J Vet Sci.
2006 Sep;7(3):299-301. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.299.
Canine renal failure syndrome in three dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Pathology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea. jeongks@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1089918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.299
Abstract
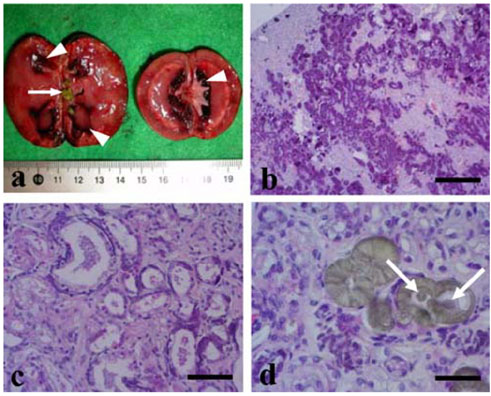
- Three dead dogs were brought to the College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University for study. Clinically, all the dogs showed emaciation, anorexia, depression, hemorrhagic vomiting and diarrhea for 7~10 days before death. All the clinical signs were first noted for about one month after feeding the dogs with commercial diets. At necropsy, all 3 dogs had severe renal damage with the same green-yellowish colored nephroliths in the renal pelvis. They also showed systemic hemorrhage and calcification of several organs, which might have been induced by uremia. Microscopically, necrosis, calcification and calculi were detected in the renal tubules, and especially in the proximal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney. These findings were supportive of a mycotoxic effect, and especially on their kidneys. However, the precise cause of the toxic effect in these cases of canine renal failure could not be determined.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cowell RL, Tyler RD, Meinkoth JH. Cowell RK, Tyler RD, Meinkoth JH, editors. Urinary sediment and cytology of the urinary tract. Diagnostic Cytology and Hematology of the Dog and Cat. 1999. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;222–224.2. Creppy EE. Update of survey, regulation and toxic effects of mycotoxins in Europe. Toxicol Lett. 2002. 127:19–28.
Article3. Gupta J, Pathak B, Sethi N, Vora VC. Histopathology of Mycotoxicosis produced in Swiss albino mice by metabolites of some fungal isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981. 41:752–757.
Article4. Huff JE. Carcinogenicity of ochratoxin A in experimental animals. IARC Sci Publ. 1991. 115:229–244.5. Jones TC, Hunt RD, King NW. Jones TC, Hunt RD, King NW, editors. Diseases caused by fungi. Veterinary Pathology. 1997. 6th ed. Baltimore, MD: Willams & Wilkins;535–547.6. Ling GV, Franti CE, Ruby AL, Johnson DL, Thurmond M. Urolithiasis in dogs. I: Mineral prevalence and interrelations of mineral composition, age, and sex. Am J Vet Res. 1998. 59:624–629.7. MaGavin MD, Carlton WW, Zachary JF. MaGavin MD, Carlton WW, Zachary JF, editors. Liver, biliary system, and exocrine pancreas. Thomson's Special Veterinary Pathology. 2001. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;110.8. Maia PP, Pereira Bastos de Siqueira ME. Occurrence of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in some Brazilian pet foods. Food Addit Contam. 2002. 19:1180–1183.9. Marquardt RR, Frohlich AA. A review of recent advances in understanding ochratoxicosis. J Anim Sci. 1992. 70:3968–3988.
Article10. Pitt JI. Toxigenic fungi: which are important? Med Mycol. 2000. 38:17–22.
Article11. Razzazi E, Bohm J, Grajewski J, Szczepaniak K, Kubber-Heiss AJ, Iben CH. Residues of ochratoxin A in pet foods, canine and feline kidneys. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2001. 85:212–216.
Article12. Scudamore KA, Hetmanski MT, Nawaz S, Naylor J, Rainbird S. Determination of mycotoxins in pet foods sold for domestic pets and wild birds using linked-column immunoassay clean-up and HPLC. Food Addit Contam. 1997. 14:175–186.
Article13. Voss KA, Riley RT, Norred WP, Bacon CW, Meredith FI, Howard PC, Plattner RD, Collins TF, Hansen DK, Porter JK. An overview of rodent toxicities: liver and kidney effects of fumonisins and Fusarium moniliforme. Environ Health Perspect. 2001. 109:259–266.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hematologic and hemodynamic findings during hemodialysis in 13 beagle dogs
- Modeling of transmission pathways on canine heartworm dynamics
- Detection of canine respiratory coronavirus from dogs with respiratory disease
- Concentrations of strontium, barium, cadmium, copper, zinc, manganese, chromium, antimony, selenium, and lead in the liver and kidneys of dogs according to age, gender, and the occurrence of chronic kidney disease
- Detection of viral infections in wild Korean raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides koreensis)