Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Jun;28(2):87-97. 10.6065/apem.2346074.037.
Cushing disease in pediatrics: an update
- Affiliations
-
- 1Universidad Cientifica del Sur, Lima, Perú
- 2School of Medicine, National University of Trujillo, Trujillo, Perú
- 3Division of Medicine, Hospital de Apoyo Chepén, Chepén, Perú
- 4Division of Endocrinology, Clínica Javier Prado, Lima, Perú
- 5Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Hospital Nacional Hipólito Unanue, Lima, Perú
- 6Division of Family Medicine, Hospital de Apoyo Chepén, Chepén, Perú
- 7Division of Pediatrics, Hospital Belén de Trujillo, Trujillo, Perú
- KMID: 2543289
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2346074.037
Abstract
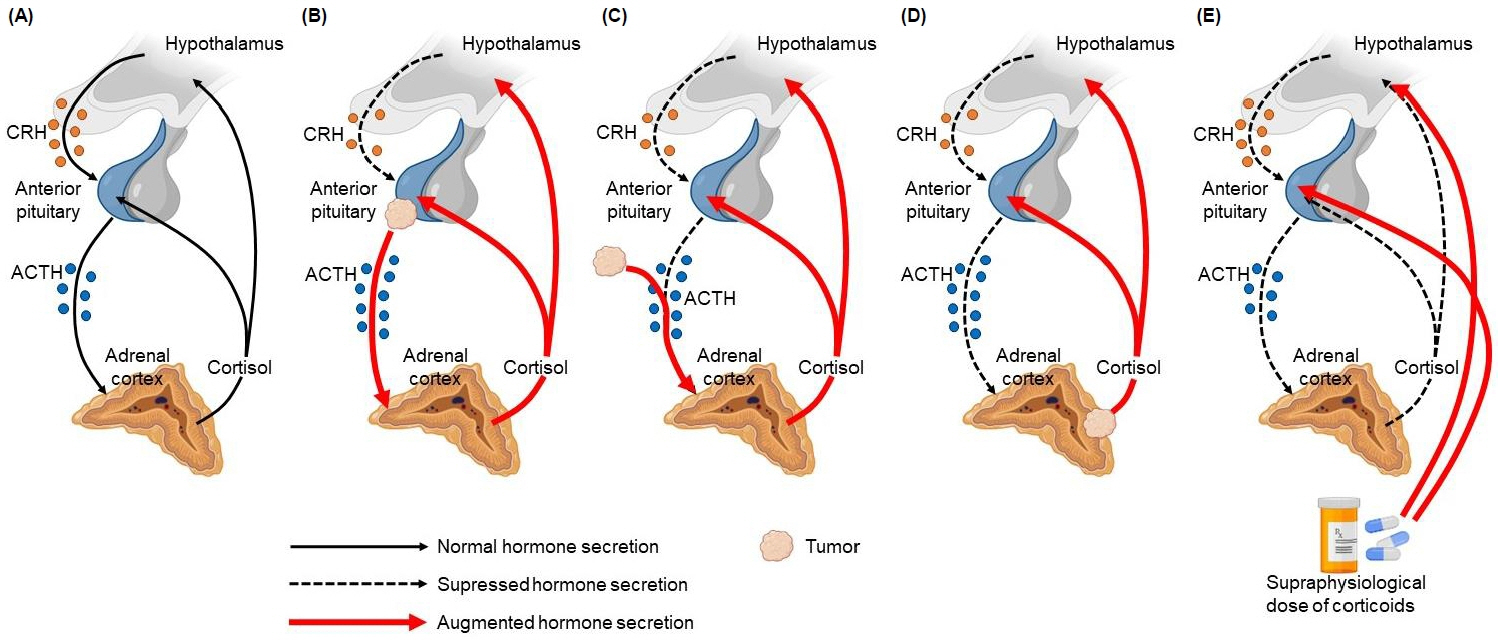
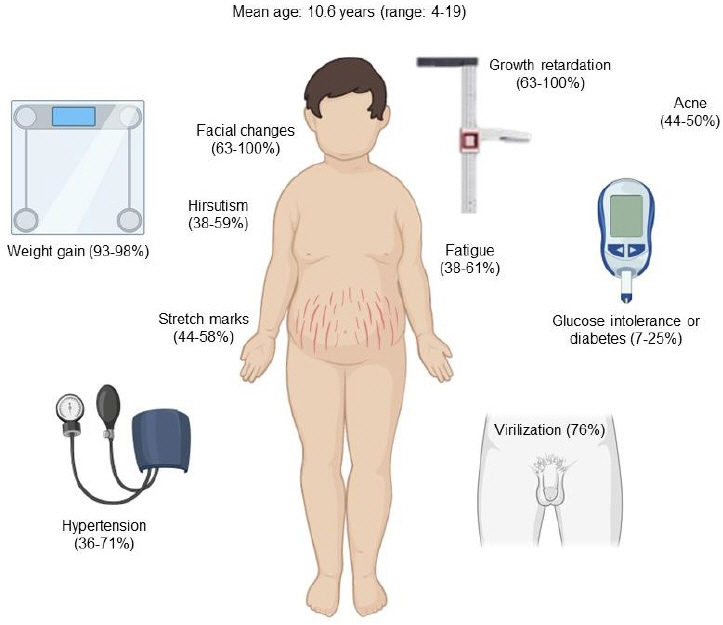
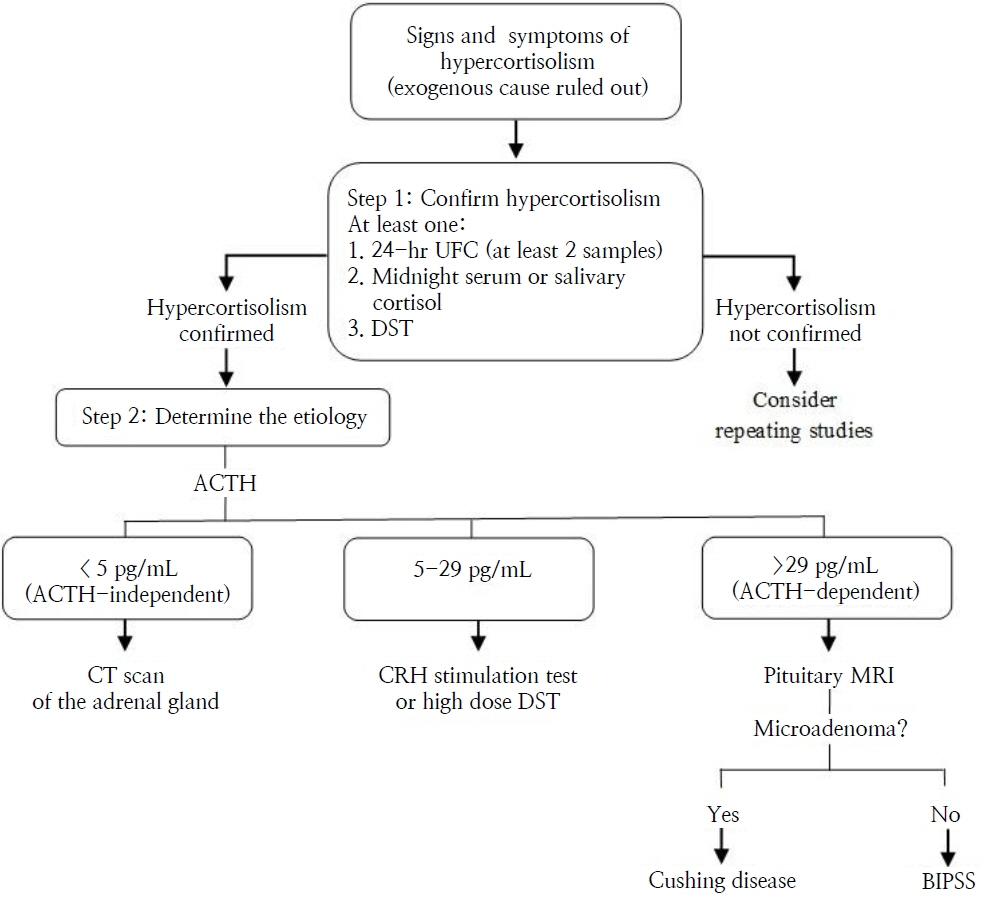
- Cushing disease (CD) is the main cause of endogenous Cushing syndrome (CS) and is produced by an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-producing pituitary adenoma. Its relevance in pediatrics is due to the retardation of both growth and developmental processes because of hypercortisolism. In childhood, the main features of CS are facial changes, rapid or exaggerated weight gain, hirsutism, virilization, and acne. Endogenous hypercortisolism should be established after exogenous CS has been ruled out based on 24-hour urinary free cortisol, midnight serum or salivary cortisol, and dexamethasone suppression test; after that, ACTH dependence should be established. The diagnosis should be confirmed by pathology. The goal of treatment is to normalize cortisol level and reverse the signs and symptoms. Treatment options include surgery, medication, radiotherapy, or combined therapy. CD represents a challenge for physicians owing to its multiple associated conditions involving growth and pubertal development; thus, it is important to achieve an early diagnosis and treatment in order to control hypercortisolism and improve the prognosis. Its rarity in pediatric patients has led physicians to have limited experience in its management. The objective of this narrative review is to summarize the current knowledge about the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of CD in the pediatric population.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lodish MB, Keil MF, Stratakis CA. Cushing’s syndrome in pediatrics: an update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2018; 47:451–62.2. Dutta K, Dutta H. Cushing’s syndrome in a child. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2021; 65:101749.3. Ferrigno R, Hasenmajer V, Caiulo S, Minnetti M, Mazzotta P, Storr HL, et al. Paediatric Cushing's disease: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical management and outcome. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021; 22:817–35.4. Zheng X, Wang H, Zhang W, Feng S, Liu Y, Li S, et al. Diagnosis, manifestations, laboratory investigations, and prognosis in pediatric and adult Cushing's disease in a large center in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:749246.5. Storr HL, Savage MO. Management of endocrine disease: paediatric Cushing’s disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015; 173:R35–45.6. Pasternak-Pietrzak K, Moszczyńska E, Jurkiewicz E, Szalecki M. Paediatric Cushing’s disease - a literature review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical symptoms, and diagnostics. Endokrynol Pol. 2020; 71:87–95.7. Storr HL, Alexandraki KI, Martin L, Isidori AM, Kaltsas GA, Monson JP, et al. Comparisons in the epidemiology, diagnostic features and cure rate by transsphenoidal surgery between paediatric and adult-onset Cushing's disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011; 164:667–74.8. Tabarin A, Assié G, Barat P, Bonnet F, Bonneville JF, Borson-Chazot F, et al. Consensus statement by the French Society of Endocrinology (SFE) and French Society of Pediatric Endocrinology & Diabetology (SFEDP) on diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2022; 83:119–41.9. Ragnarsson O, Olsson DS, Chantzichristos D, Papakok-kinou E, Dahlqvist P, Segerstedt E, et al. The incidence of Cushing's disease: a nationwide Swedish study. Pituitary. 2019; 22:179–86.10. Nayak S, Dabadghao P, Dixit P, Dwivedi V, Srivastava AK, Behari S. Cushing's disease in children: a review. Neurol India. 2020; 68:52–65.11. Baethge C, Goldbeck-Wood S, Mertens S. SANRA—a scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res Integr Peer Rev. 2019; 4:5.12. Raff H, Carroll T. Cushing’s syndrome: from physiological principles to diagnosis and clinical care. J Physiol. 2015; 593:493–506.13. Lacroix A, Feelders RA, Stratakis CA, Nieman LK. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet Lond Engl. 2015; 386:913–27.14. Stratakis CA. Cushing syndrome in pediatrics. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012; 41:793–803.15. Hernández-Ramírez LC, Stratakis CA. Genetics of Cushing's syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2018; 47:275–97.16. Albani A, Theodoropoulou M, Reincke M. Genetics of Cushing's disease. Clin Endocrinol. 2018; 88:3–12.17. Savage MO, Storr HL. Fundamental principles of clinical and biochemical evaluation underlie the diagnosis and therapy of Cushing's syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 27:1029–31.18. Güemes M, Murray PG, Brain CE, Spoudeas HA, Peters CJ, Hindmarsh PC, et al. Management of Cushing syndrome in children and adolescents: experience of a single tertiary centre. Eur J Pediatr. 2016; 175:967–76.19. Batista DL, Riar J, Keil M, Stratakis CA. Diagnostic tests for children who are referred for the investigation of Cushing syndrome. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:e575. –86.20. Gafni RI, Papanicolaou DA, Nieman LK. Nighttime salivary cortisol measurement as a simple, noninvasive, outpatient screening test for Cushing's syndrome in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2000; Jul. 137:30–5.21. Shapiro L, Elahi S, Riddoch F, Perry LA, Martin L, Akker SA, et al. Investigation for Paediatric Cushing’s Syndrome Using Twenty-Four-Hour Urinary Free Cortisol Determination. Horm Res Paediatr. 2016; 86:21–6.22. Guaraldi F, Storr HL, Ghizzoni L, Ghigo E, Savage MO. Paediatric pituitary adenomas: a decade of change. Horm Res Paediatr. 2014; 81:145–55.23. Shah NS, Lila A. Childhood Cushing disease: a challenge in diagnosis and management. Horm Res Paediatr. 2011; 76 Suppl 1:65–70.24. Turan H, Çatli G, Kardelen AD, Böer E, Akinci A, Çetinkaya S, et al. Diagnostic Value of Bilateral Petrosal Sinus Sampling in Children with Cushing Disease: A Multi-center Study. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2022; Mar. 3. 14:2936.25. Lonser RR, Wind JJ, Nieman LK, Weil RJ, DeVroom HL, Oldfield EH. Outcome of surgical treatment of 200 children with Cushing's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:892–901.26. Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Murad MH, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, et al. Treatment of Cushing's Syndrome: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:2807–31.27. Tatsi C, Stratakis CA. Pediatric Cushing syndrome; an overview. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2019; 17:100–9.28. Stratakis CA. An update on Cushing syndrome in pediatrics. Ann Endocrinol. 2018; 79:125–31.29. Buchfelder M, Schlaffer S. Pituitary surgery for Cushing's disease. Neuroendocrinology. 2010; 92:102–6.30. Marino AC, Taylor DG, Desai B, Jane JA Jr. Surgery for pediatric pituitary adenomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019; 30:465–71.31. Kanter AS, Diallo AO, Jane JA Jr, Sheehan JP, Asthagiri AR, Oskouian RJ, et al. Single-center experience with pediatric Cushing's disease. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103(5 Suppl):413–20.32. Shirvani M, Motiei-Langroudi R, Sadeghian H. Outcome of microscopic transsphenoidal surgery in Cushing disease: a case series of 96 patients. World Neurosurg. 2016; 87:170–5.33. Lu L, Wan X, Xu Y, Chen J, Shu K, Lei T. Prognostic factors for recurrence in pituitary adenomas: recent progress and future directions. Diagnostics. 2022; 12:977.34. Locatelli D, Massimi L, Rigante M, Custodi V, Paludetti G, Castelnuovo P, et al. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery for sellar tumors in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 74:1298–302.35. Storr HL, Drake WM, Evanson J, Matson M, Berney DM, Grossman AB, et al. Endonasal endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: early experience and outcome in paediatric Cushing's disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 80:270–6.36. Bora SK, Suri A, Khadgawat R, Tandon N, Suri V, Chand Sharma M, et al. Management of Cushing's disease: changing trend from microscopic to endoscopic surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020; 134:e46–54.37. Broersen LHA, Biermasz NR, van Furth WR, de Vries F, Verstegen MJT, Dekkers OM, et al. microscopic transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pituitary. 2018; 21:524–34.38. Katznelson L. Bilateral adrenalectomy for Cushing's disease. Pituitary. 2015; 18:269–73.39. Guerin C, Taieb D, Treglia G, Brue T, Lacroix A, Sebag F, et al. Bilateral adrenalectomy in the 21st century: when to use it for hypercortisolism? Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016; 23:R131–42.40. Thomas CG, Smith AT, Benson M, Griffith J. Nelson's syndrome after Cushing’s disease in childhood: a continuing problem. Surgery. 1984; 96:1067–77.41. Hopwo o d NJ, Kenny FM. Incidence of Nels on's syndrome after adrenalectomy for Cushing's disease in children: results of a nationwide survey. Am J Dis Child. 1977; 131:1353–6.42. Castinetti F, Brue T. Gamma knife for Cushing disease -time for a reappraisal? Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017; 13:628–9.43. Martirossian AN, Jacob R, Riley KO, Porterfield JR, Vaughan TB. The Novel use of stereotactic radiotherapy for remnant adrenal tissue in Nelson syndrome. AACE Clin Case Rep. 2020; 6:e33–6.44. Minniti G, Gilbert DC, Brada M. Modern techniques for pituitary radiotherapy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2008; 10:135.45. Storr HL, Plowman PN, Carroll PV, François I, Krassas GE, Afshar F, et al. Clinical and endocrine responses to pituitary radiotherapy in pediatric Cushing's disease: an effective second-line treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:34–7.46. Acharya SV, Gopal RA, Goerge J, Menon PS, Bandgar TR, Shah NS. Radiotherapy in paediatric Cushing’s disease: efficacy and long term follow up of pituitary function. Pituitary. 2010; 13:293–7.47. Feelders RA, Newell-Price J, Pivonello R, Nieman LK, Hofland LJ, Lacroix A. Advances in the medical treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:300–12.48. Tucker WS Jr, Snell BB, Island DP, Gregg CR. Reversible adrenal insufficiency induced by ketoconazole. JAMA. 1985; 253:2413–4.49. Best TR, Jenkins JK, Murphy FY, Nicks SA, Bussell KL, Vesely DL. Persistent adrenal insufficiency secondary to low-dose ketoconazole therapy. Am J Med. 1987; 82:676–80.50. European Medicines Agency. Ketoconazole: summary of product characteristics [Internet]. Amsterdam (Netherlands): European Medicines Agency;2022. [cited 2022 Dec 18]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ketoconazole-hra-epar-product-information_en.pdf.51. Medicines Committee of the Spanish Association of Pediatrics. Pediamécum [Internet]. Madrid (Spain): Medicines Committee of the Spanish Association of Pediatrics;2022. [cited 2022 Dec 18] Available from: https://www.aeped.es/comite-medicamentos/pediamecum/ketoconazol.52. Acquafredda A, Dammacco A, Cavallo T, Pesce S, Bafundi N, Dammacco F. Ketoconazole treatment of two adolescents with Cushing's disease. Pediatr Res. 1993; 33:S30.53. Carral F, Lechuga JL, Merino J, Caro J, Aguilar M. Therapeutic efficacy of ketoconazole in Cushing's syndrome. An Pediatr. 2000; 52:381–4.54. Ying YJ, Lu NX, Mei TQ, Yan ZS, De ZY. Ketoconazole associated hepatotoxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013; 26:605–10.55. Daniel E, Newell-Price JDC. Therapy of endocrine disease: steroidogenesis enzyme inhibitors in Cushing’s syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015; 172:R263–80.56. Wojcik M, Kalicka-Kasperczyk A, Luszawska-Kutrzeba T, Balwierz W, Starzyk JB. The first description of metyrapone use in severe Cushing Syndrome due to ectopic ACTH secretion in an infant with immature sacrococcygeal teratoma. Case Report. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015; 36:653–5.57. Verbeeten K, Hadjiyannakis S, Cameron M, McDonald J. Rectal metyrapone for treatment of hypercortisolism in an infant with McCune-Albright syndrome. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 22:233–6.58. HRA Pharma Rare Diseases. Metopirone® (metyrapone) capsules: US prescribing information [Internet]. Châtillon (Paris): HRA Pharma Rare Diseases;[cited 2022 Dec 20]. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/012911s036lbl.pdf.59. Al-Salama ZT. Metyrapone in Cushing's syndrome: a profile of its use. Drugs Ther Perspect. 2021; 37:393–406.60. Oddie PD, Albert BB, Hofman PL, Jefferies C, Laughton S, Carter PJ. Mitotane in the treatment of childhood adrenocortical carcinoma: a potent endocrine disruptor. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2018; 2018:18–0059.61. Kuhlen M, Mier P, Kunstreich M, Lessel L, Schneider D, Brecht I, et al. Key factors for effective mitotane therapy in children with adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2022; 29:545–55.62. Motte E, Rothenbuhler A, Gaillard S, Lahlou N, Teinturier C, Coutant R, et al. Mitotane (op'DDD) restores growth and puberty in nine children with Cushing's disease. Endocr Connect. 2018; 7:1280–7.63. Morgan FH, Laufgraben MJ. Mifepristone for management of Cushing’s syndrome. Pharmacother J Hum Pharmacol Drug Ther. 2013; 33:319–29.64. Pivonello R, Ferrigno R, De Martino MC, Simeoli C, Di Paola N, Pivonello C, et al. Medical treatment of Cushing's disease: an overview of the current and recent clinical trials. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020; 11:648.65. Banerjee RR, Marina N, Katznelson L, Feldman BJ. Mifepristone treatment of Cushing’s syndrome in a pediatric patient. Pediatrics. 2015; 136:e1377–81.66. European Medicines Agency. Osilodrostat (Isturisa®): summary of product characteristics [Internet]. Amsterdam (Netherlands): European Medicines Agency;2022. [cited 2022 Dec 18]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/isturisa-epar-product-information_en.pdf.67. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new treatment for adults with Cushing’s disease [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration;2022. [cited 2022 Dec 18]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-treatment-adults-cushings-disease.68. Meredith EL, Ksander G, Monovich LG, Papillon JP, Liu Q, Miranda K, et al. Discovery and in vivo evaluation of potent dual CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) and CYP11B1 inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013; 4:1203–7.69. Groselj U, Sikonja J, Battelino T. Osilodrostat for Cushing disease and its role in pediatrics. Horm Res Paediatr. 2022; Jan. 19. doi: 10.1159/000522054. [Epub].70. Recordati group. A phase II, Multicenter, open-label, non-comparative study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of osilodrostat in children and adolescent patients with Cushing's disease. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03708900 (Accessed December 20, 2022).71. Juszczak A, Ertorer ME, Grossman A. The therapy of Cushing’s disease in adults and children: an update. Horm Metab Res. 2013; 45:109–17.72. Güven A, Baltacıoğlu F, Dursun F, Cebeci AN, Kırmı zıbekmez H. Remission with cabergoline in adolescent boys with Cushing's disease. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013; 5:194–8.73. Yordanova G, Martin L, Afshar F, Sabin I, Alusi G, Plowman NP, et al. Long-term outcomes of children treated for Cushing's disease: a single center experience. Pituitary. 2016; 19:612–24.74. Bertrand A, Marec-Berard P, Raverot G, Trouillas J, Marabelle A. Cabergoline therapy of paraneoplastic Cushing syndrome in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010; 55:589–90.75. Pasternak-Pietrzak K, Moszczyńska E, Szalecki M. Treatment challenges in pediatric Cushing’s disease: review of the literature with particular emphasis on predictive factors for the disease recurrence. Endocrine. 2019; 66:125–36.76. Biller BM, Grossman AB, Stewart PM, Melmed S, Bertagna X, Bertherat J, et al. Treatment of adrenocorticotropin-dependent Cushing's syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:2454–62.77. Savage MO, Storr HL. Pediatric Cushing's disease: management Issues. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16(Suppl 2):S171–5.78. Batista DL, Oldfield EH, Keil MF, Stratakis CA. Postoperative testing to predict recurrent Cushing disease in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:2757–65.79. Lodish M, Dunn SV, Sinaii N, Keil MF, Stratakis CA. Recovery of the hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal axis in children and adolescents after surgical cure of Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:1483–91.80. Ironside N, Chatain G, Asuzu D, Benzo S, Lodish M, Sharma S, et al. Earlier post-operative hypocortisolemia may predict durable remission from Cushing's disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018; 178:255–63.81. He X, Findling JW, Auchus RJ. Glucocorticoid Withdrawal Syndrome following treatment of endogenous Cushing Syndrome. Pituitary. 2022; 25:393–403.82. Hochberg Z, Pacak K, Chrousos GP. Endocrine Withdrawal Syndromes. Endocr Rev. 2003; 24:523–38.83. Varlamov EV, Vila G, Fleseriu M. Perioperative management of a patient with Cushing disease. J Endocr Soc. 2022; 6:bvac010.84. Acree R, Miller CM, Abel BS, Neary NM, Campbell K, Nieman LK. Patient and provider perspectives on postsurgical recovery of Cushing syndrome. J Endocr Soc. 2021; 5:bvab109.85. Pasternak-Pietrzak K, Moszczyńska E, Roszkowski M, Szalecki M. Predictive factors for the recurrence of Cushing's disease after surgical treatment in childhood. Endokrynol Pol. 2020; 71:313–8.86. Pasternak-Pietrzak K, Moszczyńska E, Roszkowski M, Kot K, Marczak E, Grajkowska W, et al. Long-term outcome in patients after treatment for Cushing's disease in childhood. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0226033.87. Keil MF. Quality of life and other outcomes in children treated for Cushing syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:2667–78.88. Sippel RS, Elaraj DM, Kebebew E, Lindsay S, Tyrrell JB, Duh QY. Waiting for change: symptom resolution after adrenalectomy for Cushing’s syndrome. Surgery. 2008; 144:1054–60.89. Leong GM, Abad V, Charmandari E, Reynolds JC, Hill S, Chrousos GP, et al. Effects of child- and adolescent-onset endogenous Cushing syndrome on bone mass, body composition, and growth: a 7-year prospective study into young adulthood. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22:110–8.90. Lodish MB, Hsiao HP, Serbis A, Sinaii N, Rothenbuhler A, Keil MF, et al. Effects of Cushing disease on bone mineral density in a pediatric population. J Pediatr. 2010; 156:1001–5.91. Keil MF, Graf J, Gokarn N, Stratakis CA. Anthropometric measures and fasting insulin levels in children before and after cure of Cushing syndrome. Clin Nutr. 2012; 31:359–63.92. Magiakou MA, Mastorakos G, Zachman K, Chrousos GP. Blood pressure in children and adolescents with Cushing’s syndrome before and after Surgical Cure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:1734–8.93. Lodish MB, Sinaii N, Patronas N, Batista DL, Keil M, Samuel J, et al. Blood pressure in pediatric patients with Cushing syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:2002–8.94. Merke DP, Giedd JN, Keil MF, Mehlinger SL, Wiggs EA, Holzer S, et al. Children experience cognitive decline despite reversal of brain atrophy one year after resolution of Cushing syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:2531–6.95. Gkourogianni A, Sinaii N, Jackson SH, Karageorgiadis AS, Lyssikatos C, Belyavskaya E, et al. Pediatric Cushing disease: disparities in disease severity and outcomes in the Hispanic and African-American populations. Pediatr Res. 2017; 82:272–7.96. Gkourogianni A, Lodish MB, Zilbermint M, Lyssikatos C, Belyavskaya E, Keil MF, et al. Death in pediatric Cushing syndrome is uncommon but still occurs. Eur J Pediatr. 2015; 174:501–7.