J Korean Diabetes.
2012 Mar;13(1):23-26. 10.4093/jkd.2012.13.1.23.
The Effects of Postprandial Hyperglycemia on Glucose Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongsiri@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1436183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2012.13.1.23
Abstract
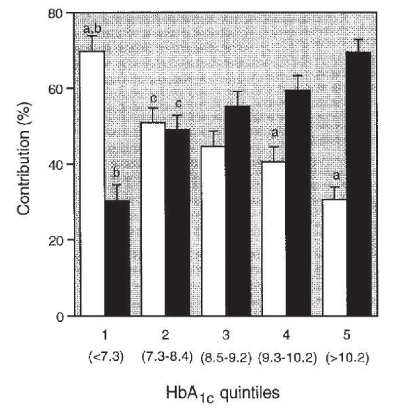
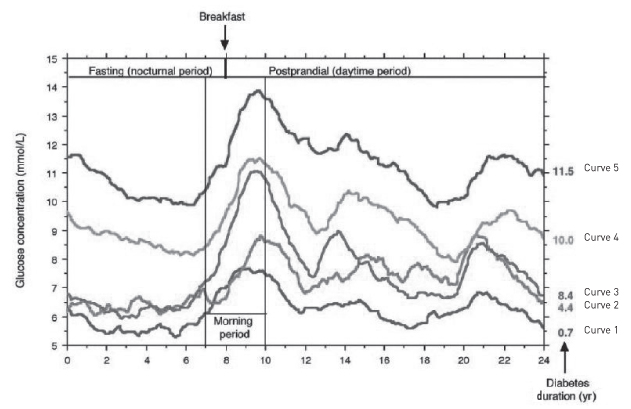
- Global diabetes prevalence is increasing every year. Glucose control is the most important aspect of diabetes management, and numerous studies on diabetes treatment have shown the importance of glucose reduction in the prevention of diabetic complications. Glucose control may be influenced by three components of glycemia (a "triad"): fasting hyperglycemia, postprandial hyperglycemia, and HbA1c. Which of these components most influences glucose control is still under debate. However, there are sufficient data to demonstrate the importance of postprandial glucose control in the prevention of cardiovascular complications. A few pivotal studies have been performed on the association of fasting or postprandial hyperglycemia with overall glucose control. These studies suggest that different components of glycemia have variable effects according to degree of glucose control. Also, glycemic variability is emphasized as a new component in glucose control. More studies should be performed to find better ways of controlling postprandial hyperglycemia for the prevention of cardiovascular complications of diabetes.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relationships between Thigh and Waist Circumference, Hemoglobin Glycation Index, and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Myung Ki Yoon, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kap Bum Huh, Chul Sik Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):319-328. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.319.
Reference
-
1. Dinneen S, Gerich J, Rizza R. Carbohydrate metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1992. 327:707–713.
Article2. Monnier L. Is postprandial glucose a neglected cardiovascular risk factor in type 2 diabetes? Eur J Clin Invest. 2000. 30:Suppl 2. 3–11.
Article3. Monnier L, Colette C, Owens D. Postprandial and basal glucose in type 2 diabetes: assessment and respective impacts. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011. 13:Suppl 1. S25–S32.
Article4. Avignon A, Radauceanu A, Monnier L. Nonfasting plasma glucose is a better marker of diabetic control than fasting plasma glucose in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:1822–1826.
Article5. Rohlfing CL, Wiedmeyer HM, Little RR, England JD, Tennill A, Goldstein DE. Defining the relationship between plasma glucose and HbA(1c): analysis of glucose profiles and HbA(1c) in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:275–278.6. Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:881–885.
Article7. Monnier L, Colette C, Dunseath GJ, Owens DR. The loss of postprandial glycemic control precedes stepwise deterioration of fasting with worsening diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:263–269.
Article8. Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. Type 2 diabetes: a well-characterised but suboptimally controlled disease. Can we bridge the divide? Diabetes Metab. 2008. 34:207–216.
Article9. Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. Glycemic variability: the third component of the dysglycemia in diabetes. Is it important? How to measure it? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008. 2:1094–1100.
Article10. Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. Integrating glycaemic variability in the glycaemic disorders of type 2 diabetes: a move towards a unified glucose tetrad concept. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009. 25:393–402.
Article11. Hirsch IB. Intensifying insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2005. 118:Suppl 5A. 21S–26S.
Article