Ewha Med J.
2022 Oct;45(4):e15. 10.12771/emj.2022.e15.
Aggressive Clinical Deterioration of Recurrent Extramammary Paget’s Disease: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Pathology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2534738
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2022.e15
Abstract
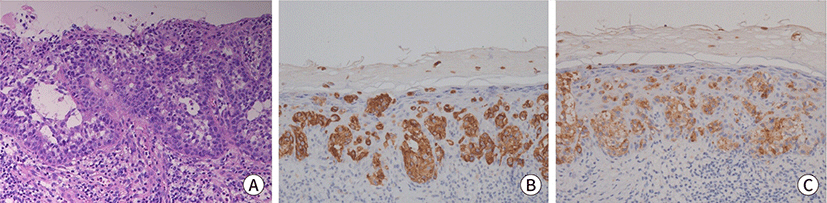
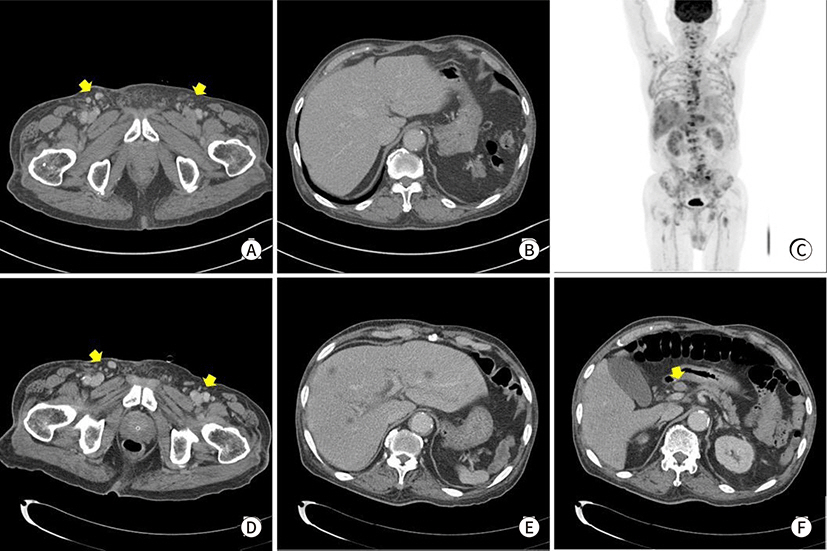
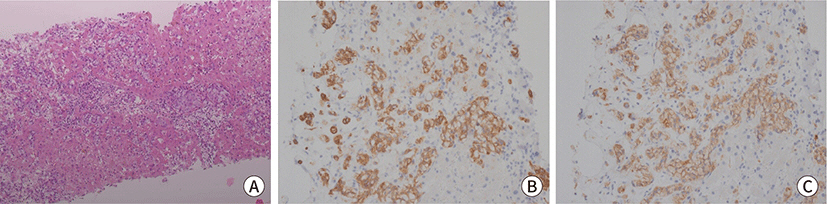
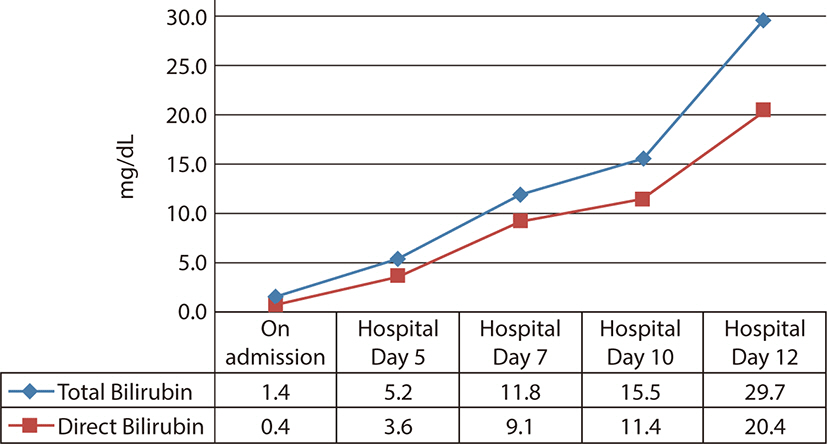
- Extramammary Paget’s Disease (EMPD) is a rare intraepithelial malignancy of apocrine bearing glands, which occur usually in the perianal region, vulva, scrotum, penis and ax-illa. Most of the disease are treated by surgical resection and the prognosis is generally good. Even though recurrent disease, it is usually slowly progressed with good prognosis. Here we describe the case of a 70-year-old male who has presented with initially just as an EMPD component of squamous cell carcinoma in inguinal skin, but he showed recur-rence of EMPD. The disease has progressed rapidly, finally he died of that EMPD in 2 months of recurrence. The purpose of this study is to report the rare case of fulminant disease course of EMPD after recurrence.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tanaka VDA, Sanches JA, Torezan L, Niwa AB, Festa Neto C. Mammary and extramammary Paget's disease: a study of 14 cases and the associated therapeutic difficulties. Clinics. 2009; 64(6):599–606. DOI: 10.1590/S1807-59322009000600018. PMID: 19578667. PMCID: PMC2705154.
Article2. Lopes Filho LL, Lopes IMRS, Lopes LRS, Enokihara MMSS, Michalany AO, Matsunaga N. Mammary and extramammary Paget's disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2015; 90(2):225–231. DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153189. PMID: 25830993. PMCID: PMC4371672.
Article3. Lloyd J, Flanagan AM. Mammary and extramammary Paget's disease. J Clin Pathol. 2000; 53(10):742–749. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.53.10.742. PMID: 11064666. PMCID: PMC1731095.
Article4. Yao H, Xie M, Fu S, Guo J, Peng Y, Cai Z, et al. Survival analysis of patients with invasive extramammary Paget disease: implications of anatomic sites. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18(1):403. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4257-1. PMID: 29636019. PMCID: PMC5894213.5. Chan JYW, Li GKH, Chung JHP, Chow VLY. Extramammary Paget’s disease: 20 years of experience in Chinese population. Int J Surg Oncol. 2012; 2012:416418. DOI: 10.1155/2012/416418. PMID: 22500220. PMCID: PMC3303748.6. Baldovini C, Betts CM, Reggiani C, Reggiani M, Foschini MP. Ultrastructural examination of a case of pagetoid Bowen disease exhibiting immunohistochemical features in common with extramammary Paget disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015; 37(7):e83–e86. DOI: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000123. PMID: 24786579.7. Guerra R, Misra S. Management of extramammary Paget's disease: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2013; 2013:436390. DOI: 10.1155/2013/436390. PMID: 24349803. PMCID: PMC3848195.8. Mehrtens SH, Tharakaram S. Extramammary Paget’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376(17):e35–e35. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm1610755. PMID: 28445673.
Article9. Nitecki R, Davis M, Watkins JC, Wu YE, Vitonis AF, Muto MG, et al. Extramammary Paget disease of the vulva: a case series examining treatment, recurrence, and malignant transformation. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018; 28(3):632–638. DOI: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001189. PMID: 29324542.
Article10. Zhang N, Gong K, Zhang X, Yang Y, Na Y. Extramammary Paget's disease of scrotum—report of 25 cases and literature review. In : Droller MJ, editor. Urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations. Amsterdam: Elsevier;2010. p. 28–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.07.002. PMID: 18805708.11. Fukuda K, Funakoshi T. Metastatic extramammary Paget’s disease: pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approach. Front Oncol. 2018; 8:38. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00038. PMID: 29503810. PMCID: PMC5820294.12. Chanda JJ. Extramammary Paget's disease: prognosis and relationship to internal malignancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985; 13(6):1009–1014. DOI: 10.1016/S0190-9622(85)70254-X.
Article13. Karam A, Dorigo O. Treatment outcomes in a large cohort of patients with invasive extramammary Paget's disease. Gynecol Oncol. 2012; 125(2):346–351. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.01.032. PMID: 22293043.
Article14. Ichiyama T, Gomi D, Fukushima T, Kobayashi T, Sekiguchi N, Sakamoto A, et al. Successful and long-term response to trastuzumab plus paclitaxel combination therapy in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive extramammary Paget's disease: a case report and review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017; 7(5):763–766. DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1422. PMID: 29181166. PMCID: PMC5700281.
Article15. Chang K, Li GX, Kong YY, Shen XX, Qu YY, Jia ZW, et al. Chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 are associated with tumor aggressiveness and prognosis in extramammary Paget disease. J Cancer. 2017; 8(13):2471–2477. DOI: 10.7150/jca.19127. PMID: 28900484. PMCID: PMC5595076.
Article