Lab Anim Res.
2010 Mar;26(1):69-74. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.69.
Proteomic Analysis of Hepatic Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Research Insituite of Life Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. pokoh@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1458942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.69
Abstract
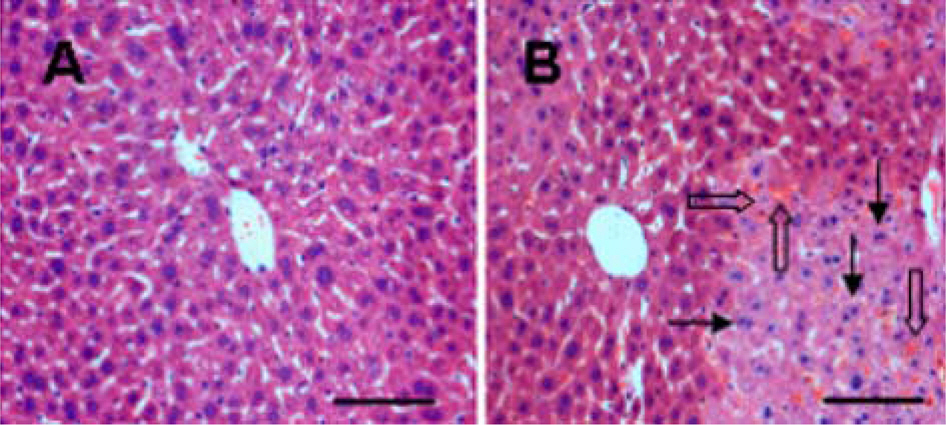
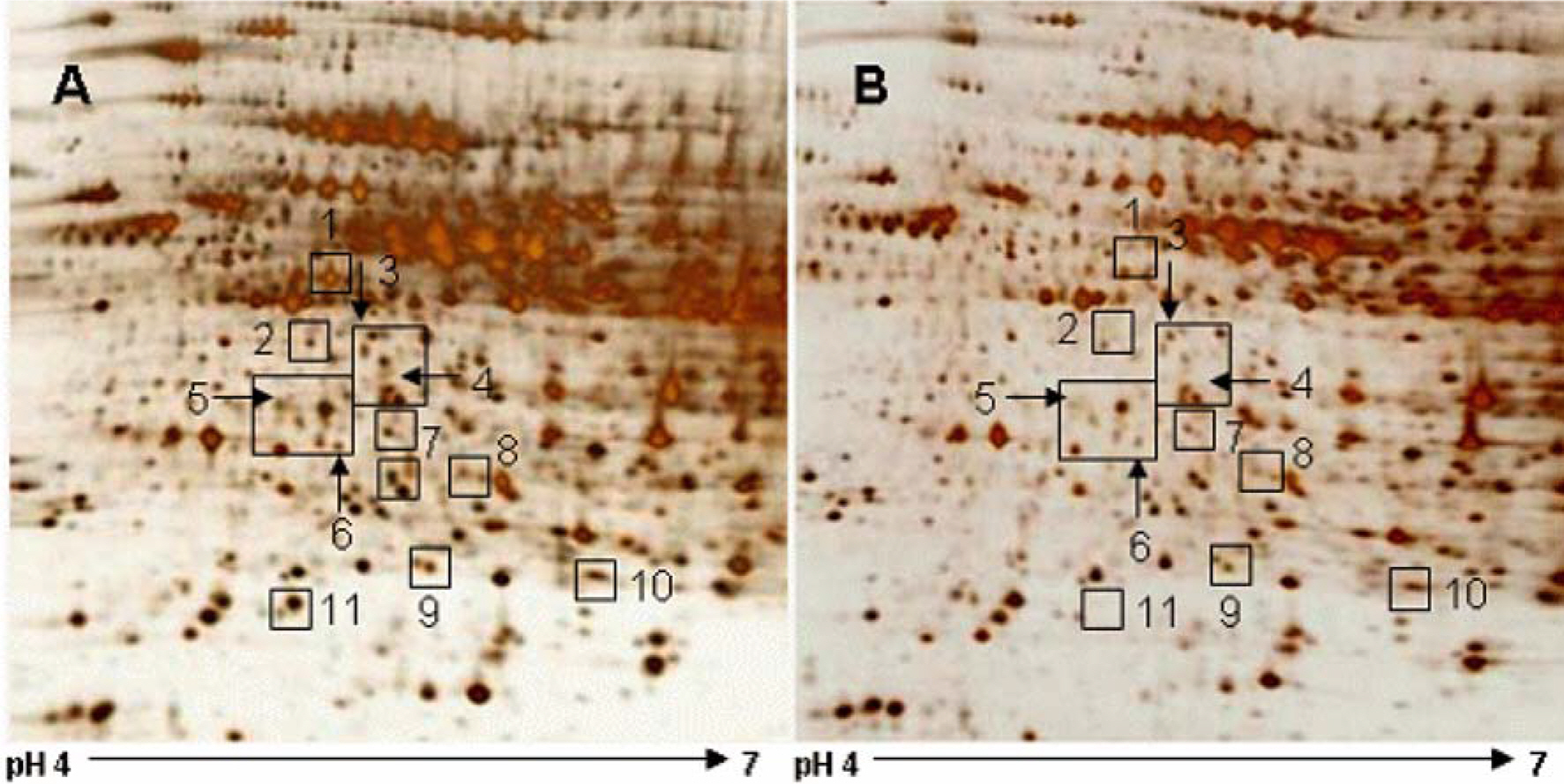
- Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is an inevitable consequence during liver surgery. I/R injury induces serious hepatic dysfunction and failure. In this study, we identified proteins that were differentially expressed between sham and I/R injured livers. Animals were subjected to hepatic ischemia for 1 hr and were sacrificed at 3hr after reperfusion. Serum ALT and AST levels were significantly increased in I/R-operated animals compared to those of sham-operated animals. Ischemic hepatic lobes of I/R-operated animals showed the hepatic lesion with unclear condensation and sinusoidal congestion. Proteins from hepatic tissue were separated using two dimensional gel electrophosresis. Protein spots with a greater than 2.5-fold change in intensity were identified by mass spectrometry. Among these proteins, glutaredoxin-3, peroxiredoxin-3, glyoxalase I, spermidine synthase, dynamin-1-like protein, annexin A4, eukaryotic initiation factor 3, eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I, 26S proteasome, proteasome alpha 1, and proteasome beta 4 levels were significantly decreased in I/R-operated animals compared to those of sham-operated animals. These proteins are related to protein synthesis, cellular growth and stabilization, anti-oxidant action. Moreover, Western blot analysis confirmed that dynamin-1-like protein levels were decreased in I/R-operated animals. Our results suggest that hepatic I/R induces the hepatic cells damage by regulation of several proteins.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Annexin A4
Blotting, Western
Estrogens, Conjugated (USP)
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor-3
Hepatocytes
Ischemia
Lactoylglutathione Lyase
Liver
Mass Spectrometry
Mice
Peptide Initiation Factors
Proteasome Endopeptidase Complex
Proteins
Reperfusion
Reperfusion Injury
Salicylamides
Spermidine Synthase
Annexin A4
Estrogens, Conjugated (USP)
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor-3
Lactoylglutathione Lyase
Peptide Initiation Factors
Proteasome Endopeptidase Complex
Proteins
Salicylamides
Spermidine Synthase
Figure
Reference
-
Wang X.., Su B.., Lee H.G.., Li X.., Perry G.., Smith M.A.., Zhu X.2009a. Impaired balance of mitochondrial fission and fusion in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 29:9090–9103.
ArticleAbe Y.., Hines I.N.., Zibari G.., Pavlick K.., Gray L.., Kitagawa Y.., Grisham M.B.2009. Mouse model of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: method for studying reactive oxygen and nitrogen metabolites in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 46:1–7.
ArticleChattopadhyay M.K.., Tabor C.W.., Tabor H.2003. Polyamines protect Escherichia coli cells from the toxic effect of oxygen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100:2261–2265.
ArticleEum H.A.., Cha Y.N.., Lee S.M.2007. Necrosis and apoptosis: Sequence of liver damage following reperfusion after 60min ischemia in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 358:500–505.
ArticleHom J.R.., Gewandter J.S.., Michael L.., Sheu S.S.., Yoon Y.2007. Thapsigargin induces biphasic fragmentation of mitochondria through calcium-mediated mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. J. Cell Physiol. 212:498–508.
ArticleJaeschke H.., Bautista A.P.., Spolarics Z.., Spitzer J.J.1992. Superoxide generation by neutrophils and Kupffer cells during in vivo reperfusion after hepatic ischemia in rats. J. Leukoc. Biol. 52:377–382.
ArticleJaeschke H.2003. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 284:14–26.Jaeschke H.2006. Mechanisms of liver injury. II. Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced liver cellinjury during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and other acute inflammatory conditions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 290:1083–1088.Koo A.., Komatsu H.., Tao G.., Inoue M.., Guth P.H.., Kaplowitz N.1992. Contribution of no-reflow phenomenon to hepatic injury after ischemia-reperfusion: evidence for a role for superoxide anion. Hepatology. 15:507–514.
ArticleKuboki S.., Schuster R.., Blanchard J.., Pritts T.A.., Wong H.R.., Lentsch A.B.2007. Role of heat shock protein 70 in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292:1141–1149.
ArticleKumagai T.., Nangaku M.., Inagi R.2008. Pathophysiological role of the glyoxalase system in renal hypoxic injury. Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 1126:265–267.
ArticleKumagai T.., Nangaku M.., Kojima I.., Nagai R.., Ingelfinger J.R.., Miyata T.., Fujita T.., Inagi R.2009. Glyoxalase I overexpression ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 296:912–921.
ArticleMinton K.W.., Tabor H.., Tabor C.W.1990. Paraquat toxicity is increased in Escherichia coli defective in the synthesis of polyamines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 87:2851–2855.
ArticlePitts K.R.., Yoon Y.., Krueger E.W.., McNiven M.A.1999. The dynamin-like protein DLP-1 is essential for normal distribution and morphology of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 10:4403–4417.
ArticlePronobesh C.., Dagagi A.V.., Pallab C.., Kumar W.A.2008. Protective role of the calcium channel blocker amlodipine against mitochondrial injury in ischemia and reperfusion injury of rat liver. Acta. Pharm. 58:421–428.
ArticleRhodes R.S.., DePalma R.G.1980. Mitochondrial dysfunction of the liver and hypoglycemia in hemorrhagic shock. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 150:347–352.Suen D.F.., Norris K.L.., Youle R.J.2008. Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 22:1577–1590.
ArticleThornalley P.J.2003. Glyoxalase I-structure, function and a critical role in the enzymatic defence against glycation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31:1343–1348.Thornalley P.J.2008. Protein and nucleotide damage by glyoxal and methylglyoxal in physiological systems-role in ageing and disease. Drug Metabol. Drug Interact. 23:125–150.
ArticleWang X.., Su B.., Fujioka H.., Zhu X.2008. Dynamin-like protein 1 reduction underlies mitochondrial morphology and distribution abnormalities in fibroblasts from sporadic Alzheimer's disease patients. Am. J. Pathol. 173:470–482.
ArticleWang X.., Su B.., Lee H.G.., Li X.., Perry G.., Smith M.A.., Wang, H., Lim, P.J., Karbowski, M. and Monteiro M.J.2009b. Effects of overexpression of huntingtin proteins on mitochondrial integrity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18:737–752.
ArticleWu H.., Min J.., Ikeguchi Y.., Zeng H.., Dong A.., Loppnau P.., Pegg A.E.., Plotnikov A.N.2007. Structure and mechanism of spermidine synthases. Biochemistry. 46:8331–8339.
ArticleZhao Y.J.., Xu C.Q.., Zhang W.H.., Zhang L.., Bian S.L.., Huang Q.., Sun H.L.., Li Q.F.., Zhang Y.Q.., Tian Y.., Wang R.., Yang B.F.., Li W.M.2007. Role of polyamines in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and their interactions with nitric oxide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 562:236–246.
ArticleZwacka R.M.., Zhang Y.., Halldorson J.., Schlossberg H.., Dudus L.., Engelhardt J.F.1997. CD4(+) T-lymphocytes mediate ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory responses in mouse liver. J. Clin. Invest. 100:279–289.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Experimental Study in Mice for Inducing the Optimal Hepatic Ischemia Followed by Reperfusion
- Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury with respect to oxidative stress and inflammatory response: a narrative review
- SP600125, a selective JNK inhibitor, aggravates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Protective Effects of Geniposide and Genipin against Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice
- CD44 Disruption Attenuates Murine Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury