J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Feb;27(2):177-183. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.177.
The Ability of beta-Cells to Compensate for Insulin Resistance is Restored with a Reduction in Excess Growth Hormone in Korean Acromegalic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kw1234@skku.edu
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1120155
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.177
Abstract
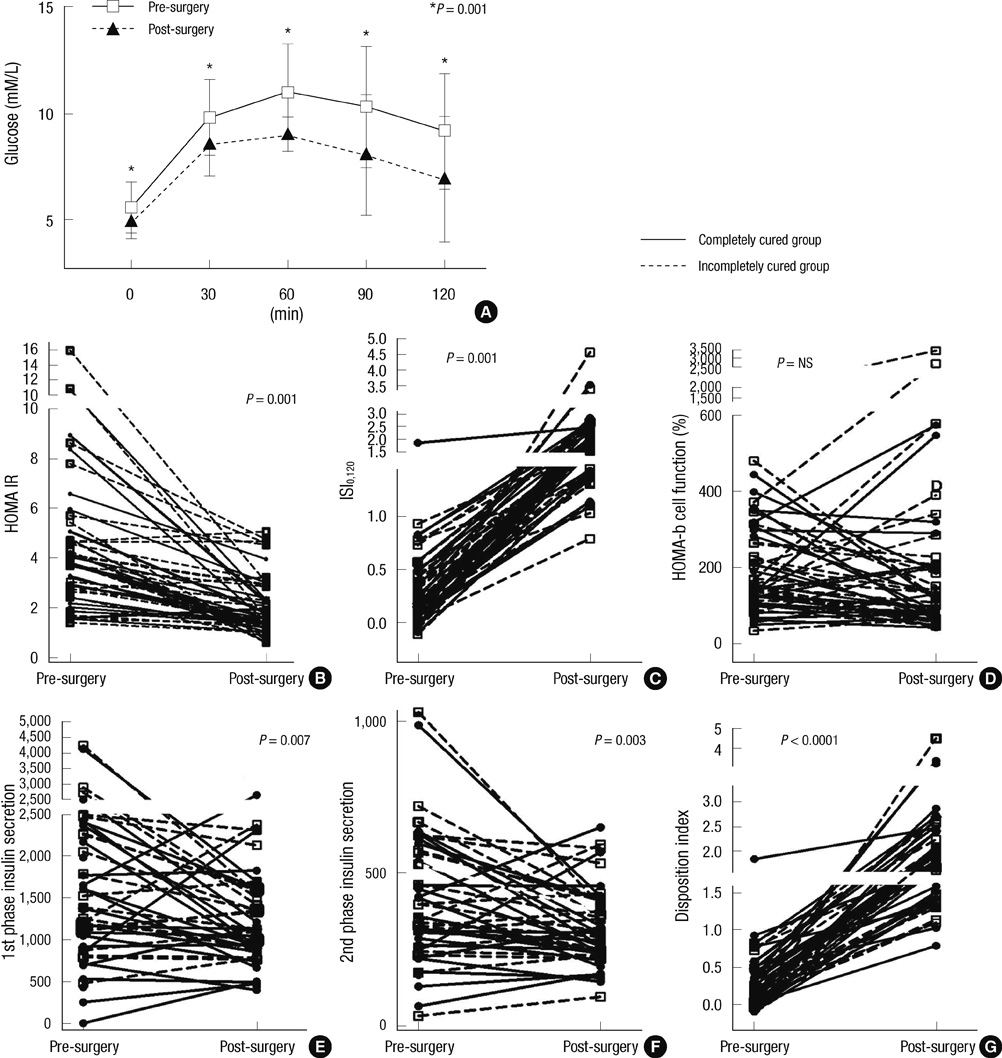
- The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of diabetes and to study the effects of excess growth hormone (GH) on insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in Korean acromegalic patients. One hundred and eighty-four acromegalic patients were analyzed to assess the prevalence of diabetes, and 52 naive acromegalic patients were enrolled in order to analyze insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. Patients underwent a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test with measurements of GH, glucose, insulin, and C-peptide levels. The insulin sensitivity index and beta-cell function index were calculated and compared according to glucose status. Changes in the insulin sensitivity index and beta-cell function index were evaluated one to two months after surgery. Of the 184 patients, 17.4% were in the normal glucose tolerance (NGT) group, 45.1% were in the pre-diabetic group and 37.5% were in the diabetic group. The insulin sensitivity index (ISI0,120) was significantly higher and the HOMA-IR was lower in the NGT compared to the diabetic group (P = 0.001 and P = 0.037, respectively). The ISI0,120 and disposition index were significantly improved after tumor resection. Our findings suggest that both insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function are improved by tumor resection in acromegalic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acromegaly/*diagnosis/etiology/metabolism
Adult
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Blood Glucose/analysis
C-Peptide/analysis
Diabetes Mellitus/epidemiology
Female
Glucose Tolerance Test
Human Growth Hormone/secretion
Humans
Insulin/blood/secretion
*Insulin Resistance
Insulin-Secreting Cells/cytology/*physiology
Male
Middle Aged
Prediabetic State/epidemiology
Republic of Korea
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kreze A, Kreze-Spirova E, Mikulecky M. Risk factors for glucose intolerance in active acromegaly. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001. 34:1429–1433.2. Espinosa-de-los-Monteros AL, González B, Vargas G, Sosa E, Mercado M. Clinical and biochemical characteristics of acromegalic patients with different abnormalities in glucose metabolism. Pituitary. 2011. 14:231–235.3. Biering H, Knappe G, Gerl H, Lochs H. Prevalence of diabetes in acromegaly and Cushing syndrome. Acta Med Austriaca. 2000. 27:27–31.4. Beck P, Schalch DS, Parker ML, Kipnis DM, Daughaday WH. Correlative studies of growth hormone and insulin plasma concentrations with metabolic abnormalities in acromegaly. J Lab Clin Med. 1965. 66:366–379.5. Trimble ER, Atkinson AB, Buchanan KD, Hadden DR. Plasma glucagon and insulin concentrations in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980. 51:626–631.6. Foss MC, Saad MJ, Paccola GM, Paula FJ, Piccinato CE, Moreira AC. Peripheral glucose metabolism in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 72:1048–1053.7. Wasada T, Aoki K, Sato A, Katsumori K, Muto K, Tomonaga O, Yokoyama H, Iwasaki N, Babazono T, Takahashi C, Iwamoto Y, Omori Y, Hizuka N. Assessment of insulin resistance in acromegaly associated with diabetes mellitus before and after transsphenoidal adenomectomy. Endocr J. 1997. 44:617–620.8. Møller N, Schmitz O, Jøorgensen JO, Astrup J, Bak JF, Christensen SE, Alberti KG, Weeke J. Basal- and insulin-stimulated substrate metabolism in patients with active acromegaly before and after adenomectomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992. 74:1012–1019.9. Kasayama S, Otsuki M, Takagi M, Saito H, Sumitani S, Kouhara H, Koga M, Saitoh Y, Ohnishi T, Arita N. Impaired beta-cell function in the presence of reduced insulin sensitivity determines glucose tolerance status in acromegalic patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000. 52:549–555.10. Kinoshita Y, Fujii H, Takeshita A, Taguchi M, Miyakawa M, Oyama K, Yamada S, Takeuchi Y. Impaired glucose metabolism in Japanese patients with acromegaly is restored after successful pituitary surgery if pancreatic {beta}-cell function is preserved. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011. 164:467–473.11. Coculescu M, Niculescu D, Lichiardopol R, Purice M. Insulin resistance and insulin secretion in non-diabetic acromegalic patients. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2007. 115:308–316.12. Stelmachowska-Banaś M, Zdunowski P, Zgliczynski W. Abnormalities in glucose homeostasis in acromegaly. Does the prevalence of glucose intolerance depend on the level of activity of the disease and the duration of the symptoms? Endokrynol Pol. 2009. 60:20–24.13. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2010. Diabetes Care. 2010. 33:S11–S61.14. Phillips DI, Clark PM, Hales CN, Osmond C. Understanding oral glucose tolerance: comparison of glucose or insulin measurements during the oral glucose tolerance test with specific measurements of insulin resistance and insulin secretion. Diabet Med. 1994. 11:286–292.15. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.16. Gutt M, Davis CL, Spitzer SB, Llabre MM, Kumar M, Czarnecki EM, Schneiderman N, Skyler JS, Marks JB. Validation of the insulin sensitivity index (ISI(0,120)): comparison with other measures. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000. 47:177–184.17. Bergman RN, Ader M, Huecking K, Van Citters G. Accurate assessment of beta-cell function: the hyperbolic correction. Diabetes. 2002. 51:S212–S220.18. Stumvoll M, Mitrakou A, Pimenta W, Jenssen T, Yki-Järvinen H, Van Haeften T, Renn W, Gerich J. Use of the oral glucose tolerance test to assess insulin release and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:295–301.19. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:2016–2020.20. Jaffrain-Rea ML, Moroni C, Baldelli R, Battista C, Maffei P, Terzolo M, Correra M, Ghiggi MR, Ferretti E, Angeli A, Sicolo N, Trischitta V, Liuzzi A, Cassone R, Tamburrano G. Relationship between blood pressure and glucose tolerance in acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2001. 54:189–195.21. Puder JJ, Nilavar S, Post KD, Freda PU. Relationship between disease-related morbidity and biochemical markers of activity in patients with acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90:1972–1978.22. Nielsen JH, Galsgaard ED, Møldrup A, Friedrichsen BN, Billestrup N, Hansen JA, Lee YC, Carlsson C. Regulation of beta-cell mass by hormones and growth factors. Diabetes. 2001. 50:S25–S29.23. Rosenfalck AM, Maghsoudi S, Fisker S, Jørgensen JO, Christiansen JS, Hilsted J, Vølund AA, Madsbad S. The effect of 30 months of low-dose replacement therapy with recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) on insulin and C-peptide kinetics, insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, glucose effectiveness, and body composition in GH-deficient adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:4173–4181.24. Hansen I, Tsalikian E, Beaufrere B, Gerich J, Haymond M, Rizza R. Insulin resistance in acromegaly: defects in both hepatic and extrahepatic insulin action. Am J Physiol. 1986. 250:E269–E273.25. Muggeo M, Bar RS, Roth J, Kahn CR, Gorden P. The insulin resistance of acromegaly: evidence for two alterations in the insulin receptor on circulating monocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979. 48:17–25.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acromegaly Presenting with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in human
- Relationship of Insulin like Growth Factor I with Pharmacologically Stimulated Growth Hormone Secretion in Growth Hormone Deficient Children
- Changes in Growth Hormone-Axis Function in Nutrient Excess or Deprivation
- Diabetes and Endocrine Disease