J Korean Soc Radiol.
2012 Feb;66(2):193-197. 10.3348/jksr.2012.66.2.193.
Tophaceous Gout Involving the Whole Spine: An Unusual Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. merita@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 1439413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2012.66.2.193
Abstract
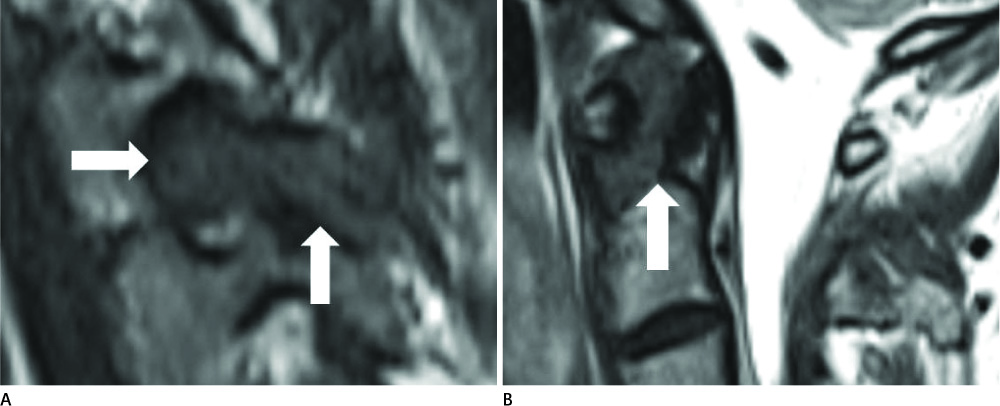
- Gout is a relatively common, crystal deposition disease, in which monosodium urate crystals are deposited in joint and periarticular tissues of the extremities. Involvement of the spine is exceedingly rare. Most patients with spinal gout present with symptomatic spinal cord compression. Diffuse involvement of tophi deposition inside the spinal central canal has not been reported. We now present a case of chronic tophaceous gout with extensive spinal involvement that resulted in diffuse spinal cord compression and led to paraplegia.
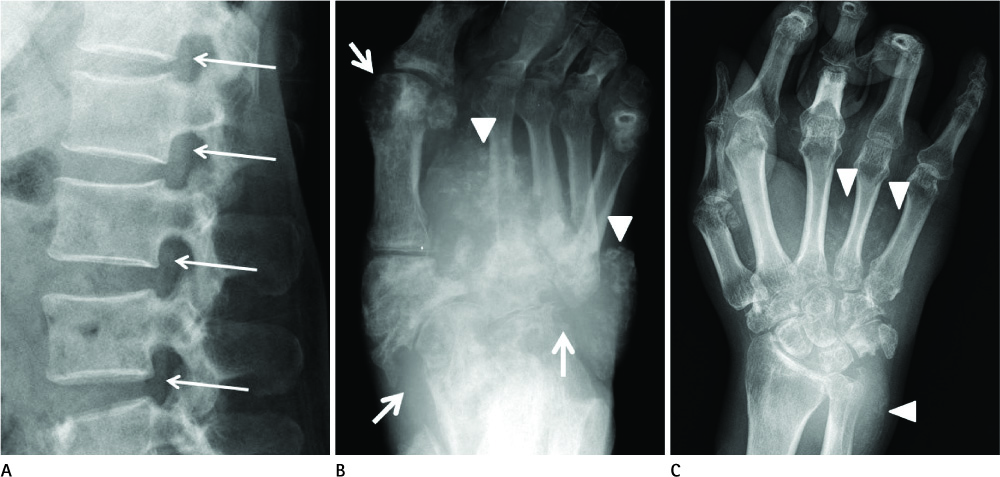
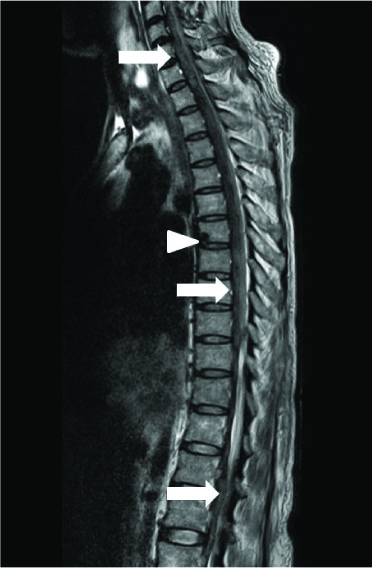
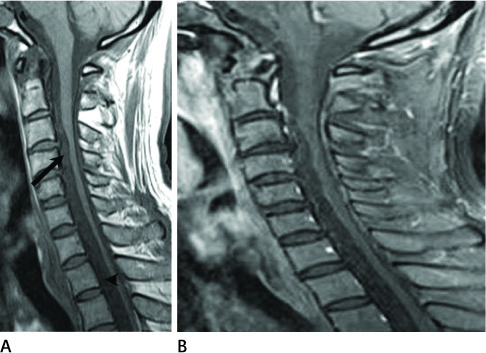
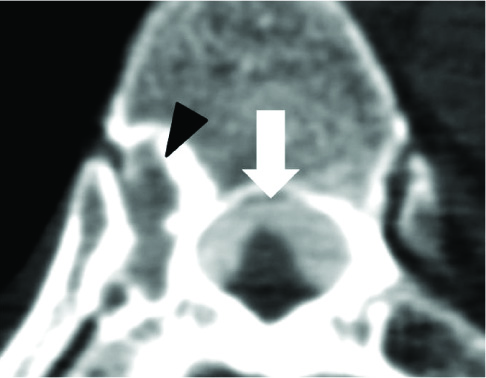
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Chronic Tophaceous Gout in Multiple Spines: A Case Report and Literature Review
Kyoung Hwa Lee, Hyun Sun Woo, Mi Ryoung Seo, Hee Jung Ryu, Hyo Jin Choi, Han Joo Baek
J Rheum Dis. 2015;22(4):250-255. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.4.250.
Reference
-
1. Richette P, Bardin T. Gout. Lancet. 2010; 375:318–328.2. Ning TC, Keenan RT. Unusual clinical presentations of gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010; 22:181–187.3. Oaks J, Quarfordt SD, Metcalfe JK. MR features of vertebral tophaceous gout. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:W658–W659.4. Butteriss D, Soh C. A case of spinal cord compression of unknown cause. Br J Radiol. 2006; 79:775–777.5. Desai MA, Peterson JJ, Garner HW, Kransdorf MJ. Clinical utility of dual-energy CT for evaluation of tophaceous gout. Radiographics. 2011; 31:1365–1375. discussion 1376-13776. Paquette S, Lach B, Guiot B. Lumbar radiculopathy secondary to gouty tophi in the filum terminale in a patient without systemic gout: case report. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:986–988.7. Yu JS, Chung C, Recht M, Dailiana T, Jurdi R. MR imaging of tophaceous gout. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:523–527.8. Hsu CY, Shih TT, Huang KM, Chen PQ, Sheu JJ, Li YW. Tophaceous gout of the spine: MR imaging features. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57:919–925.9. Bonaldi VM, Duong H, Starr MR, Sarazin L, Richardson J. Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine mimicking an epidural abscess: MR features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1949–1952.10. Duprez TP, Malghem J, Vande Berg BC, Noel HM, Munting EA, Maldague BE. Gout in the cervical spine: MR pattern mimicking diskovertebral infection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:151–153.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tophaceous Gout Involving the Bipartitle Patella: A Case Report
- Tophaceous Gout in the Rotator Cuff with Impingement Syndrome: A Case Report
- Tophaceous Gout of the Lumbar Spine Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis and Epidural Abscess
- Intratendinous Tophaceous Gout Mimicking Cellulitis after Achilles Tendon Repair
- Symptomatic Tophaceous Gout in the Bilateral Patellae