Korean J Transplant.
2023 Dec;37(4):293-298. 10.4285/kjt.23.0044.
Delayed diagnosis of bronchobiliary fistula complicating a pediatric living donor liver transplantation: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Hepatology, Centre for Liver and Biliary Sciences, Max Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- 2Department of Liver Transplant Surgery, Centre for Liver and Biliary Sciences, Max Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi, India
- KMID: 2550241
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.23.0044
Abstract
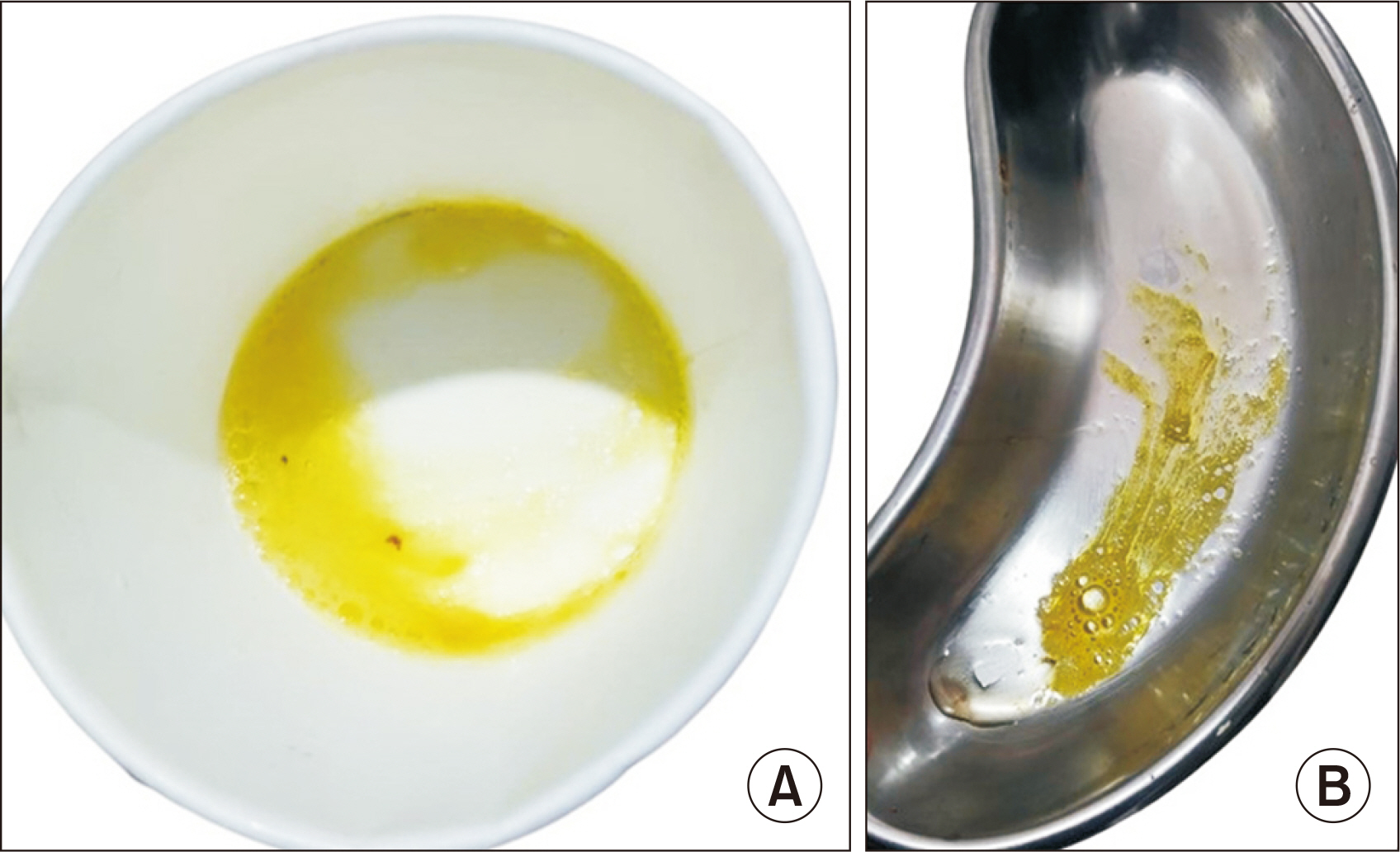
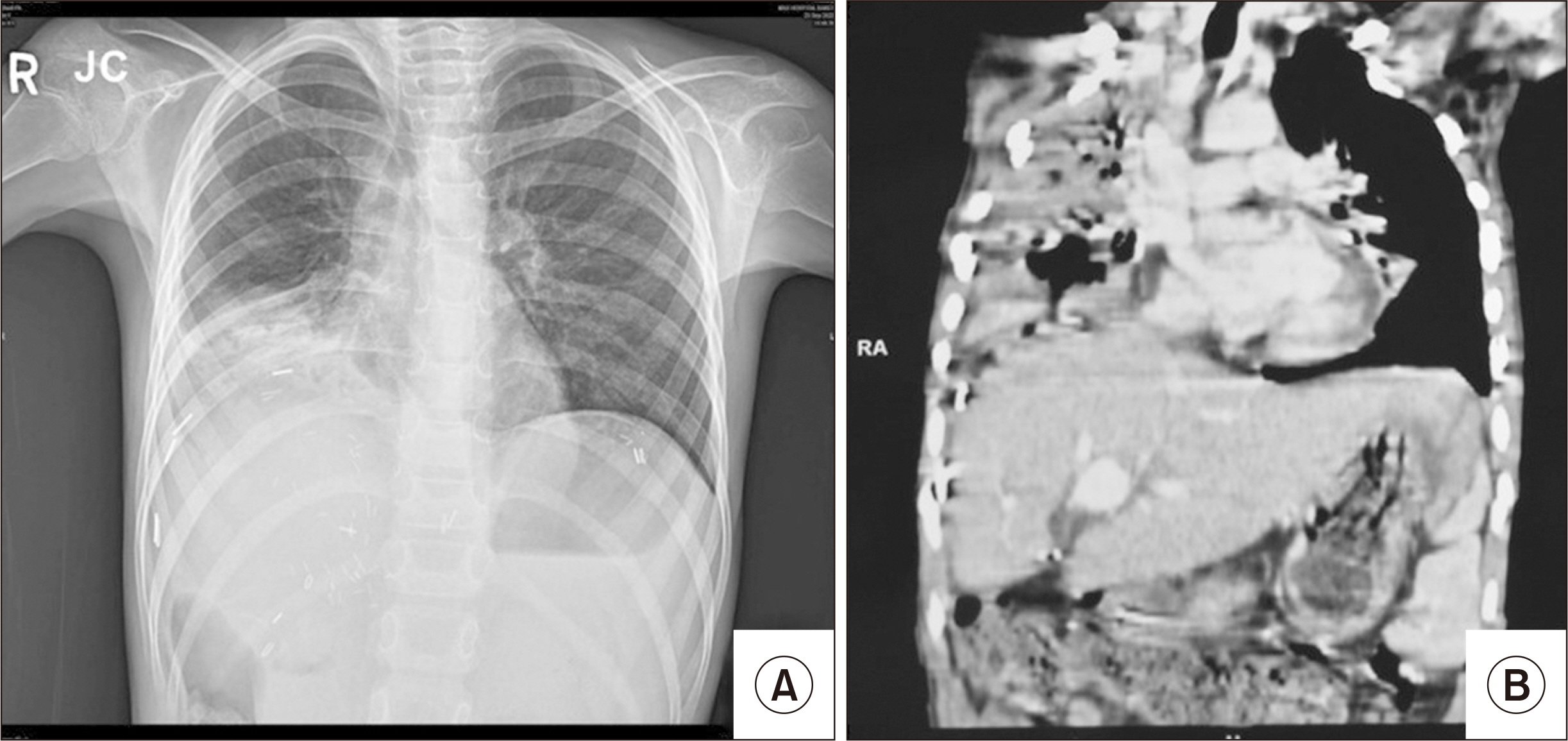
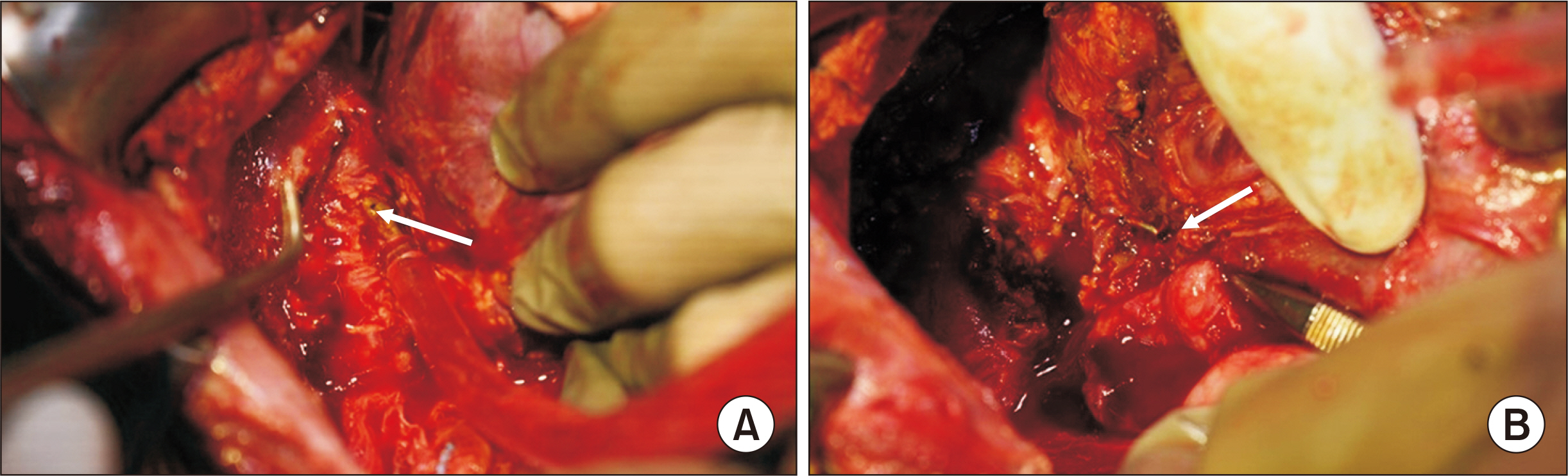
- Bronchobiliary fistula (BBF) is a very rare condition in children. Only a few pediatric BBF cases have been reported, in the context of a ruptured hydatid cyst or liver abscess. BBF after living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) has not been reported in the pediatric literature. We report a 7-year-old female child with Wilson disease, who developed BBF post-LDLT. She had a clinically uneventful course in the immediate post-transplant pe-riod. She was readmitted on postoperative day (POD) 75 with a productive cough and respiratory difficulty, which was diagnosed as bilioptysis secondary to BBF. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography was attempted but failed. Exploratory laparotomy showed a fistula from the strictured biliary anastomotic site to the right thoracic cavity; it was excised, and a Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy was performed. She tol-erated the procedure well and remained clinically well on follow-up through POD 185. BBF is extremely rare in children. This is the first case report of BBF in a child following LDLT. BBF requires a high index of suspicion for a timely intervention to prevent subsequent complications.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peacock TB. 1850; Case in which hydatids were expectorated, and one of suppuration in a hydatid cyst of the liver communicating with the lungs. Edinb Med Surg J. 74:33–46.2. Kumar P, Mehta P, Ismail J, Agarwala S, Jana M, Lodha R, et al. 2015; Brocho-biliary fistula: a rare complication after ruptured liver abscess in a 3½ year old child. Lung India. 32:489–91. DOI: 10.4103/0970-2113.164157. PMID: 26628766. PMCID: PMC4587006.3. Yang L, Guo Z, Yang L, Ju W, Wang D, He X. Orthotopic liver transplantation in a pediatric patient with iatrogenic Budd-Chiari syndrome complicated by bronchobiliary fistula. Pediatr Transplant. 2017; 21:DOI: 10.1111/petr.13008. PMID: 28745424.4. Chaing MH, Chen CW, Lu CH. 2020; Successful treatment of bronchobiliary fistula after living donor liver transplantation: a case report. Transplant Proc. 52:2778–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.01.171. PMID: 32434746.5. Yeatman CF, Fisher RA, Carucci LR, Halvorsen RA. 2004; Bronchobiliary fistula after liver transplantation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 28:717–20. DOI: 10.1097/01.rct.0000131583.52386.cf. PMID: 15480050.6. Eryigit H, Oztas S, Urek S, Olgac G, Kurutepe M, Kutlu CA. 2007; Management of acquired bronchobiliary fistula: 3 case reports and a literature review. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2:52. DOI: 10.1186/1749-8090-2-52. PMID: 18053192. PMCID: PMC2217537.7. Liao GQ, Wang H, Zhu GY, Zhu KB, Lv FX, Tai S. 2011; Management of acquired bronchobiliary fistula: a systematic literature review of 68 cases published in 30 years. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3842–9. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3842. PMID: 21987628. PMCID: PMC3181447.8. Pappas SC, Sasaki A, Minuk GY. 1982; Bronchobiliary fistula presenting as cough with yellow sputum. N Engl J Med. 307:1027. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198210143071623. PMID: 7110295.9. Pandey VK, Prabhudesai A, Goyal S, Nasa V, Yadav V, Singh SA, et al. 2022; Safety and feasibility of immediate tracheal extubation of small pediatric patients after living donor liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 26:e14401. DOI: 10.1111/petr.14401. PMID: 36177941.10. Pandey Y, Varma S, Chikkala BR, Acharya R, Verma S, Balradja I, et al. 2020; Outcome of pediatric liver transplants in patients with less than 10 kg of body weight is not worse. Exp Clin Transplant. 18:707–11. DOI: 10.6002/ect.2020.0308. PMID: 33187463.11. Rahimi MT, Hares R, Rahman H, Hoshang MS, Hofiani SM. 2023; Management of acquired bronchobiliary fistula: a case report. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 95:102669. DOI: 10.1016/j.epsc.2023.102669.12. Kuo YS, Lee SC, Chang H, Hsieh CB, Huang TW. 2014; Thoracoscopic surgery for bronchobiliary fistula: a case report. J Cardiothorac Surg. 9:139. DOI: 10.1186/s13019-014-0139-z. PMID: 25230847. PMCID: PMC4172870.13. Hai S, Iimuro Y, Hirano T, Suzumura K, Yada A, Fujimoto J. 2016; Bronchobiliary fistula caused after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report. Surg Case Rep. 2:147. DOI: 10.1186/s40792-016-0273-z. PMID: 27921278. PMCID: PMC5138177.14. Miranda García M, Martakoush María A, Cobos Briz M. 2018; Bronchobiliary fistula, a late complication of liver surgery. Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). 54:285–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.arbr.2017.09.015. PMID: 29102340.15. Lazarou V, Moris D, Papalampros A, Tsilimigras DI, Karachaliou GS, Petrou A. 2019; Bronchobiliary fistula after hepatectomy: a case report and review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. 11:602–6. DOI: 10.3892/mco.2019.1935. PMID: 31798877. PMCID: PMC6870047.16. Moumen M, el Fares F. 1991; Bilio-bronchial fistula of hydatid origin. Apropos of 8 cases. J Chir (Paris). 128:188–92.17. Thrumurthy SG, Anuruddha AH, De Zoysa MI, Samarasekera DN. ERCP for the treatment of traumatic biliobronchial and biliocutaneous fistulas. Endoscopy. 2011; 43 Suppl 2 UCTN:E42. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1255898. PMID: 21287444.18. Deshmukh H, Prasad S, Patankar T, Patel V. 1999; Percutaneous management of a broncho-biliary fistula complicating ruptured amebic liver abscess. Am J Gastroenterol. 94:289–90.19. Kostopanagiotou K, George RS, Kefaloyannis E, Papagiannopoulos K. 2015; Novel technique in managing bronchobiliary fistula in adults: endobronchial embolization using silicone spigots in 2 cases. Ann Thorac Med. 10:67–8.20. Tocchi A, Mazzoni G, Miccini M, Drumo A, Cassini D, Colace L, et al. 2007; Treatment of hydatid bronchobiliary fistulas: 30 years of experience. Liver Int. 27:209–14. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01435.x. PMID: 17311615.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric liver transplantation in Korea: long-term outcomes and allocations
- Why is my phlegm green? A rare case of bronchobiliary fistula
- Liver retransplantation for adult recipients
- Percutaneous Treatment of a Bronchobiliary Fistula Caused by Cholelithiasis: Case Report
- Surgical Treatment of Bronchobiliary Fistula with Pulmonary Resection and Omentopexy