Yonsei Med J.
2007 Feb;48(1):78-89. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.1.78.
Long-term Outcome after Prophylactic Lamivudine Treatment on Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hemakim@yumc. yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1093527
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.1.78
Abstract
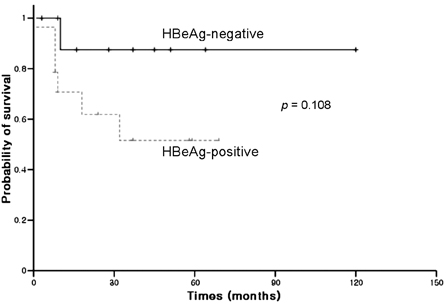
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is the frequent complication after cytotoxic chemotherapy in HBsAg-positive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) patients. Pre-chemotherapy viral load may be a risk factor and HBeAg-positive status is associated with increased viral load. The aim of this study was to investigate the long-term treatment outcome of lamivudine in preventing HBV reactivation and its associated morbidity according to HBeAg status. Twenty-four adult HBsAg-positive NHL patients were taken 100mg of lamivudine daily before the initiation of chemotherapy. The median duration of lamivudine therapy was 11.5 months (range: 1-54 months) and the median number of chemotherapy cycles was 6 (range: 1-16 cycles). The steroid containing chemotherapy regimens were used in 18 patients (75%), and the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody containing chemotherapy regimen was used in 6 patients (25%). Four patients received autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation without resultant HBV reactivation. Hepatitis related to HBV reactivation was developed in 1 patient among 14 HBeAg-positive patients and no one among 10 HBeAg-negative. One patient developed HBV reactivation after lamivudine withdrawal, and 4 patients developed the YMDD (tyrosine-methionine-aspartate-aspartate) mutation during lamivudine therapy. There were no statistical differences in HBV reactivation rate during chemotherapy according to the HBeAg status. Our results demonstrate that lamivudine should be considered preemptively before the chemotherapy for all HBsAg-positive NHL patients to prevent HBV reactivation, regardless of pre-chemotherapy HBeAg status. Finally, compared with the chronic hepatitis B patients, similar rate of HBV reactivation after lamivudine withdrawal and development of YMDD mutation was observed in NHL patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andre F. Hepatitis B epidemiology in Asia, the Middle East and Africa. Vaccine. 2000. 18:Suppl 1. S20–S22.
Article2. Liaw YF, Leung N, Guan R, Lau GK, Merican I, McCaughan G, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2005 update. Liver Int. 2005. 25:472–489.
Article3. Lok AS, McMahon BJ; Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Chronic hepatitis B: update of recommendations. Hepatology. 2004. 39:857–861.
Article4. Hoofnagle JH, Dusheiko GM, Schafer DF, Jones EA, Micetich KC, Young RC, et al. Reactivation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection by cancer chemotherapy. Ann Intern Med. 1982. 96:447–449.
Article5. Vento S, Cainelli F, Longhi MS. Reactivation of replication of hepatitis B and C viruses after immunosuppressive therapy: an unresolved issue. Lancet Oncol. 2002. 3:333–340.
Article6. Ohtsu T, Sai T, Oka M, Sugai Y, Tobinai K. Activation of hepatitis B virus infection by chemotherapy containing glucocorticoid in hepatitis B virus carriers with hematologic malignancies. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1991. 21:360–365.7. Xunrong L, Yan AW, Liang R, Lau GK. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation after cytotoxic or immunosuppressive therapy-pathogenesis and management. Rev Med Virol. 2001. 11:287–299.
Article8. Yeo W, Chan PK, Zhong S, Ho WM, Steinberg JL, Tam JS, et al. Frequency of hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study of 626 patients with identification of risk factors. J Med Virol. 2000. 62:299–307.
Article9. Cheng AL, Hsiung CA, Su IJ, Chen PJ, Chang MC, Tsao CJ, et al. Lymphoma Committee of Taiwan Cooperative Oncology Group. Steroid-free chemotherapy decreases risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in HBV-carriers with lymphoma. Hepatology. 2003. 37:1320–1328.
Article10. Leaw SJ, Yen CJ, Huang WT, Chen TY, Su WC, Tsao CJ. Preemptive use of interferon or lamivudine for hepatitis B reactivation in patients with aggressive lymphoma receiving chemotherapy. Ann Hematol. 2004. 83:270–275.
Article11. Simpson ND, Simpson PW, Ahmed AM, Nguyen MH, Garcia G, Keeffe EB, et al. Prophylaxis against chemotherapy-induced reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection with Lamivudine. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. 37:68–71.
Article12. Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1521–1531.
Article13. Idilman R. Lamivudine prophylaxis in HBV carriers with haemato-oncological malignancies who receive chemotherapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. 55:828–831.
Article14. Lau GK, Yiu HH, Fong DY, Cheng HC, Au WY, Lai LS, et al. Early is superior to deferred preemptive lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B patients undergoing chemotherapy. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:1742–1749.
Article15. Yeo W, Ho WM, Hui P, Chan PK, Lam KC, Lee JJ, et al. Use of lamivudine to prevent hepatitis B virus reactivation during chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004. 88:209–215.
Article16. Yeo W, Chan PK, Ho WM, Zee B, Lam KC, Lei KI, et al. Lamivudine for the prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B s-antigen seropositive cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:927–934.
Article17. Rossi G, Pelizzari A, Motta M, Puoti M. Primary prophylaxis with lamivudine of hepatitis B virus reactivation in chronic HbsAg carriers with lymphoid malignancies treated with chemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 2001. 115:58–62.
Article18. Shibolet O, Ilan Y, Gillis S, Hubert A, Shouval D, Safadi R. Lamivudine therapy for prevention of immunosuppressive-induced hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Blood. 2002. 100:391–396.
Article19. Song BC, Cui XJ, Kim H. Hepatitis B virus genotypes in Korea: an endemic area of hepatitis B virus infection. Intervirology. 2005. 48:133–137.
Article20. Zhong S, Yeo W, Schroder C, Chan PK, Wong WL, Ho WM, et al. High hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA viral load is an important risk factor for HBV reactivation in breast cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Viral Hepat. 2004. 11:55–59.
Article21. Yeo W, Chan PK, Zhong S, Ho WM, Steinberg JL, Tam JS, et al. Frequency of hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study of 626 patients with identification of risk factors. J Med Virol. 2000. 62:299–307.
Article22. Tsutsumi Y, Kawamura T, Saitoh S, Yamada M, Obara S, Miura T, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in a case of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma treated with chemotherapy and rituximab: necessity of prophylaxis for hepatitis B virus reactivation in rituximab therapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. 45:627–629.
Article23. Tsutsumi Y, Tanaka J, Kawamura T, Miura T, Kanamori H, Obara S, et al. Possible efficacy of lamivudine treatment to prevent hepatitis B virus reactivation due to rituximab therapy in a patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2004. 83:58–60.
Article24. Ma SY, Lau GK, Cheng VC, Liang R. Hepatitis B reactivation in patients positive for hepatitis B surface antigen undergoing autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003. 44:1281–1285.
Article25. Hui CK, Cheung WW, Au WY, Lie AK, Zhang HY, Yueng YH, et al. Hepatitis B reactivation after withdrawal of pre-emptive lamivudine in patients with haematological malignancy on completion of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Gut. 2005. 54:1597–1603.
Article26. Song BC, Suh DJ, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS. Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion after lamivudine therapy is not durable in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea. Hepatology. 2000. 32:803–806.
Article27. Paik YH, Chung HY, Ryu WS, Lee KS, Lee JS, Kim JH, et al. Emergence of YMDD motif mutant of hepatitis B virus during short-term lamivudine therapy in South Korea. J Hepatol. 2001. 35:92–98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of successful allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a HBV-positive severe aplastic anemia patient with prophylactic lamivudine treatment
- The Prophylactic Use of Lamivudine Can Maintain Dose-Intensity of Adriamycin in Hepatitis-B Surface Antigen (HBs Ag)-positive Patients with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Who Receive Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
- A Case of Reactivation of Hepatitis B and Fulminant Hepatitis which developed 3 months following Chemotherapy Including Rituximab in a Patient with Lymphoma
- Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in a Surface Antigen-negative and Antibody-positive Patient after Rituximab Plus CHOP Chemotherapy
- The management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B in Korean children