Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Mar;57(3):194-197. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.3.194.
A Case of Acute Pancreatitis due to Afferent Loop Syndrome with Internal Hernia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seether@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 1128360
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.3.194
Abstract
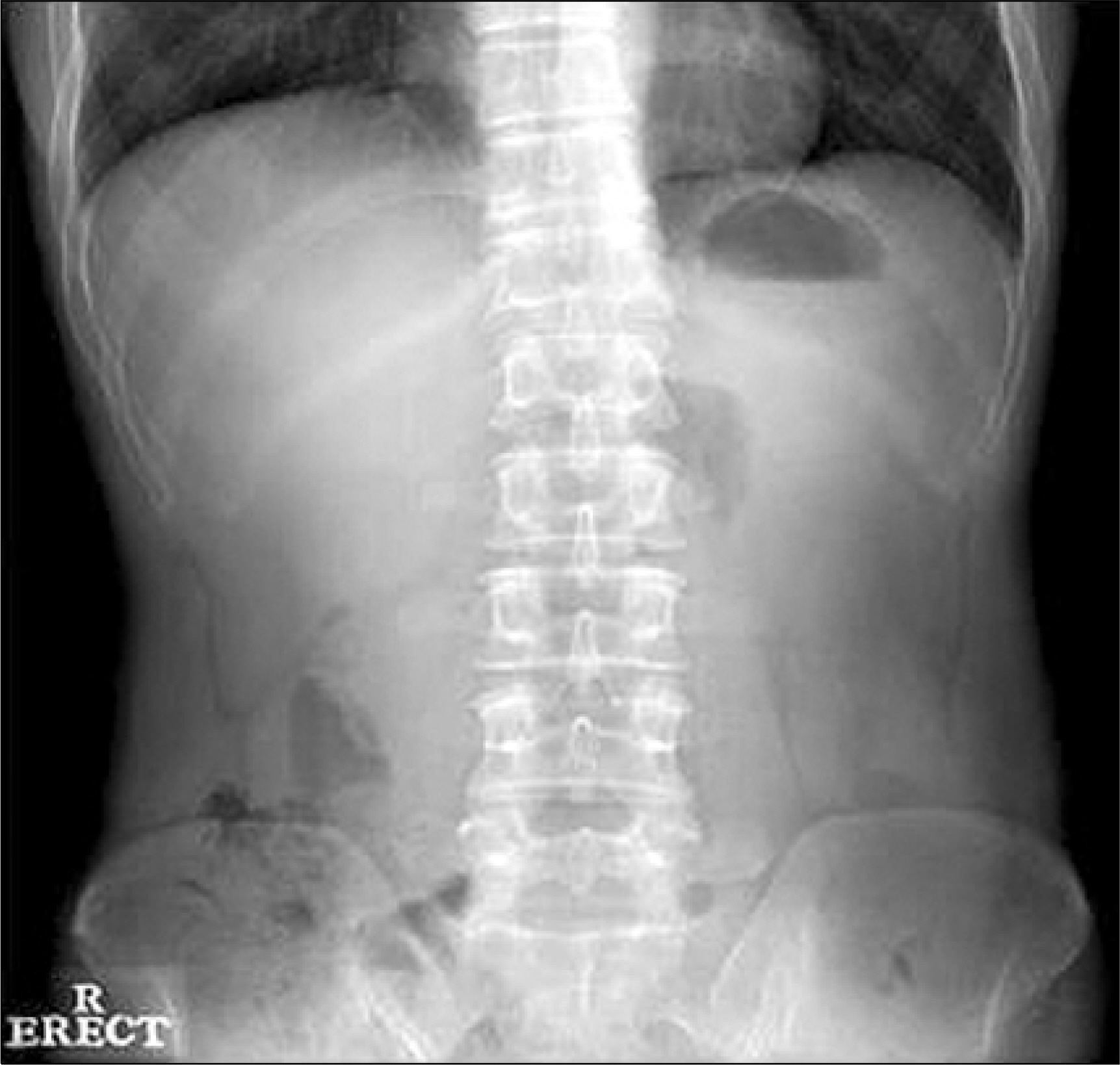
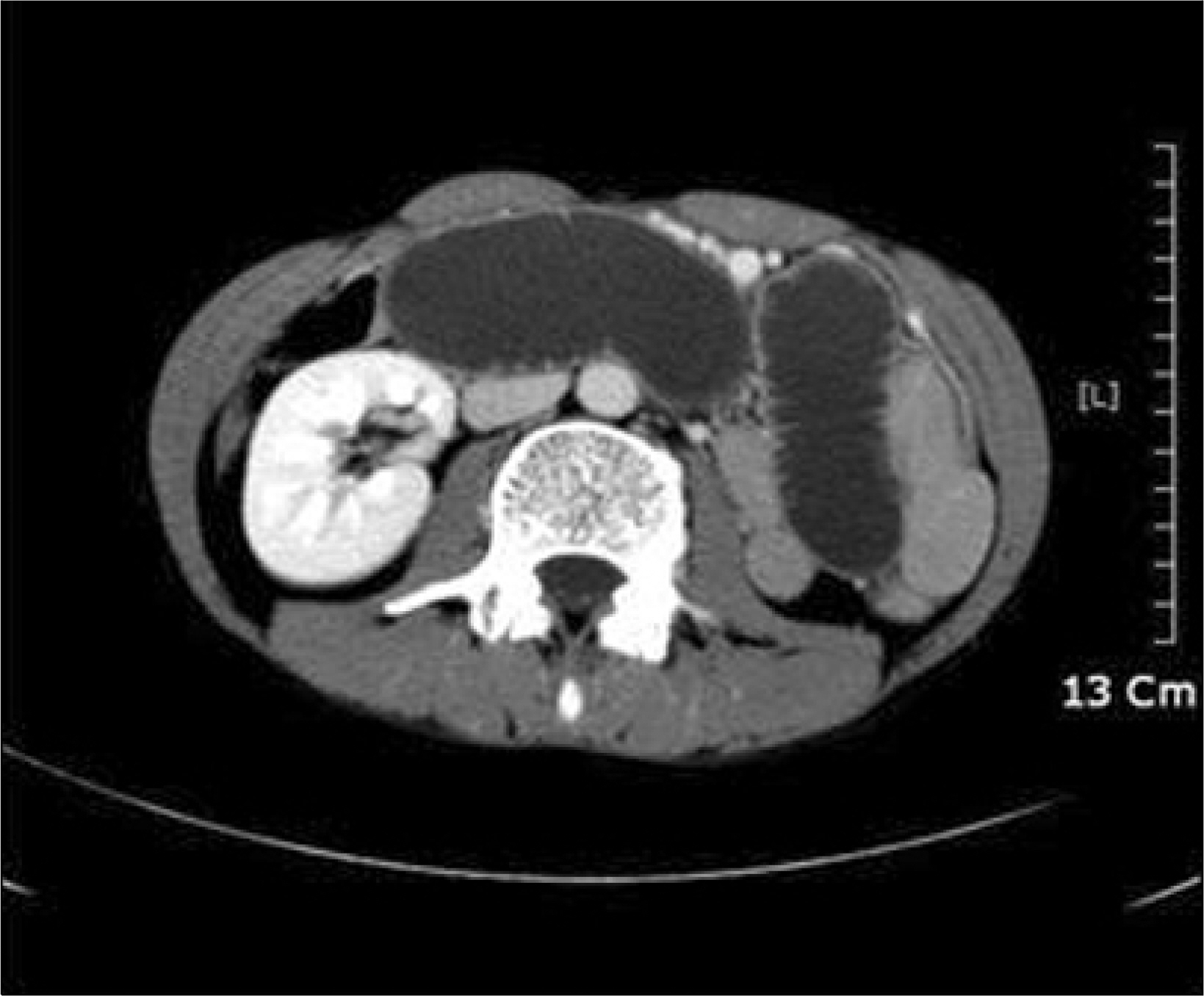
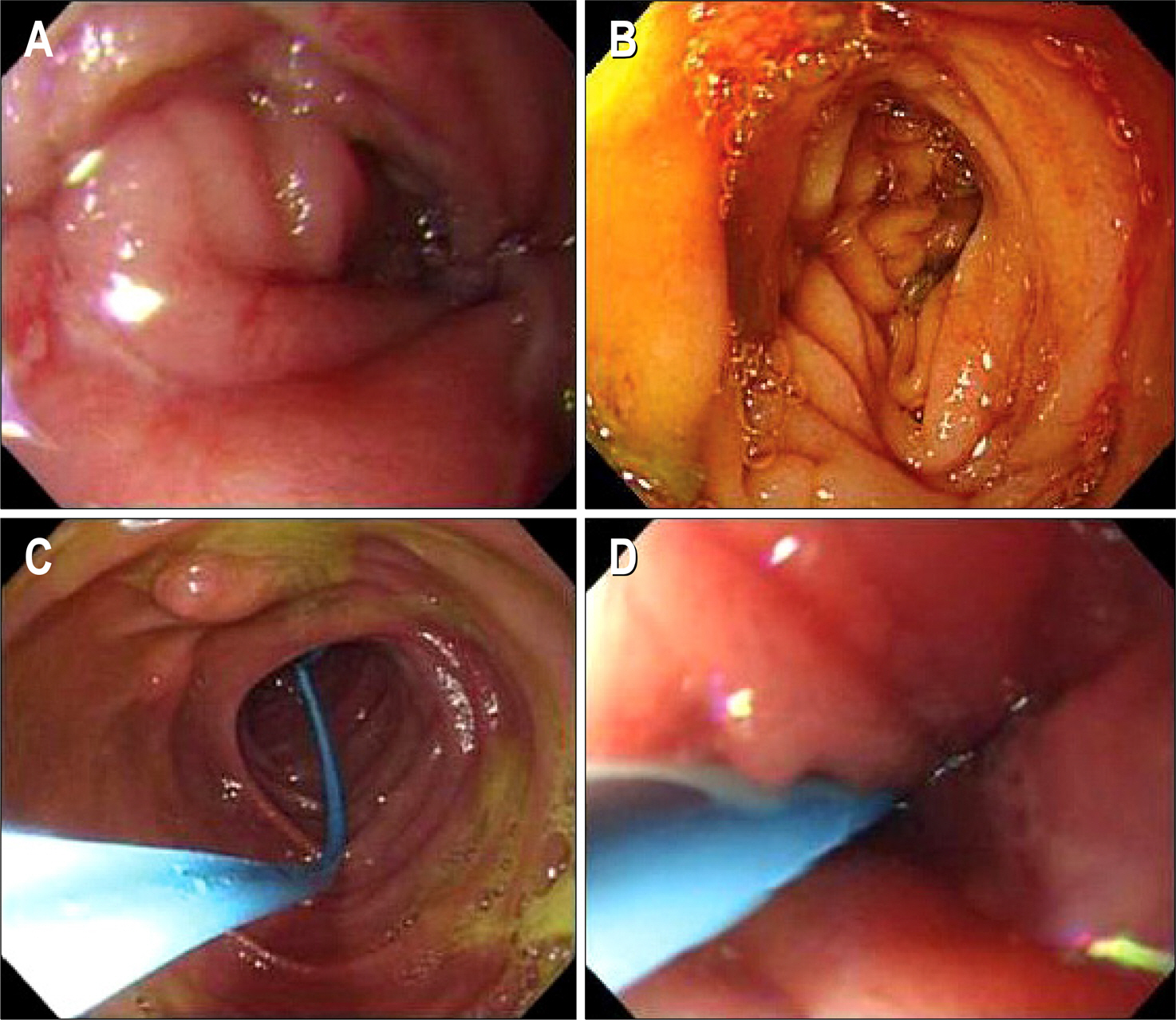
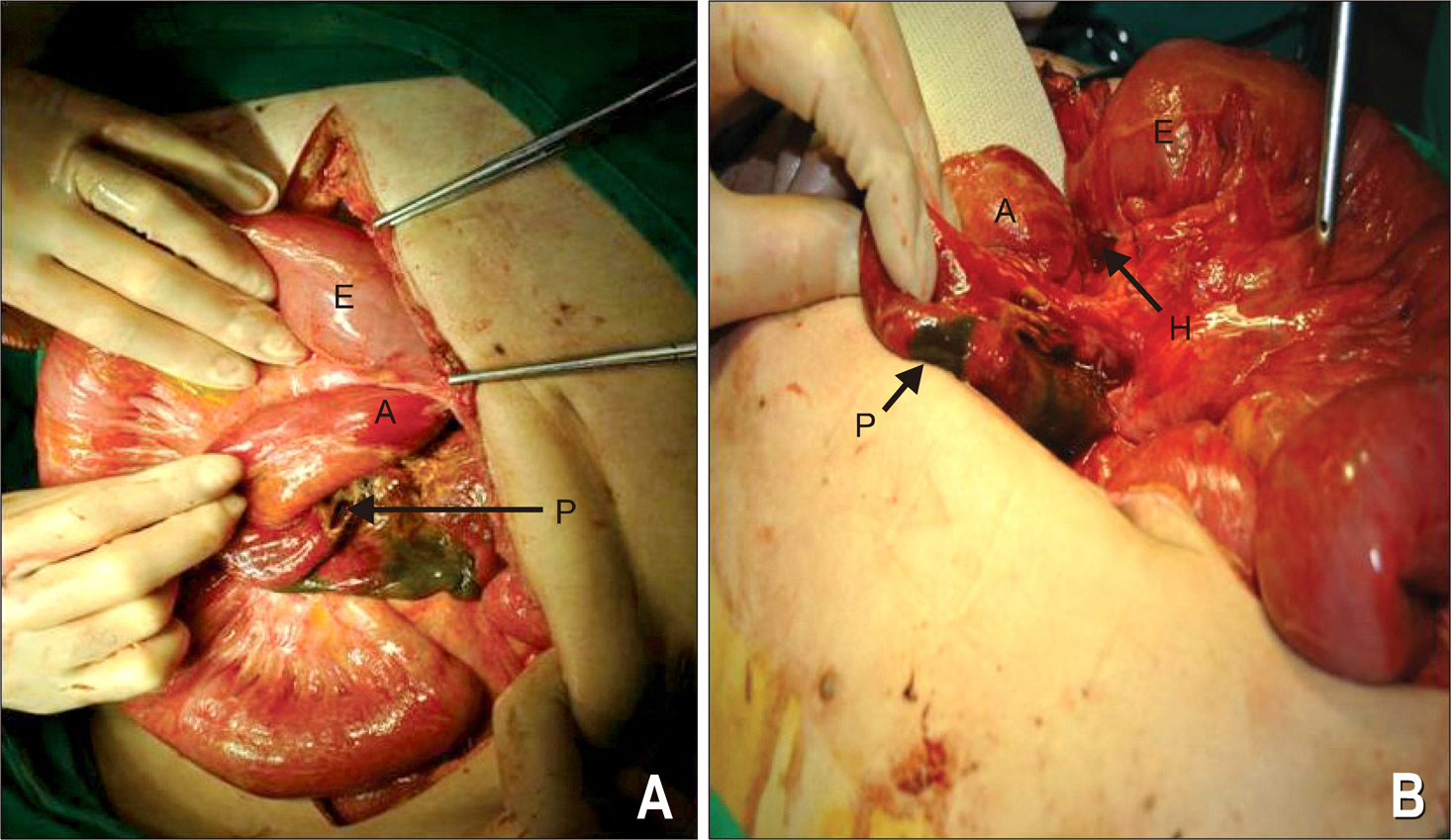
- Acute pancreatitis and afferent loop syndrome (ALS) have similar symptoms and physical findings. Accurate early diagnosis is essential, as the management of acute pancreatitis is predominantly conservative whereas ALS usually requires surgery. We experienced one case of pancreatitis due to ALS with internal hernia. Laboratory findings of patient showed elevated serum amylase, lipase and WBC count. One day after admission, diagnosis was modified as acute pancreatitis caused by ALS on computed tomography. Patient was managed with surgical treatment and operation finding revealed ALS due to internal hernia. He was recovered well after surgical treatment and discharged without significant sequelae.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Dias AR, Lopes RI. Biliary stone causing afferent loop syndrome and pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:6229–6231.
Article2. Park SJ, Kang HH, Park IG, et al. Two cases of afferent loop syndrome accompanying acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2001; 38:296–299.3. Perry T Jr. Post-gastrectomy proximal jejunal loop obstruction simulating acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1954; 140:119–121.
Article4. Beveridge CJ, Zammit-Maempel I. Afferent loop obstruction: CT appearances of an unusual cause of acute pancreatitis. Clin Radiol. 1999; 54:188–189.
Article5. Wolfler A. Gastro-enterostomie. Zentralbl F Chir. 1881; 8:705–708.6. Toye DK, Williams JA. Post-gastrectomy bile vomiting. Lancet. 1965; 2:524–526.
Article7. Young R, Roach HD, Finch-Jones M. More than pancreatitis? Br J Radiol. 2006; 79:858–859.
Article8. Kuwabara Y, Nishitani H, Numaguchi Y, Kamoi I, Matsuura K, Saito S. Afferent loop syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980; 4:687–689.
Article9. Gayer G, Barsuk D, Hertz M, Apter S, Zissin R. CT diagnosis of afferent loop syndrome. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57:835–839.
Article10. Hasuda K, Makino Y, Arata T, Yamada T. Afferent loop obstruction diagnosed by sonography and computed tomography. Br J Radiol. 1991; 64:1156–1158.
Article11. Stewardson RH, Bombeck CT, Nyhus LM. Critical operative management of small bowel obstruction. Ann Surg. 1978; 187:189–193.
Article12. Herrington JL Jr. The afferent loop syndrome: additional experience with its surgical management. Am Surg. 1968; 34:321–329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Afferent Loop Syndrome Treated by Endoscopic Drainage Procedure using Nasogastric Tube
- Acute Abdomen Caused by Complicated Afferent Loop Syndrome after Gastrectomy
- Two Cases of Afferent Loop Syndrome Accompanying Acute Pancreatitis
- Recurrent Pancreatitis Caused by Afferent Loop Syndrome with Pathologic Features of Type II Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- Acute Pancreatitis Associated with Diaphragmatic Hernia in an Adult