J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Feb;36(1):39-42. 10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.1.39.
Effect of bovine bone (Bio-Oss(R)) and platelet rich plasma, platelet poor plasma on sinus bone graft in rabbit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Medicine, Korea University, Korea. jaesrim@korea.ac.kr
- 2EB Dental Clinic, Korea.
- KMID: 1457817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.1.39
Abstract
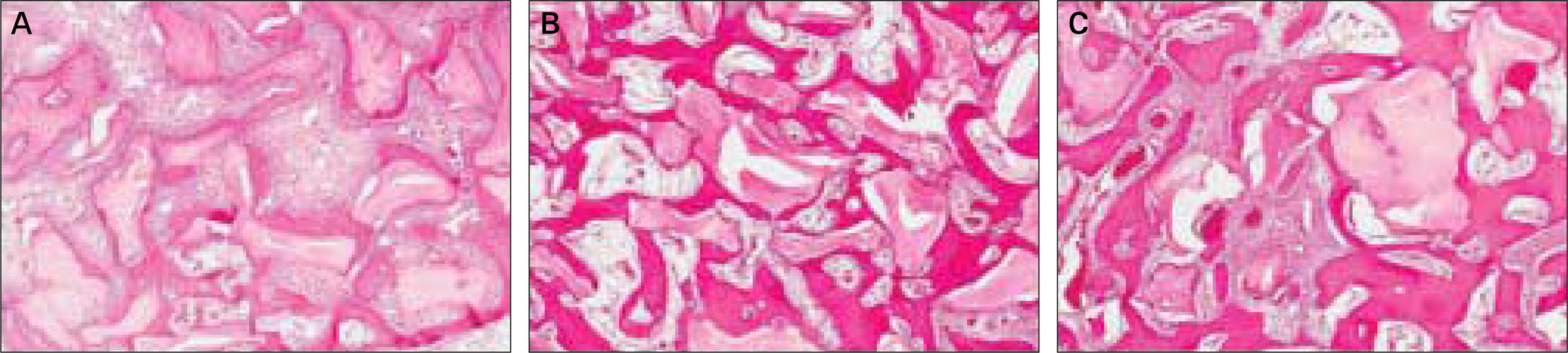
- Maxillary sinus lift and bone graft are used to reconstruct atrophic maxilla molar area for endosseous dental implants. Many different grafting materials and techniques can be used for maxillary sinus bone graft. Bio-Oss(R) has been proposed as bone substitute and successfully utilized as osteoconductive filler. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) is an autologous material with many growth factors, such as PDGF, TGF-beta, IGF, VEGF, facilitating bone healing process. And Platelet poor plasma (PPP) is the by-product in procedure of producing PRP. Six rabbits were used as experimental animal. Both maxillary sinus were grafted with Bio-Oss(R) and PRP, and Bio-Oss(R) and PPP. Rabbits were sacrificed at 4, 8 and 12 weeks. The grafting sites were evaluated by histomorphometric analysis. As a result, using PRP showed excellent bone formation in the early stage, but no further significant effect after that. In late stage, the ability of bone formation of using PRP was even worse than using PPP. The further studies need to be considered in this case.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blood Platelets
Bone Substitutes
Dental Implants
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Maxilla
Maxillary Sinus
Molar
Osteogenesis
Plasma
Platelet-Rich Plasma
Rabbits
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transplants
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Bone Substitutes
Dental Implants
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tatum OH. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent Clin North Am. 1986; 30:207–29.2. Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg. 1980; 38:613–8.3. Piattelli M, Favero GA, Scarano A, Orsini G, Piattelli A. Bone reactions to anorganic bovine bone (Bio-Oss) used in sinus augmentation procedures: a histologic long-term report of 20 cases in humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999; 14:835–40.4. Tadjoedin ES, de Lange GL, Bronckers AL, Lyaruu DM, Burger EH. Deproteinized cancellous bovine bone (Bio-Oss) as bone substitute for sinus floor elevation. A retrospective, histomorpho-metrical study of five cases. J Clin Periodontol. 2003; 30:261–70.5. Aghaloo TL, Moy PK, Freymiller EG. Evaluation of platelet-rich plasma in combination with anorganic bovine bone in the rabbit cranium: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004; 19:59–65.6. Fontana S, Olmedo DG, Linares JA, Guglielmotti MB, Crosa ME. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on the peri-implant bone response: an experimental study. Implant Dent. 2004; 13:73–8.7. Ha JW, Kim SG, Cho SI, Lee CW, Chung TY, Kim SH, et al. Use of platelet-rich plasma. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 23:452–7.8. Seong DH, Min SK. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on autogenous bone graft remodelling in rabbit. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 26:34–44.9. Oh SY, Kim SG, Cho SI, Kim JD. Xenobone grafting with platelet-rich plasma gel and Bio-Oss: radiological in humans. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 24:489–92.10. Jakse N, Tangl S, Gilli R, Berghold A, Lorenzoni M, Eskici A, et al. Influence of PRP on autogenous sinus grafts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003; 14:578–83.
Article11. Dudziak ME, Block MS. Ridge augmentation with PRP/PPP and mineralized bone in dogs. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61(8S):41a–42.
Article12. Choi BH, Im CJ, Huh JY, Suh JJ, Lee SH. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration in autogenous bone graft. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 33:56–9.
Article13. Harris D, Farrell B, Block MS. Zygomatic arch defects grafted with mineralized bone with PRP or PPP in dogs. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61(8S):42–3.
Article14. Wiltfang J, Kloss FR, Kessler P, Nkenke E, Schultze-Mosgau S, Zimmermann R, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma on bone healing in combination with autogenous bone and bone substitutes in critical-size defects. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:187–93.
Article15. Sa ′ nchez AR, Sheridan PJ, Eckert SE, Weaver AL. Regenerative potential of platelet-rich plasma added to xenogenic bone grafts in peri-implant defects: a histomorphometric analysis in dogs. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:1637–44.16. Klongnoi B, Rupprecht S, Kessler P, Thorwarth M, Wiltfang J, Schlegel KA. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on a bioglass and autogenous bone in sinus augmentation. An explorative study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17:312–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Xenobone Grafting With Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel And Bio-Oss: Radiological In Humans
- Effect of platelet-rich plasma on autogenous bone graft remodelling in rabbit
- Use of Platelet-rich Plasma
- A radiographical study on the changes in height of grafting materials after sinus lift: a comparison between two types of xenogenic materials
- Augmented bony change following platelet rich plasma(PRP) application on maxillary defect