Korean J Radiol.
2011 Oct;12(5):579-587. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.579.
Radiofrequency Ablation for Treating Liver Metastases from a Non-Colorectal Origin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology and the Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 1116443
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.579
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We wanted to assess the safety and efficacy of performing radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in patients with non-colorectal liver metastases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this retrospective study, 25 patients with 40 hepatic metastases (M:F = 17:8; mean age, 57 years; tumor size, 0.5-5.0 cm) from a non-colorectal origin (stomach, biliary, breast, pancreas, kidney and skin) were treated with RFA. The RFA procedures were performed using either an internally cooled electrode or a clustered electrode under ultrasound or CT guidance. Contrast-enhanced CT scans were obtained immediately after RFA and follow-up CT scans were performed within three months after ablation and subsequently at least every six months. The intrahepatic disease-free interval was estimated and the overall survival from the time of the initial RFA was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS
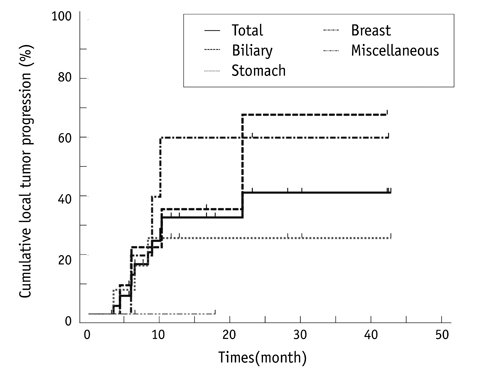
No intraprocedural deaths occurred, but four major complications developed, including abscesses (n = 3) and pneumothorax (n = 1). Technical effectiveness was determined on the initial follow-up images. During the follow-up period (range, 5.9-68.6 months; median time, 18.8 months) for 37 tumors in 22 patients where technical effectiveness was achieved, 12 lesions (32%, 12 of 37) showed local tumor progression and new intrahepatic metastases occurred in 13 patients (59%, 13 of 22). The median intrahepatic disease-free interval was 10.1 months. The 1-year, 3-year and 5-year overall survival rates after RFA were 86%, 39% and 19%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
RFA showed intermediate therapeutic effectiveness for the treatment of non-colorectal origin liver metastases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fong Y, Sun RL, Jarnagin W, Blumgart LH. An analysis of 412 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma at a Western center. Ann Surg. 1999. 229:790–799. discussion 799-800.2. Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology. 1999. 30:1434–1440.3. Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Long-term survival and pattern of recurrence after resection of small hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with preserved liver function: implications for a strategy of salvage transplantation. Ann Surg. 2002. 235:373–382.4. Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Franchini C, Pina CD, Lera J, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2005. 234:961–967.5. Choi D, Lim HK, Rhim H, Kim YS, Lee WJ, Paik SW, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma as a first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in a large single-institution series. Eur Radiol. 2007. 17:684–692.6. Fukuda S, Itamoto T, Nakahara H, Kohashi T, Ohdan H, Hino H, et al. Clinicopathologic features and prognostic factors of resected solitary small-sized hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005. 52:1163–1167.7. Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Meloni F, Dellanoce M, et al. Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients. Radiology. 2001. 221:159–166.8. Iannitti DA, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW, Murphy B. Hepatic radiofrequency ablation. Arch Surg. 2002. 137:422–426. discussion 427.9. Machi J, Oishi AJ, Sumida K, Sakamoto K, Furumoto NL, Oishi RH, et al. Long-term outcome of radiofrequency ablation for unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer: evaluation of prognostic factors and effectiveness in first- and second-line management. Cancer J. 2006. 12:318–326.10. Abitabile P, Hartl U, Lange J, Maurer CA. Radiofrequency ablation permits an effective treatment for colorectal liver metastasis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007. 33:67–71.11. Sorensen SM, Mortensen FV, Nielsen DT. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: long-term survival. Acta Radiol. 2007. 48:253–258.12. Gillams AR, Lees WR. Five-year survival in 309 patients with colorectal liver metastases treated with radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:1206–1213.13. Hur H, Ko YT, Min BS, Kim KS, Choi JS, Sohn SK, et al. Comparative study of resection and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. Am J Surg. 2009. 197:728–736.14. Oshowo A, Gillams A, Harrison E, Lees WR, Taylor I. Comparison of resection and radiofrequency ablation for treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg. 2003. 90:1240–1243.15. Veltri A, Sacchetto P, Tosetti I, Pagano E, Fava C, Gandini G. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: small size favorably predicts technique effectiveness and survival. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008. 31:948–956.16. Ahn YO. Cancer in Korea: present features. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002. 32:Suppl. S32–S36.17. Shin HR. Global activity of cancer registries and cancer control and cancer incidence statistics in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2008. 41:84–91.18. Khan SA, Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB, Beck A, Elliott P, Thomas HC. Changing international trends in mortality rates for liver, biliary and pancreatic tumours. J Hepatol. 2002. 37:806–813.19. Kim HO, Hwang SI, Hong HP, Yoo CH. Radiofrequency ablation for metachronous hepatic metastases from gastric cancer. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009. 19:208–212.20. An JY, Kim JY, Choi MG, Noh JH, Choi D, Sohn TS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatic metastasis from gastric adenocarcinoma. Yonsei Med J. 2008. 49:1046–1051.21. Carditello A, Scisca C, Stilo F, Parisi A, Basile M. The possible role of radiofrequency as complementary treatment of locally advanced gastric cancer. Ann Ital Chir. 2005. 76:39–41.22. Kim JH, Won HJ, Shin YM, Kim PN, Lee SG, Hwang S. Radiofrequency ablation for recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after curative resection. Eur J Radiol. 2010. Epub ahead of print.23. Carrafiello G, Lagana D, Cotta E, Mangini M, Fontana F, Bandiera F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: preliminary experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010. 33:835–839.24. Sofocleous CT, Nascimento RG, Gonen M, Theodoulou M, Covey AM, Brody LA, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the management of liver metastases from breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 189:883–889.25. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Meloni F, Ierace T, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of liver metastases from breast cancer: initial experience in 24 patients. Radiology. 2001. 220:145–149.26. Lawes D, Chopada A, Gillams A, Lees W, Taylor I. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) as a cytoreductive strategy for hepatic metastasis from breast cancer. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006. 88:639–642.27. Gunabushanam G, Sharma S, Thulkar S, Srivastava DN, Rath GK, Julka PK, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases from breast cancer: results in 14 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007. 18:67–72.28. Rath GK, Julka PK, Thulkar S, Sharma DN, Bahl A, Bhatnagar S. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastasis: results of treatment in forty patients. J Cancer Res Ther. 2008. 4:14–17.29. Penka I, Kaplan Z, Sefr R, Sirotek L, Eber Z, Ondrak M. Use of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of malignant liver lesions. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008. 55:562–567.30. Mazzaglia PJ, Berber E, Milas M, Siperstein AE. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of neuroendocrine liver metastases: a 10-year experience evaluating predictors of survival. Surgery. 2007. 142:10–19.31. Fan WJ, Wu PH, Zhang L, Huang JH, Zhang FJ, Gu YK, et al. Radiofrequency ablation as a treatment for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. 14:4540–4545.32. Gervais DA, Arellano RS, Mueller PR. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of ovarian cancer metastasis to the liver: indications, outcomes, and role in patient management. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 187:746–750.33. Yokoyama T, Egami K, Miyamoto M, Watanabe H, Hasegawa H, Iida S, et al. Percutaneous and laparoscopic approaches of radiofrequency ablation treatment for liver cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2003. 10:425–427.34. Kim SW, Rhim H, Park M, Kim H, Kim YS, Choi D, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas adjacent to the gallbladder with internally cooled electrodes: assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:366–376.35. Kang TW, Rhim H, Kim EY, Kim YS, Choi D, Lee WJ, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for the hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:34–42.36. Yoo CH, Noh SH, Shin DW, Choi SH, Min JS. Recurrence following curative resection for gastric carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2000. 87:236–242.37. Kwok CM, Wu CW, Lo SS, Shen KH, Hsieh MC, Lui WY. Survival of gastric cancer with concomitant liver metastases. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. 51:1527–1530.38. Okano K, Maeba T, Ishimura K, Karasawa Y, Goda F, Wakabayashi H, et al. Hepatic resection for metastatic tumors from gastric cancer. Ann Surg. 2002. 235:86–91.39. Sakamoto Y, Ohyama S, Yamamoto J, Yamada K, Seki M, Ohta K, et al. Surgical resection of liver metastases of gastric cancer: an analysis of a 17-year experience with 22 patients. Surgery. 2003. 133:507–511.40. Koga R, Yamamoto J, Ohyama S, Saiura A, Seki M, Seto Y, et al. Liver resection for metastatic gastric cancer: experience with 42 patients including eight long-term survivors. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007. 37:836–842.41. D'Angelica M, Gonen M, Brennan MF, Turnbull AD, Bains M, Karpeh MS. Patterns of initial recurrence in completely resected gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2004. 240:808–816.42. Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, Mori Y, Tonouchi H, Kusunoki M, et al. Prospective study of arterial infusion chemotherapy followed by radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver metastasis of gastric cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005. 16:1747–1751.43. Hasegawa S, Ikai I, Fujii H, Hatano E, Shimahara Y. Surgical resection of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: analysis of survival and postoperative complications. World J Surg. 2007. 31:1256–1263.44. Valverde A, Bonhomme N, Farges O, Sauvanet A, Flejou JF, Belghiti J. Resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a Western experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999. 6:122–127.45. El Rassi ZE, Partensky C, Scoazec JY, Henry L, Lombard-Bohas C, Maddern G. Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: presentation, diagnosis, pathology and management. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1999. 25:375–380.46. McMasters KM, Tuttle TM, Leach SD, Rich T, Cleary KR, Evans DB, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiation for extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Surg. 1997. 174:605–608. discussion 608-609.47. Khan SA, Thomas HC, Davidson BR, Taylor-Robinson SD. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 2005. 366:1303–1314.48. Vlastos G, Smith DL, Singletary SE, Mirza NQ, Tuttle TM, Popat RJ, et al. Long-term survival after an aggressive surgical approach in patients with breast cancer hepatic metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004. 11:869–874.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer: A Literature Review
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodule
- Liver Metastases in Colorectal Cancer
- Comparison of Radiofrequency Ablation and Resection for Hepatic Metastasis from Colorectal Cancer
- Ablation therapy for patients with colorectal liver metastases with and without extrahepatic metastases: evaluation of long-term outcomes and prognostic factors