Lab Anim Res.
2011 Dec;27(4):369-371. 10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.369.
Antifibrotic activity a fermentation filtrate of Ganoderma lucidum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Food Safety Support Organization, Korea Food Industry Association, Seoul, Korea.
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. solar93@cbu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1444974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.369
Abstract
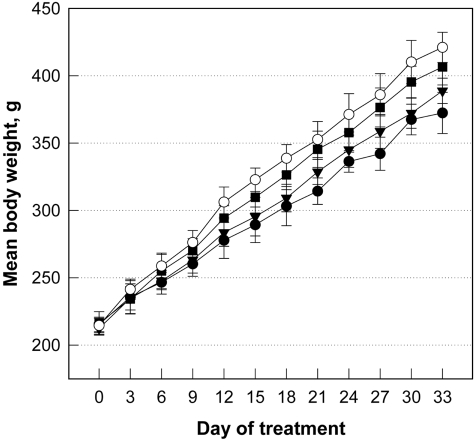
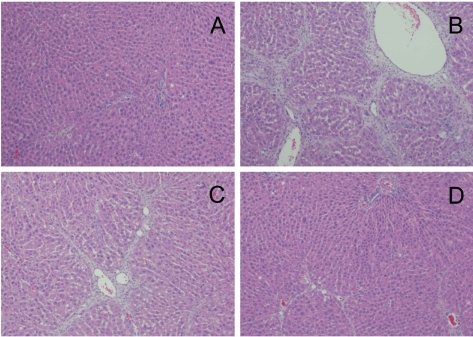
- The effects of a fermentation filtrate of Ganoderma lucidum (FGL) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic fibrosis were investigated in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were orally administered with FGL (20 or 100 mg/kg) for 33 days, and orally administered with CCl4 (1.0 mL/kg; 2 mL/kg of 50% in corn oil) at 3-day intervals 1 h after FGL treatment. Body and liver weights, blood and histopathological findings in accordance with hydroxyproline concentrations were analyzed. Chronic exposure to CCl4 reduced the body weight gain, but increased liver weights and fibrosis, resulting in 3.35-fold increase in hydroxyproline level. Although FGL did not significantly reduce the CCl4-induced body and liver weight changes, it attenuated the increases in the hepatic fibrosis and hydroxyproline contents. Taken together, it is suggested that FGL might prevent hepatic fibrosis, and that FGL or its ingredient could be a potential candidate for the prevention of chronic hepatic disorders.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hwang JM, Tseng TH, Tsai YY, Lee HJ, Chou FP, Wang CJ, Chu CY. Protective effects of baicalein on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatic toxicity in rat hepatocytes. J Biomed Sci. 2005; 12(2):389–397. PMID: 15917992.
Article2. Zou Y, Yang Y, Li J, Li W, Wu Q. Prevention of hepatic injury by a traditional Chinese formulation, BJ-JN, in mice treated with Bacille-Calmette-Guérin and lipopolysaccharide. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006; 107(3):442–448. PMID: 16697540.
Article3. Ozenirler S, Dinçer S, Akyol G, Ozoğul C, Oz E. The protective effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on CCl4-induced hepatic damage. Acta Physiol Hung. 1997; 85(3):277–285. PMID: 10101542.4. Lin JM, Lin CC, Chen MF, Ujiie T, Takada A. Radical scavenger and antihepatotoxic activity of Ganoderma formosanum, Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma neojaponicum. J Ethnopharmacol. 1995; 47(1):33–41. PMID: 7564419.5. Gao YH, Huang M, Lin ZB, Zhou SF. Hepatoprotective Activity and the Mechanisms of Action of Ganoderma lucidum (Curt.:Fr.) P. Karst. (Ling Zhi, Reishi Mushroom) (Aphyllophoromycetideae). Inter J Medic Mushrooms. 2003; 5:111–131.6. Zhou CY, Jia W, Yang Y, Bai YQ. Experimental studies on prevention of several kinds of fungi polysaccharides against alcohol-induced hepatic injury. Edible Fungi. 2002; 24:36–37.7. Wang MY, Liu Q, Che QM, Lin ZB. Effects of total Triterpenoids Extract from Ganoderma Iucidum (Curt: Fr) P Karst (Reishi mushroom) on experimental liver injury models induced by carbon tetrachloride or D-galactosamine in mice. Acta Pharmaceut Sin. 2000; 35:326–329.8. Sun J, He H, Xie BJ. Novel antioxidant peptides from fermented mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. J Agric Food Chem. 2004; 52(21):6646–6652. PMID: 15479035.9. Shi Y, Sun J, He H, Guo H, Zhang S. Hepatoprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum peptides against D-galactosamine-induced liver injury in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008; 117(3):415–419. PMID: 18406549.10. Kwon SC, Shin S, Jeon JH, Park D, Jang MJ, Kim JJ, Kim CH, Jeong JH, Kim YB. Anti-allergic effects of rose petal extract and Ganoderma lucidum culture on mast cell-mediated allergy model. Lab Anim Res. 2008; 24:93–97.11. Jeon JH, Kwon SC, Park D, Shin S, Jang MJ, Joo SS, Kang H, Kim SH, Oh JY, Jeong JH, Kim YB. Effects of red and white rose petal extracts and Ganoderma lucidum culture on ovalbumin-induced atopic dermatitis. Lab Anim Res. 2008; 24(3):347–354.12. Jeon JH, Shin S, Park D, Jang JY, Choi BI, Kang JK, Joo SS, Hwang SY, Kim JC, Kim BY, Kim MR, Kim YB. Fermentation filtrates of Rubus coreanus relax the corpus cavernosum and increase sperm count and motility. J Med Food. 2008; 11(3):474–478. PMID: 18800894.13. Kim EJ, Shin S, Jang JY, Choi B, Park D, Jeon JH, Park JH, Hwang SY, Kim YB. Effects of Hwalgidan® on hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Lab Anim Res. 2007; 23(1):59–67.14. Fort J, Oberti F, Pilette C, Veal N, Gallois Y, Douay O, Rousselet MC, Rosenbaum J, Calès P. Antifibrotic and hemodynamic effects of the early and chronic administration of octreotide in two models of liver fibrosis in rats. Hepatology. 1998; 28(6):1525–1531. PMID: 9828216.
Article15. Yorozu K, Fujii E, Teruya S, Ogawa Y, Ito H, Suzuki M, Sugimoto T. Lobular difference in fibrotic changes in rat cirrhosis model induced by carbon tetrachloride. J Toxicol Pathol. 2004; 17(4):267–274.
Article16. Bhandarkar MR, Khan A. Antihepatotoxic effect of Nymphaea stellata willd., against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in albino rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004; 91(1):61–64. PMID: 15036469.17. Sherlock S, Dooley J. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 1997. 10th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science Press;p. 303–384.18. Anthony PP, Ishak KG, Nayak NC, Poulsen HE, Scheuer PJ, Sobin LH. The morphology of cirrhosis: definition nomenclature and classification. Bull World Health Organ. 1977; 55(4):521–540. PMID: 304393.19. Anthony PP, Ishak KG, Nayak NC, Poulsen HE, Scheuer PJ, Sobin LH. The morphology of cirrhosis. Recommendations on definition, nomenclature, and classification by a working group sponsored by the World Health Organization. J Clin Pathol. 1978; 31(5):395–414. PMID: 649765.
Article20. Wu YW, Fang HL, Lin WC. Post-treatment of Ganoderma lucidum reduced liver fibrosis induced by thioacetamide in mice. Phytother Res. 2010; 24(4):494–499. PMID: 19621343.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Characteristics of Ganoderma lucidum According to Geographical Origins : Consideration of Growth Characteristics(I)
- Comparison of Characteristics of Ganoderma lucidum According to Geographical Origins : Consideration of Morphological Characteristics(II)
- Occupational asthma induced by ganoderma spores
- Taxonomic Position and Species Identity of the Cultivated Yeongji 'Ganoderma lucidum' in Korea
- Optimal Medium Conditions for the Detection of Cellulolytic Activity in Ganoderma lucidum