J Vet Sci.
2011 Sep;12(3):281-286. 10.4142/jvs.2011.12.3.281.
Sedative and analgesic effects of intravenous xylazine and tramadol on horses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Surgery/Anesthesiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. inhyunglee@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1067401
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2011.12.3.281
Abstract
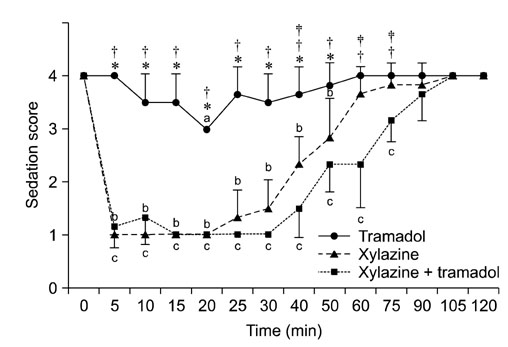
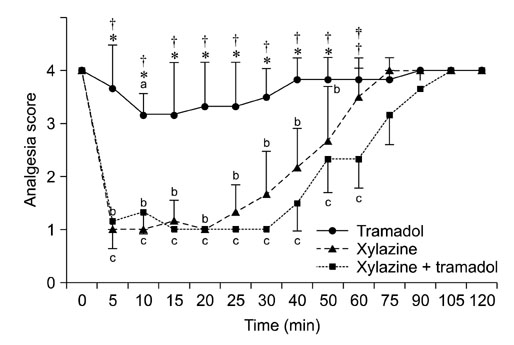
- This study was performed to evaluate the sedative and analgesic effects of xylazine (X) and tramadol (T) intravenously (IV) administered to horses. Six thoroughbred saddle horses each received X (1.0 mg/kg), T (2.0 mg/kg), and a combination of XT (1.0 and 2.0 mg/kg, respectively) IV. Heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), rectal temperature (RT), indirect arterial pressure (IAP), capillary refill time (CRT), sedation, and analgesia (using electrical stimulation and pinprick) were measured before and after drug administration. HR and RR significantly decreased from basal values with X and XT treatments, and significantly increased with T treatment (p < 0.05). RT and IAP also significantly increased with T treatment (p < 0.05). CRT did not change significantly with any treatments. The onset of sedation and analgesia were approximately 5 min after both X and XT treatments; however, the XT combination produced a longer duration of sedation and analgesia than X alone. Two horses in the XT treatment group displayed excited transient behavior within 5 min of drug administration. The results suggest that the XT combination is useful for sedation and analgesia in horses. However, careful monitoring for excited behavior shortly after administration is recommended.
MeSH Terms
-
Analgesics, Opioid/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Animals
Blood Pressure
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Heart Rate
Horses/*physiology
Hypnotics and Sedatives/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Male
Respiratory Rate
Tramadol/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Xylazine/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Sedative, analgesic, behavioral and clinical effects of intravenous nalbuphine-xylazine combination in camels (Camelus dromedarius)
Ahmed H. Khalil, Atef S. Abd Al-Galil, Ahmed A. Sabek, Mohamed M. Zeineldin, Seham Y. Abo-Kora
J Vet Sci. 2019;20(5):. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e55.
Reference
-
1. Bryant CE, England GC, Clarke KW. Comparison of the sedative effects of medetomidine and xylazine in horses. Vet Rec. 1991. 129:421–423.
Article2. Carregaro AB, Luna SPL, Mataqueiro MI, de Queiroz-Neto A. Effects of buprenorphine on nociception and spontaneous locomotor activity in horses. Am J Vet Res. 2007. 68:246–250.
Article3. DeRossi R, Jorge TP, Ossuna MR, Carneiro RPB, Alves OD, Zanenga NF. Sedation and pain management with intravenous romifidine-butorphanol in standing horses. J Equine Vet Sci. 2009. 29:75–81.
Article4. Dhanjal JK, Wilson DV, Robinson E, Tobin TT, Dirokulu L. Intravenous tramadol: effects, nociceptive properties, and pharmacokinetics in horses. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009. 36:581–590.
Article5. England GCW, Clarke KW. Alpha2 adrenoceptor agonists in the horse-a review. Br Vet J. 1996. 152:641–657.6. England GC, Clarke KW, Goossens L. A comparison of the sedative effects of three alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists (romifidine, detomidine and xylazine) in the horse. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1992. 15:194–201.
Article7. García-Quetglas E, Azanza JR, Sádaba B, Muñoz MJ, Gil I, Campanero MA. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol enantiomers and their respective phase I metabolites in relation to CYP2D6 phenotype. Pharmacol Res. 2007. 55:122–130.
Article8. Giorgi M, Soldani G, Manera C, Ferrarini PL, Sgorbini M, Saccomanni G. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol and its metabolites M1, M2 and M5 in horses following intravenous, immediate release (fasted/fed) and sustained release single dose administration. J Equine Vet Sci. 2007. 27:481–488.
Article9. Kerr DD, Jones EW, Huggins K, Edwards WC. Sedative and other effects of xylazine given intravenously to horses. Am J Vet Res. 1972. 33:525–532.10. LeBlanc PH. Chemical restraint for surgery in the standing horse. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 1991. 7:521–533.
Article11. Mastrocinque S, Fantoni DT. A comparison of preoperative tramadol and morphine for the control of early postoperative pain in canine ovariohysterectomy. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2003. 30:220–228.
Article12. Moens Y, Lanz F, Doherr MG, Schatzmann U. A comparison of the antinociceptive effects of xylazine, detomidine and romifidine on experimental pain in horses. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2003. 30:183–190.
Article13. Natalini CC, Robinson EP. Effects of epidural opioid analgesics on heart rate, arterial blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temperature, and behavior in horses. Vet Ther. 2003. 4:364–375.14. Natalini CC, Robinson EP. Evaluation of the analgesic effects of epidurally administered morphine, alfentanil, butorphanol, tramadol, and U50488H in horses. Am J Vet Res. 2000. 61:1579–1586.
Article15. Pypendop BH, Siao KT, Ilkiw JE. Effects of tramadol hydrochloride on the thermal threshold in cats. Am J Vet Res. 2009. 70:1465–1470.
Article16. Raffa RB, Friderichs E, Reimann W, Shank RP, Codd EE, Vaught JL. Opioid and nonopioid components independently contribute to the mechanism of action of tramadol, an 'atypical' opioid analgesic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992. 260:275–285.17. Rohrbach H, Korpivaara T, Schatzmann U, Spadavecchia C. Comparison of the effects of the alpha-2 agonists detomidine, romifidine and xylazine on nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation in horses. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009. 36:384–395.
Article18. Scott LJ, Perry CM. Tramadol: a review of its use in perioperative pain. Drugs. 2000. 60:139–176.19. Shilo Y, Britzi M, Eytan B, Lifschitz T, Soback S, Steinman A. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol in horses after intravenous, intramuscular and oral administration. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2008. 31:60–65.
Article20. Yamashita K, Tsubakishita S, Futaok S, Ueda I, Hamaguchi H, Seno T, Katoh S, Izumisawa Y, Kotani T, Muir WW. Cardiovascular effects of medetomidine, detomidine and xylazine in horses. J Vet Med Sci. 2000. 62:1025–1032.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sedative, analgesic, behavioral and clinical effects of intravenous nalbuphine-xylazine combination in camels (Camelus dromedarius)
- Intravenous Regional Anesthesia Using Mepivacaine and Tramadol
- The Effect of Intrathecal Tramadol and Clonidine on Saddle Block with Heavy Bupivacaine
- The Combined Effect of Epidural Tramadol and Clonidine for Postoperative Analgesia
- Tramadol as a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blocker of Peripheral Sodium Channels Na v 1.7 and Na v 1.5