. Stover M. Distal femur fractures: current treatment, results and problems. Injury. 2001; 32:SC3–SC13.22. Vallier HA, Hennessey TA, Sontich JK, Patterson BM. Failure of LCP condylar plate fixation in the distal part of the femur. A report of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:846–853.
Article23. Volpin G, Dowd GS, Stein H, Bentley G. Degenerative arthritis after intra-articular fractures of the knee. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:634–638.
Article24. Yune SH, Rhee KJ, Park CH, Byun KY, Lee SY, Rho SK. Importance of maintenance medial buttress in treatment of supra-condylar and inter-condylar (T-condylar) fracture of the femur. J Korean Soc Fract. 1996; 9:567–573.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Importance of maintenance medial buttress in treatment of supra-condylar and inter-condylar(T-condylar) fracture of the femur
- Treatment of Clavicle Medial End Fracture Using Double-plate Fixation
- Effect of Additional Medial Locking Plate Fixation and Autogenous Bone Graft for Distal Femur Nonunion after Lateral Locking Plate Fixation
- Modified Lateral Approach to the Distal Humerus Fractures