Anat Cell Biol.
2011 Jun;44(2):151-159. 10.5115/acb.2011.44.2.151.
Surface models of the male urogenital organs built from the Visible Korean using popular software
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. dissect@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1447425
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2011.44.2.151
Abstract
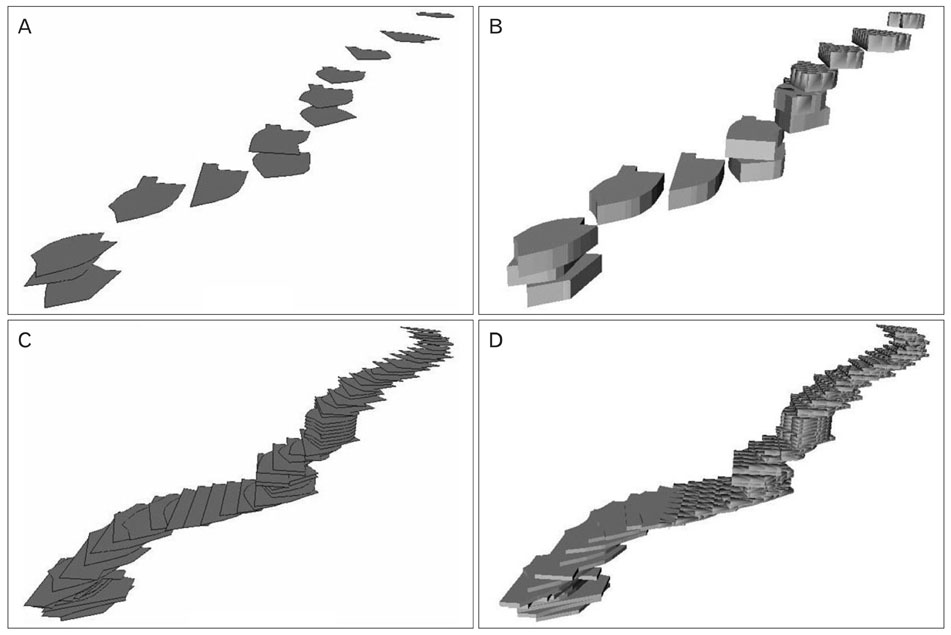
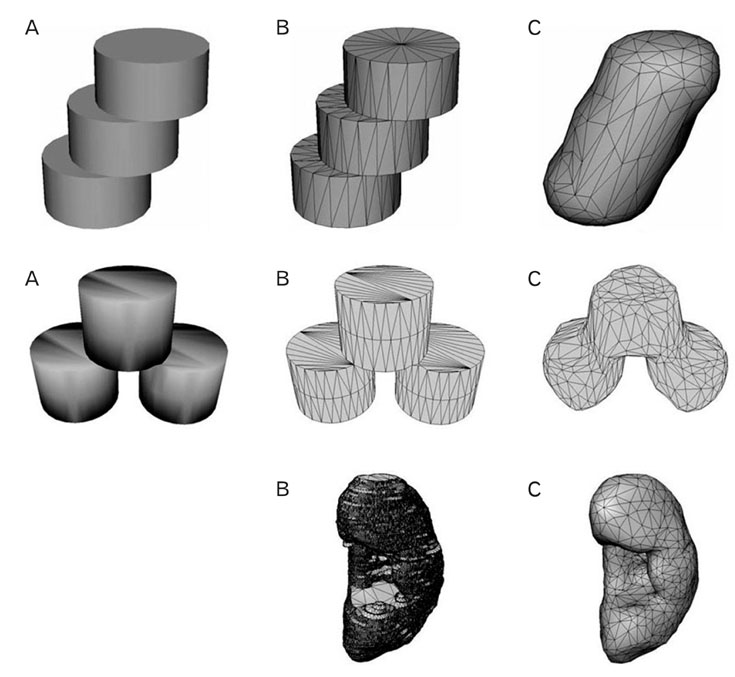
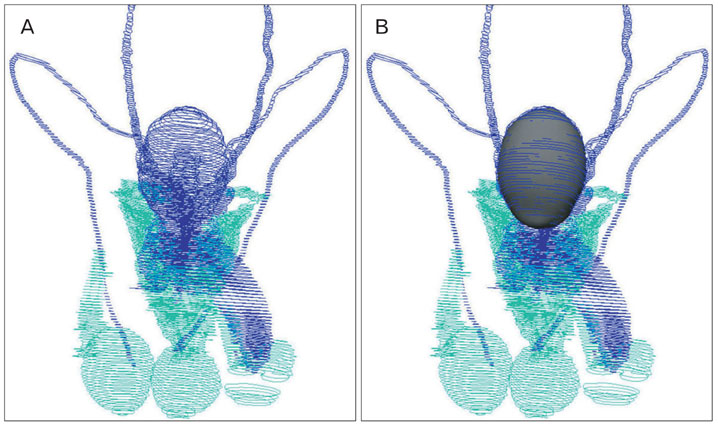
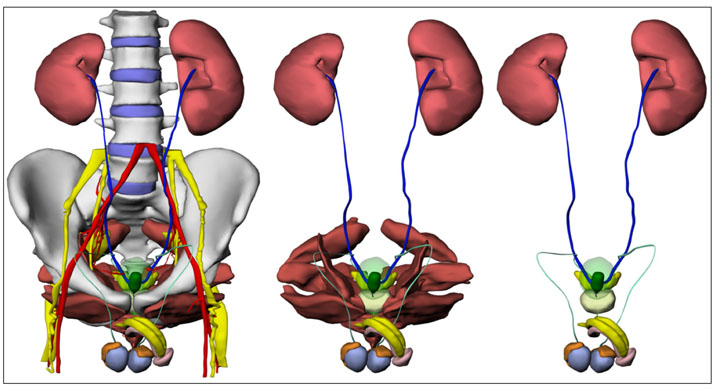
- Unlike volume models, surface models, which are empty three-dimensional images, have a small file size, so they can be displayed, rotated, and modified in real time. Thus, surface models of male urogenital organs can be effectively applied to an interactive computer simulation and contribute to the clinical practice of urologists. To create high-quality surface models, the urogenital organs and other neighboring structures were outlined in 464 sectioned images of the Visible Korean male using Adobe Photoshop; the outlines were interpolated on Discreet Combustion; then an almost automatic volume reconstruction followed by surface reconstruction was performed on 3D-DOCTOR. The surface models were refined and assembled in their proper positions on Maya, and a surface model was coated with actual surface texture acquired from the volume model of the structure on specially programmed software. In total, 95 surface models were prepared, particularly complete models of the urinary and genital tracts. These surface models will be distributed to encourage other investigators to develop various kinds of medical training simulations. Increasingly automated surface reconstruction technology using commercial software will enable other researchers to produce their own surface models more effectively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Spitzer V, Ackerman MJ, Scherzinger AL, Whitlock D. The visible human male: a technical report. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1996. 3:118–130.2. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Shin BS, Park HS. Visible Korean human: its techniques and applications. Clin Anat. 2006. 19:216–224.3. Zhang SX, Heng PA, Liu ZJ. Chinese visible human project. Clin Anat. 2006. 19:204–215.4. Tang L, Chung MS, Liu Q, Shin DS. Advanced features of whole body sectioned images: virtual Chinese human. Clin Anat. 2010. 23:523–529.5. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH, Park HS. Visible Korean human: improved serially sectioned images of the entire body. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005. 24:352–360.6. Uhl JF, Park JS, Chung MS, Delmas V. Three-dimensional reconstruction of urogenital tract from Visible Korean human. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006. 288:893–899.7. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH. Technical report on semiautomatic segmentation using the Adobe Photoshop. J Digit Imaging. 2005. 18:333–343.8. Shin DS, Park JS, Lee SB, Lee SH, Chung J, Chung MS. Surface model of the gastrointestinal tract constructed from the Visible Korean. Clin Anat. 2009. 22:601–609.9. Park JS, Shin DS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Chung J. Technique of semiautomatic surface reconstruction of the Visible Korean human data using commercial software. Clin Anat. 2007. 20:871–879.10. Shin DS, Chung MS, Lee JW, Park JS, Chung J, Lee SB, Lee SH. Advanced surface reconstruction technique to build detailed surface models of the liver and neighboring structures from the Visible Korean human. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. 24:375–383.11. Jang HG, Chung MS, Shin DS, Park SK, Cheon KS, Park HS, Park JS. Segmentation and surface reconstruction of the detailed ear structures, identified in sectioned images. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011. 294:559–564.12. Shin DS, Chung MS, Park JS, Park HS, Lee SB, Lee SH, Choi HN, Riemer M, Handels H, Lee JE, Jung W. Three-dimensional surface models of detailed lumbosacral structures reconstructed from the Visible Korean. Ann Anat. 2011. 193:64–70.13. Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology. Terminologia anatomica: international anatomical terminology. 1998. New York, Stuttgart: Thieme.14. Jin Y, Chen G, Zhang SX, Tang LW, Liu GJ, Li K, Dong JH. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the pancreas and its surrounding structures. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2008. 32:277–283.15. Wu Y, Zhang SX, Luo N, Qiu MG, Tan LW, Li QY, Liu GJ, Li K. Creation of the digital three-dimensional model of the prostate and its adjacent structures based on Chinese Visible human. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010. 32:629–635.16. Haas A, Fischer MS. Three-dimensional reconstruction of histological sections using modern product-design software. Anat Rec. 1997. 249:510–516.17. Park JS, Jung YW, Lee JW, Shin DS, Chung MS, Riemer M, Handels H. Generating useful images for medical applications from the Visible Korean human. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008. 92:257–266.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Visible Korean: Movable Surface Models of the Foot
- Portable Document Format File Showing the Surface Models of Cadaver Whole Body
- Three Software Tools for Viewing Sectional Planes, Volume Models, and Surface Models of a Cadaver Hand
- Advanced Surface Reconstruction Technique to Build Detailed Surface Models of the Liver and Neighboring Structures from the Visible Korean Human
- Dawn of the Visible Monkey: Segmentation of the Rhesus Monkey for 2D and 3D Applications