Predictive Risk Factors for Refracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon 301-725, Korea. sky20525@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon 301-725, Korea.
- 3Kangwon National University School of Medicine and Hospital, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Chuncheon 200-722, Korea.
- KMID: 2266810
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.844
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To identify risk factors for developing a vertebral refracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. METHOD: A retrospective analysis of 60 patients who had undergone percutaneous vertebroplasty between January 2008 and April 2010 was conducted. All patients were observed for a 1 year follow-up period, and fracture was defined when it was both clinically reported and radiographically confirmed. Twenty-seven patients with a refractured vertebra and 33 patients without a refracture were included. Of the 60 patients, 20 presented with a refracture from a cemented vertebra, whereas the remaining 40 patients did not. Clinical, imaging and procedure-related factors for each group were analyzed by the Fisher's exact, chi-square, and the Mann-Whitney U-tests.
RESULTS
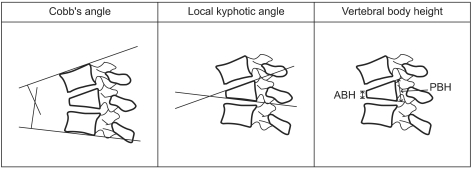
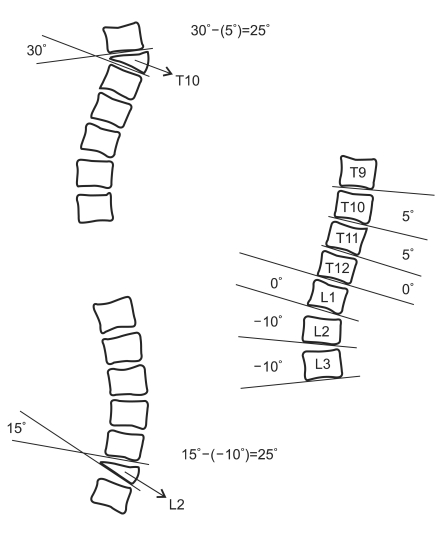
Local kyphotic angle and sagittal index were significant as a result of researching various risk factors related to vertebral refracture (p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively) and refracture from a cemented vertebra itself (p=0.004, p<0.001, respectively). Other factors were not significant.
CONCLUSION
Patients who had a high preoperative local kyphotic angle and a high sagittal index required a close follow-up and attention.
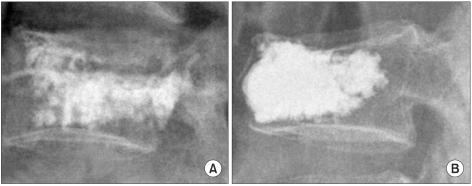
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Clinical Results and Efficacy of Selective Nerve Root Blocks with Vertebroplasty in Treatment of Patients with Osteoporotic Compression Fracture Accompanied by Spinal Stenosis
Sang-Hyuk Min, Sung-Hyun Yoon
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2014;49(3):202-208. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.3.202.Risk Factors for Subsequent Vertebral Compression Fracture Following Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
Sung Soo Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Jung Hoon Kim, Dong Ju Lim, Byung Wan Choi, Jin Hwan Kim, Jin Hyok Kim, Jun Seung Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2016;51(6):479-485. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.6.479.Early Onset Subsequent Vertebral Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Verteroplasty
Jong-Kil Kim, Byeong-Yeol Choi, Young-Chul Park, Dong-Hyun Kim
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2019;54(1):24-29. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.1.24.Gradual Height Decrease of Augmented Vertebrae after Vertebroplasty at the Thoracolumbar Junction
Han San Oh, Tae Wan Kim, Hyun Gon Kim, Kwan Ho Park
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(1):18-21. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.1.18.
Reference
-
1. Sohn JM, Kim KW, Ha KY, Ha NK, Kim YH, Kim JH. Risk factors for the progressive osteoporotic spinal fracture. J Korean Spine Surg. 2009; 16:153–159.
Article2. Kim SW, Chung YK. Long term follow-up of osteoporotic vertebral fractures according to the morphologic analysis of fracture pattern. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2000; 7:611–617.3. Kallmes DF, Jensen ME. Percutaneous vertebroplasty. Radiology. 2003; 229:27–36. PMID: 14519867.
Article4. Lin WC, Lee YC, Lee CH, Kuo YL, Cheng YF, Lui CC, Cheng TT. Refractures in cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:592–599. PMID: 18204942.
Article5. Ahn Y, Lee JH, Lee HY, Lee SH, Keem SH. Predictive factors for subsequent vertebral fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9:129–136. PMID: 18764744.
Article6. Grados F, Depriester C, Cayrolle G, Hardy N, Deramond H, Fardellone P. Long-term observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39:1410–1414. PMID: 11136886.
Article7. Trout AT, Kallmes DF, Kaufmann TJ. New fractures after vertebroplasty: adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:217–223. PMID: 16418388.8. Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, Pfiefer BA, Pazianos AG, Choi IS. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology. 2003; 226:119–124. PMID: 12511679.
Article9. Heo DH, Kuh SU. Progressive, repeated lumbar compression fracture at the same level after vertebral kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate cement. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 6:559–562. PMID: 17561745.10. Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, Heini PF. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:748–752. PMID: 12188498.11. Kim SH, Kang HS, Choi JA, Ahn JM. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol. 2004; 45:440–445. PMID: 15323398.
Article12. Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL. Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR. 2004; 25:175–180. PMID: 14970015.13. Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Juttmann JR, van der Graaf Y, Fransen H, Lampmann LE. The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006; 17:71–76. PMID: 16415135.
Article14. Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Dion JE. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1897–1904. PMID: 9403451.15. Tanigawa N, Komemushi A, Kariya S, Kojima H, Shomura Y, Omura N, Sawada S. Relationship between cement distribution pattern and new compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR. 2007; 189:W348–W352. PMID: 18029848.
Article16. Farcy JP, Weidenbaum M, Glassman SD. Sagittal index in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine. 1990; 15:958–965. PMID: 2259988.
Article17. Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR. 2001; 22:373–381. PMID: 11156786.18. Choi DJ, Ahn DK, Lee S, Park KY, Jun YW, Kim KS. Operative treatment of delayed collapse of osteoporotic vertebral fracture with claudication: transpedicular bone graft and pedicle screw fixation. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2007; 14:73–78.19. Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, Hanley DA, Barton I, Broy SB, Licata A, Benhamou L, Geusens P, Flowers K, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001; 285:320–323. PMID: 11176842.
Article20. Syed MI, Patel NA, Jan S, Harron MS, Morar K, Shaikh A. New symptomatic vertebral compression fractures within a year following vertebroplasty in osteoporotic women. AJNR. 2005; 26:1601–1604. PMID: 15956537.21. Lin WC, Cheng TT, Lee YC, Wang TN, Cheng YF, Lui CC, Yu CY. New vertebral osteoporotic compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: retrospective analysis of risk factors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:225–231. PMID: 18341954.22. Teng MM, Wei CJ, Wei LC, Luo CB, Lirng JF, Chang FC, Liu CL, Chang CY. Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR. 2003; 24:1893–1900. PMID: 14561624.23. Kim SK, Kim MH, Lee SC, Min SH, Lee JW. The effect of vertebral wedge angle to the change of kyphotic angle by the posterior instrumentation method in thoracolumbar spine fracture. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2009; 16:160–166.
Article24. Son KH, Chung NS, Jeon CH. Measurement of vertebral compression and kyphosis in the thoraco lumbar and lumbar fractures. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2010; 17:120–126.25. Ratcliffe JF. Arterial changes in the human vertebral body associated with aging. The ratios of peripheral to central arteries and arterial coiling. Spine. 1986; 11:235–240. PMID: 3715624.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predictive Risk Factors for Refracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Lumbar Root Injury by the Leakage of Bone Cement after the Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A case report
- Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Considerations for the Safe Procedures
- Fatal Hemothorax Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture