J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Sep;85(3):109-115. 10.4174/jkss.2013.85.3.109.
The effect of duodenojejunal bypass for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients below body mass index 25 kg/m2: one year follow-up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. gshur@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1426342
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.85.3.109
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The goals of this study are to evaluate the effect of duodenojejunal bypass (DJB) for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients below body mass index (BMI) 25 kg/m2 in one year follow-up, and to compare the results of 1 week which we have reported in 2011.
METHODS
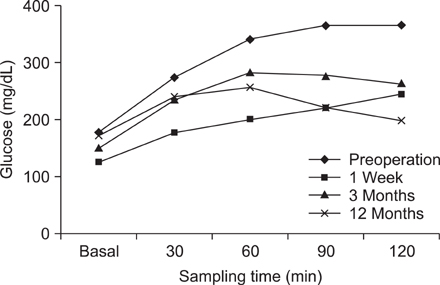
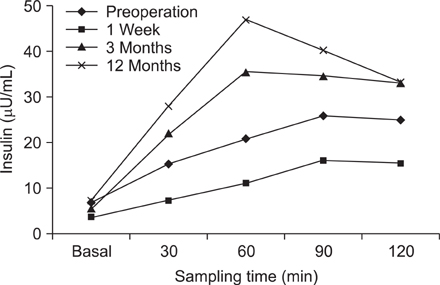
In this prospective observational study, there were 31 type 2 diabetic patients who underwent DJB at Inha University Hospital from July 2009 to January 2011. We did laboratories such as 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), insulin level and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), etc. and compared their changes of preoperative, a week, 3 months, and 12 months.
RESULTS
Mean BMI was 23.1 +/- 1.3 kg/m2, mean duration of T2DM was 8.3 +/- 4.7 and mean age was 46.6 +/- 7.7 years. There were a significant decrease of 75-g OGTT levels and increase of insulin secretion after 3 months. 13.3% showed diabetic remission (HbA1c < 6.0, medication cessation) and 26.7% showed diabetic improvement. The rates of remission and improvement much declined comparing with that of postoperative 1 week although those were determined by fasting and postprandial 2 hour level of glucose.
CONCLUSION
This is the first study of metabolic surgery in Korean diabetes patients in the healthy weight range. DJB exerted positive influences on insulin resistance as well as beta cell function. Early effects on T2DM after DJB could be estimated as one of good modalities, although the effectiveness seems to be unacceptable. Further studies are mandatory for evaluation of the effectiveness of metabolic surgery and finding prognostic factors.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Inzucchi SE. Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes: scientific review. JAMA. 2002; 287:360–372.2. Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, Torgerson J, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2683–2693.3. Rubino F, Forgione A, Cummings DE, Vix M, Gnuli D, Mingrone G, et al. The mechanism of diabetes control after gastrointestinal bypass surgery reveals a role of the proximal small intestine in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Ann Surg. 2006; 244:741–749.4. Salinari S, Bertuzzi A, Asnaghi S, Guidone C, Manco M, Mingrone G. First-phase insulin secretion restoration and differential response to glucose load depending on the route of administration in type 2 diabetic subjects after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:375–380.5. Guidone C, Manco M, Valera-Mora E, Iaconelli A, Gniuli D, Mari A, et al. Mechanisms of recovery from type 2 diabetes after malabsorptive bariatric surgery. Diabetes. 2006; 55:2025–2031.6. Laferrere B, Teixeira J, McGinty J, Tran H, Egger JR, Colarusso A, et al. Effect of weight loss by gastric bypass surgery versus hypocaloric diet on glucose and incretin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:2479–2485.7. Pories WJ, Caro JF, Flickinger EG, Meelheim HD, Swanson MS. The control of diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in the morbidly obese with the Greenville Gastric Bypass. Ann Surg. 1987; 206:316–323.8. Kang KC, Shin SH, Lee YJ, Heo YS. Influence of gastrectomy for stomach cancer on type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 30 kg/m2. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:347–355.9. Hong IK, Kim JY, Lee YJ, Choe YM, Choi SK, Heo YS, et al. The effect of duodenojejunal bypass for T2DM patients below BMI 25 kg/m2 in early postoperative period. J Korean Surg Soc. 2011; 80:103–110.10. Prentki M, Nolan CJ. Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116:1802–1812.11. Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 1995; 222:339–350.12. Pories WJ, MacDonald KG Jr, Flickinger EG, Dohm GL, Sinha MK, Barakat HA, et al. Is type II diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) a surgical disease? Ann Surg. 1992; 215:633–642.13. Lee WJ, Huang MT, Wang W, Lin CM, Chen TC, Lai IR. Effects of obesity surgery on the metabolic syndrome. Arch Surg. 2004; 139:1088–1092.14. Madan AK, Orth W, Ternovits CA, Tichansky DS. Metabolic syndrome: yet another co-morbidity gastric bypass helps cure. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006; 2:48–51.15. Mottin CC, Vontobel Padoin A, Schroer CE, Barancelli FT, Glock L, Repetto G. Behavior of type 2 diabetes mellitus in morbid obese patients submitted to gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2008; 18:179–181.16. Rubino F, Marescaux J. Effect of duodenal-jejunal exclusion in a non-obese animal model of type 2 diabetes: a new perspective for an old disease. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:1–11.17. Cohen R, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Schiavon CA. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for BMI < 35 kg/m(2): a tailored approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006; 2:401–404.18. Patriti A, Facchiano E, Sanna A, Gulla N, Donini A. The enteroinsular axis and the recovery from type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:840–848.19. Gutniak M, Orskov C, Holst JJ, Ahren B, Efendic S. Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1992; 326:1316–1322.20. Drucker DJ. Biological actions and therapeutic potential of the glucagon-like peptides. Gastroenterology. 2002; 122:531–544.21. Gautier JF, Fetita S, Sobngwi E, Salaun-Martin C. Biological actions of the incretins GIP and GLP-1 and therapeutic perspectives in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2005; 31(3 Pt 1):233–242.22. Geloneze B, Geloneze SR, Chaim E, Hirsch FF, Felici AC, Lambert G, et al. Metabolic surgery for non-obese type 2 diabetes: incretins, adipocytokines, and insulin secretion/resistance changes in a 1-year interventional clinical controlled study. Ann Surg. 2012; 256:72–78.23. Garcia-Caballero M, Valle M, Martinez-Moreno JM, Miralles F, Toval JA, Mata JM, et al. Resolution of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome in normal weight 24-29 BMI patients with One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass. Nutr Hosp. 2012; 27:623–631.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of gastrectomy for stomach cancer on type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 30 kg/m2
- Three-year result of efficacy for type 2 diabetes mellitus control between laparoscopic duodenojejunal bypass compared with laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- The Effect of Metformin in Obese Pediatric Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- The Effect of Duodenojejunal Bypass for T2DM Patients Below BMI 25 kg/m2 in Early Postoperative Period
- The effect of long Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes and body mass index < 35 kg/m2: preliminary results