J Korean Diabetes.
2021 Jun;22(2):153-159. 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.2.153.
A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Presenting as a Deterioration in Glycemic Control in a Patient with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Presbyterian Medical Center, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2526194
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2021.22.2.153
Abstract
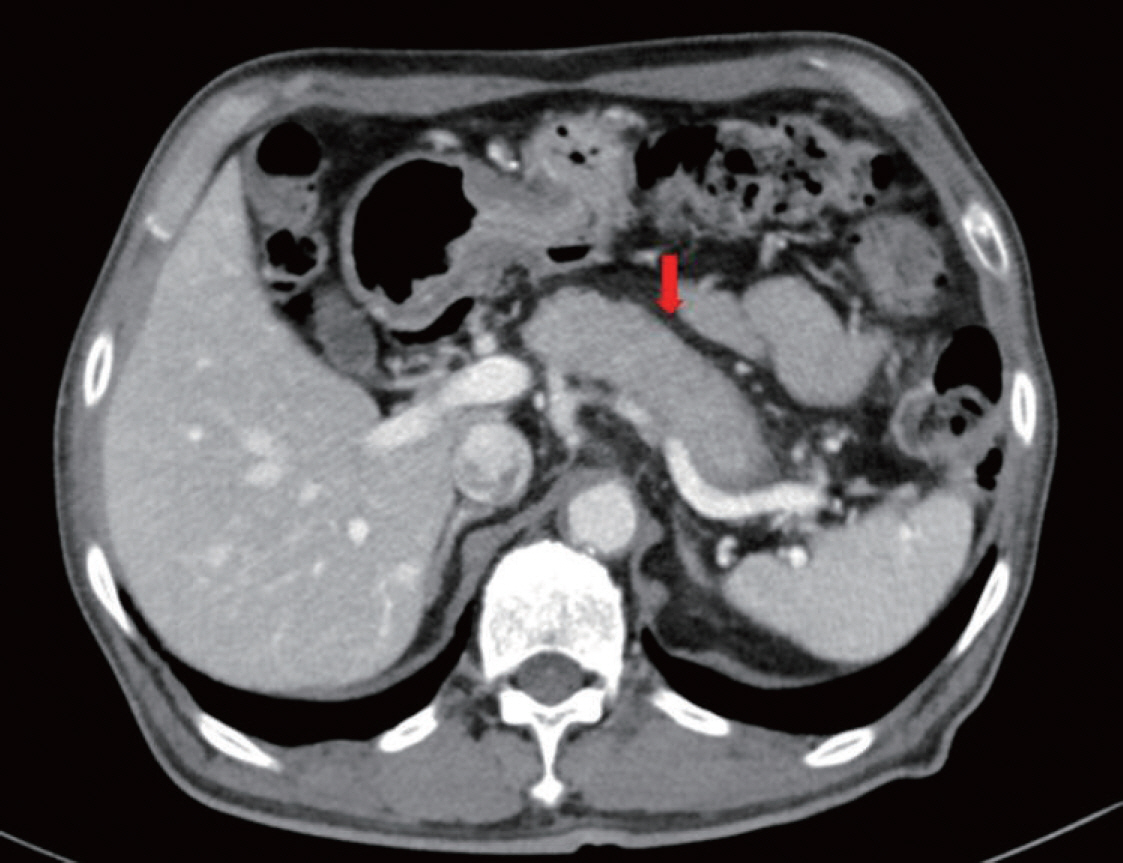
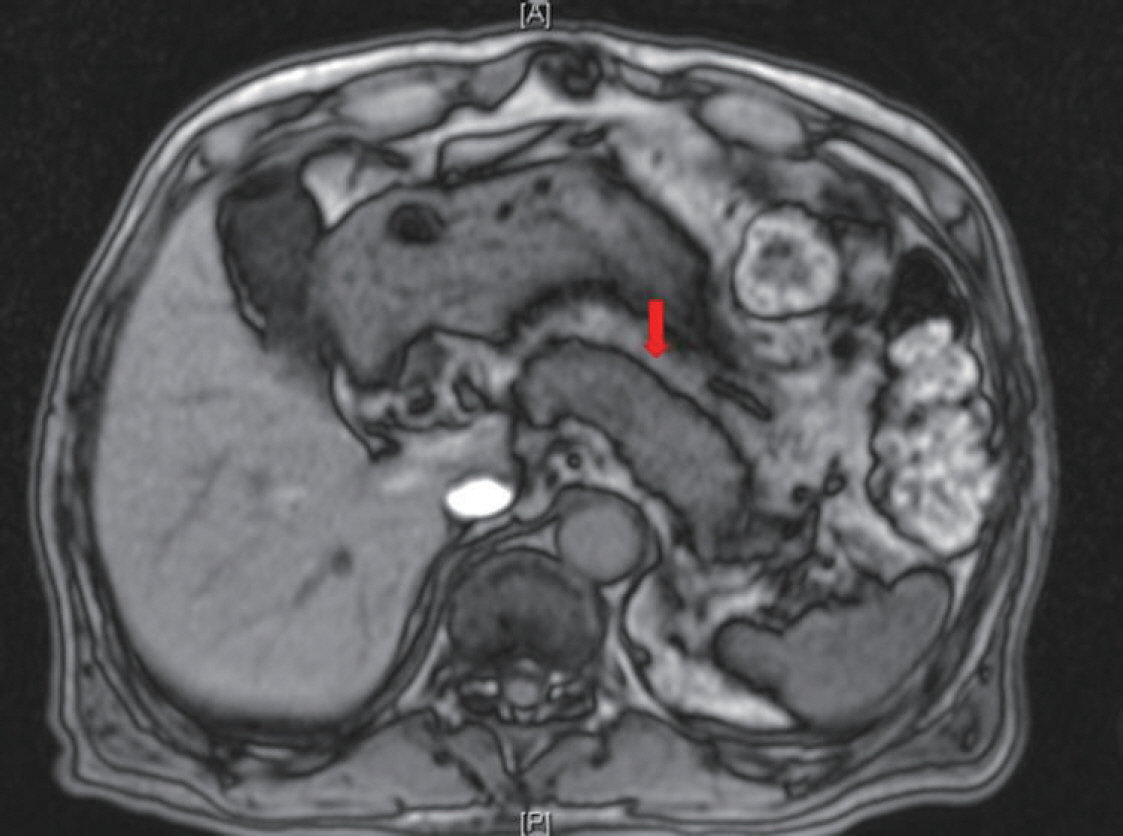
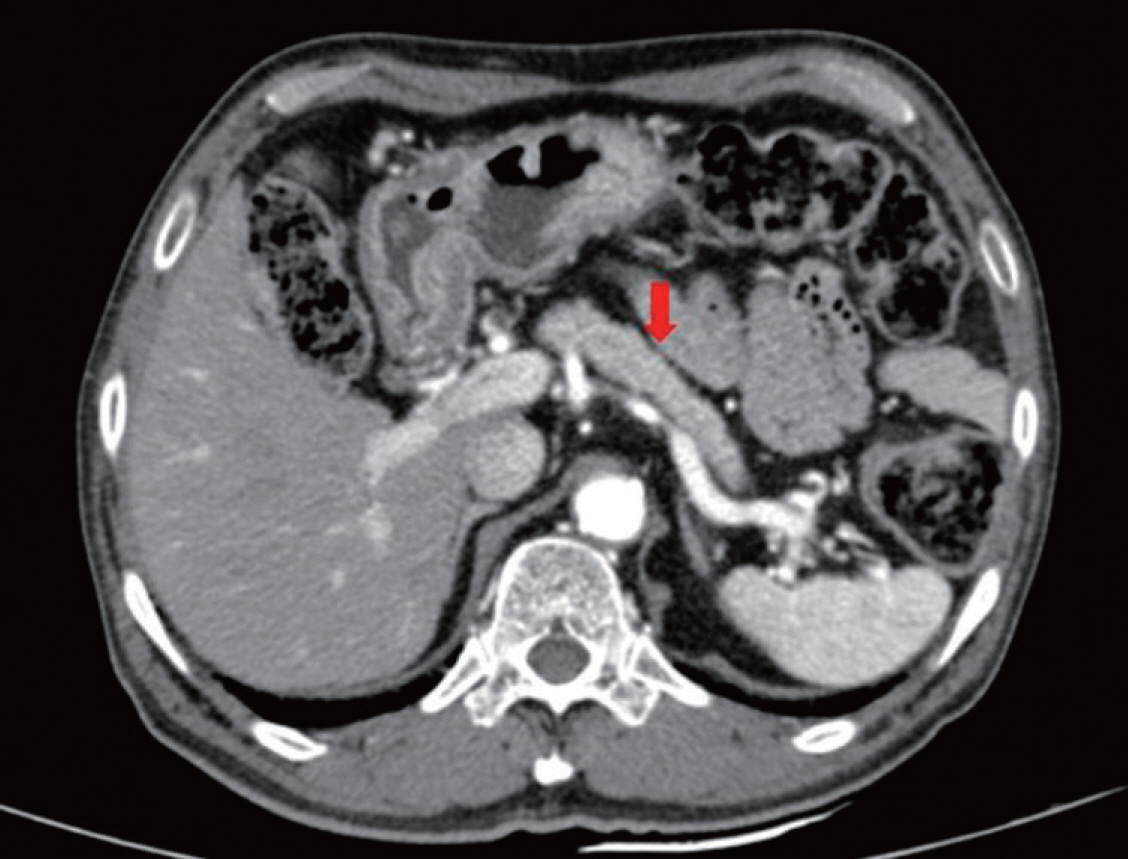
- The present article demonstrates an unusual case of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), focusing on the cause of deterioration in glycemic control and weight loss in a patient with pre-existing type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). A 67-year-old man was diagnosed with type 2 DM 23 years prior and presented with weight loss of approximately 6 kg over a period of 3 months and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of 9.1%. His carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) level was elevated to 158.54 U/mL (normal, 0~37 U/mL). Considering these findings, we needed to rule out hidden malignancy. Computed tomography of the abdomen showed diffuse swelling of the pancreas uncinated process. The serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) level was elevated to 2,418 mg/dL (normal, 700~1,600 mg/dL), and IgG4 level was elevated to 1,115.0 mg/dL (normal range, 3.9~86.4 mg/dL). This case highlights that AIP should be considered as a cause of significant weight loss and a deterioration in glycemic control in patients with DM. Furthermore, a pancreatic imaging study should be considered in clinical practice to differentiate pancreatic cancer and AIP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–8.
Article2. Nishimori I, Tamakoshi A, Kawa S, Tanaka S, Takeuchi K, Kamisawa T, et al. Influence of steroid therapy on the course of diabetes mellitus in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: findings from a nationwide survey in Japan. Pancreas. 2006; 32:244–8.
Article3. Nishino T, Toki F, Oyama H, Shimizu K, Shiratori K. Long-term outcome of autoimmune pancreatitis after oral prednisolone therapy. Intern Med. 2006; 45:497–501.
Article4. Maire F, Le Baleur Y, Rebours V, Vullierme MP, Couvelard A, Voitot H, et al. Outcome of patients with type 1 or 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:151–6.
Article5. Miyamoto Y, Kamisawa T, Tabata T, Hara S, Kuruma S, Chiba K, et al. Short and long-term outcomes of diabetes mellitus in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis after steroid therapy. Gut Liver. 2012; 6:501–4.
Article6. Lee HW, Moon SH, Kim MH, Cho DH, Jun JH, Nam K, et al. Relapse rate and predictors of relapse in a large single center cohort of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis: long-term follow-up results after steroid therapy with short-duration maintenance treatment. J Gastroenterol. 2018; 53:967–77.
Article7. Yan T, Ke Y, Chen Y, Xu C, Yu C, Li Y. Serological characteristics of autoimmune pancreatitis and its differential diagnosis from pancreatic cancer by using a combination of carbohydrate antigen 19-9, globulin, eosinophils and hemoglobin. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0174735.
Article8. Miyazawa M, Takatori H, Shimakami T, Kawaguchi K, Kitamura K, Arai K, et al. Prognosis of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis after corticosteroid therapy-induced remission in terms of relapse and diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0188549.
Article9. Cai O, Tan S. From pathogenesis, clinical manifestation, and diagnosis to treatment: an overview on autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017; 2017:3246459.
Article10. The Japan Pancreas Society, the Ministry of Health and Welfare Investigation Research Team for Intractable Pancreatic Disease. Clinical diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis 2011 (proposal). J Jpn Pancreas (Suizo). 2012. 27:17–25.11. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Yamaguchi H, Nakazawa T, Katoh R, Itakura J, et al. Small invasive ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas associated with lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis. Pathol Int. 2009; 59:744–7.
Article12. Ranković B, Limbaeck-Stokin C, Dsokić M, Stanisavljević D, Volavšek M. Simultaneous occurrence of pancreatic mixed acinar-ductal adenocarcinoma and primary follicular lymphoma of the duodenum, accompanied by increased number of IgG4 plasma cells in tumor-free parenchyma as concomitant IgG4-related disease or reaction to tumor? A case report. Pol J Pathol. 2017; 68:86–91.
Article13. Okazaki K, Chari ST, Frulloni L, Lerch MM, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, et al. International consensus for the treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2017; 17:1–6.
Article14. Park SJ, Kim MH, Moon SH, Han JH, Park DH, Lee SS, et al. Clinical characteristics, recurrence features, and treatment outcomes of 55 patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 52:230–46.15. Hirano K, Isogawa A, Tada M, Isayama H, Takahara N, Miyabayashi K, et al. Long-term prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis in terms of glucose tolerance. Pancreas. 2012; 41:691–5.
Article16. Matsubayashi H, Ishiwatari H, Imai K, Kishida Y, Ito S, Hotta K, et al. Steroid therapy and steroid response in autoimmune pancreatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 21:257.
Article17. Noguchi K, Nakai Y, Mizuno S, Isayama H, Hirano K, Kanai S, et al. Insulin secretion improvement during steroid therapy for autoimmune pancreatitis according to the onset of diabetes mellitus. J Gastroenterol. 2020; 55:198–204.
Article18. Masuda A, Shiomi H, Matsuda T, Takenaka M, Arisaka Y, Azuma T, et al. The relationship between pancreatic atrophy after steroid therapy and diabetes mellitus in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2014; 14:361–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis presenting as an obstructive jaundice
- Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Ulcerative Colitis Manifesting as Acute Pancreatitis
- Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Steroid Therapy
- Differentiation of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis Presenting as Clinical Acute Pancreatitis
- Adolescent Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis